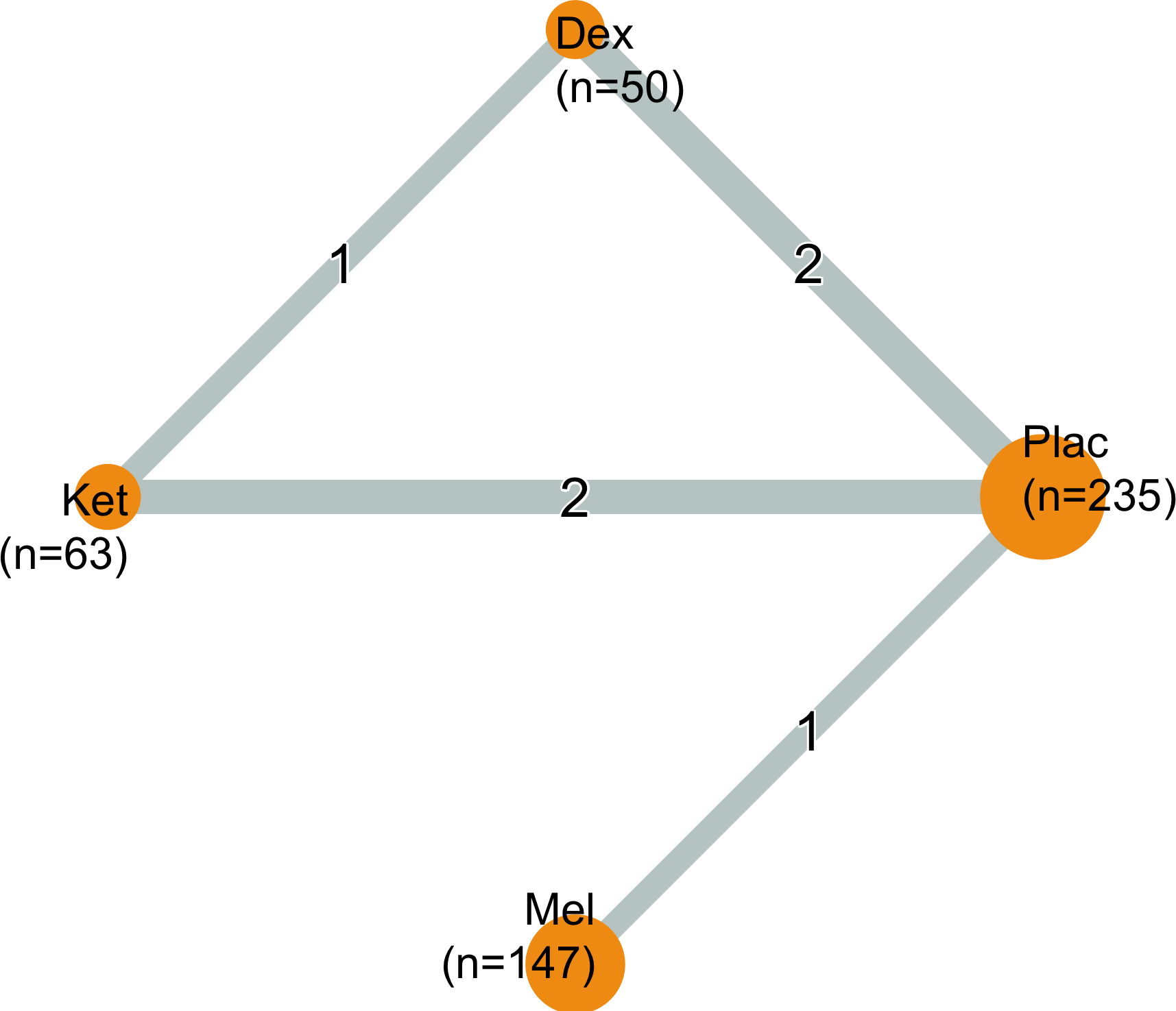
| Outcome | RCT | NRSI | Dexmedetomidine | Placebo* | GRADE† | Effect | Estimate (95% CI) |
I 2 | (95% PI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (Total) | N (Total) | ||||||||
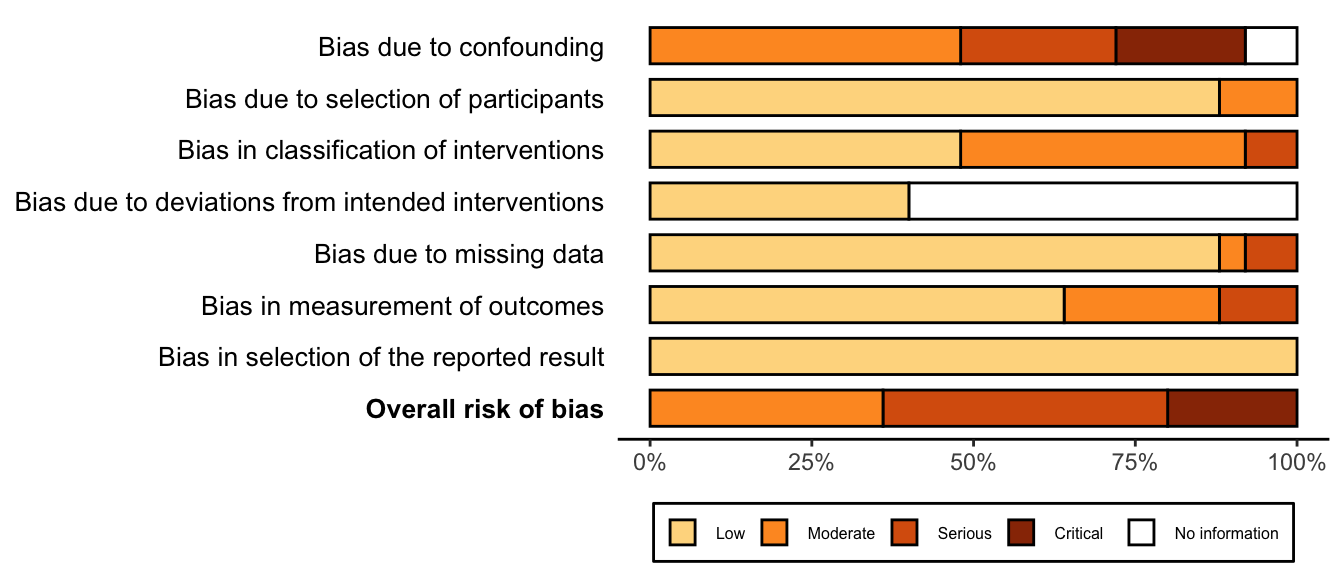
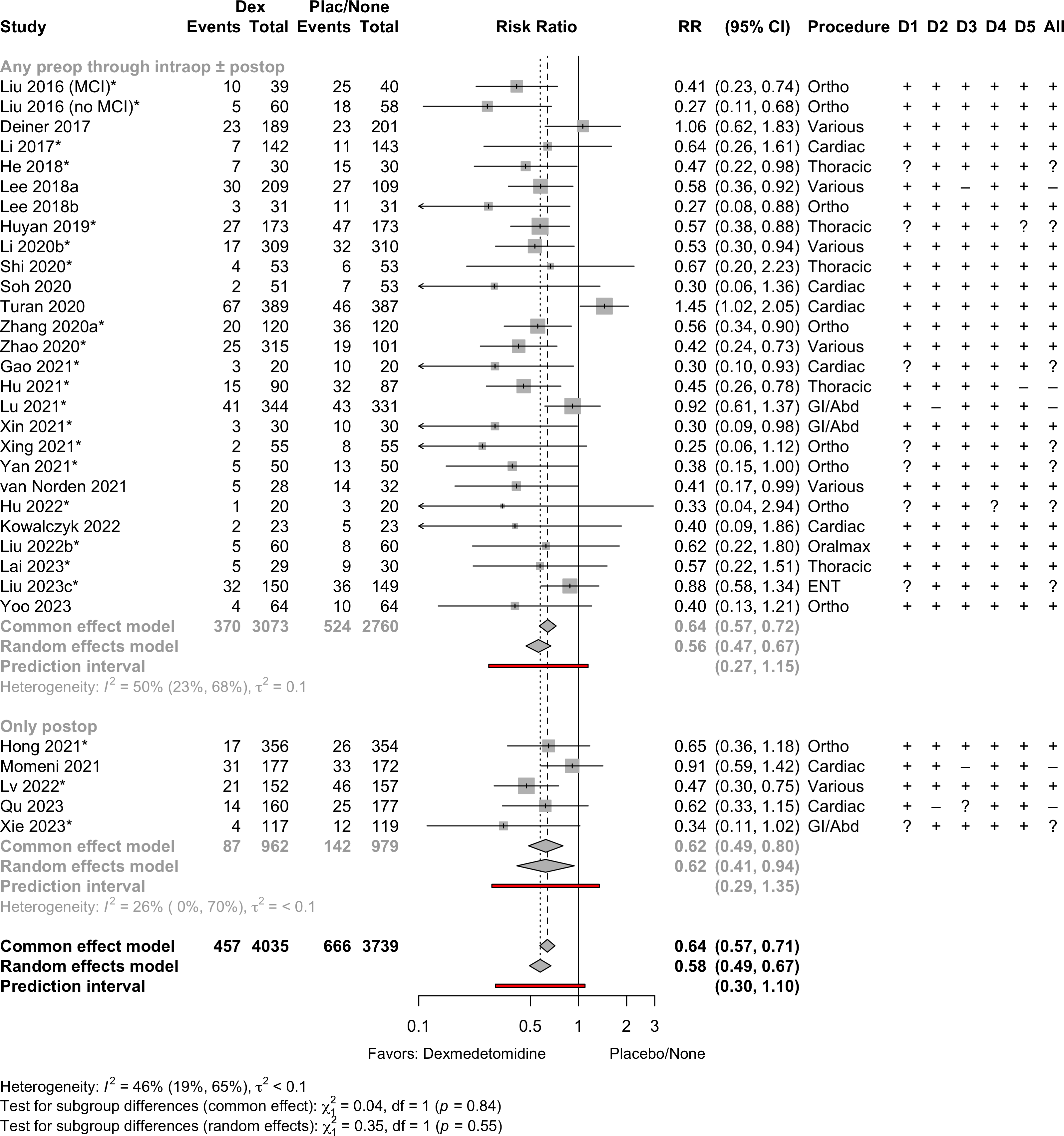
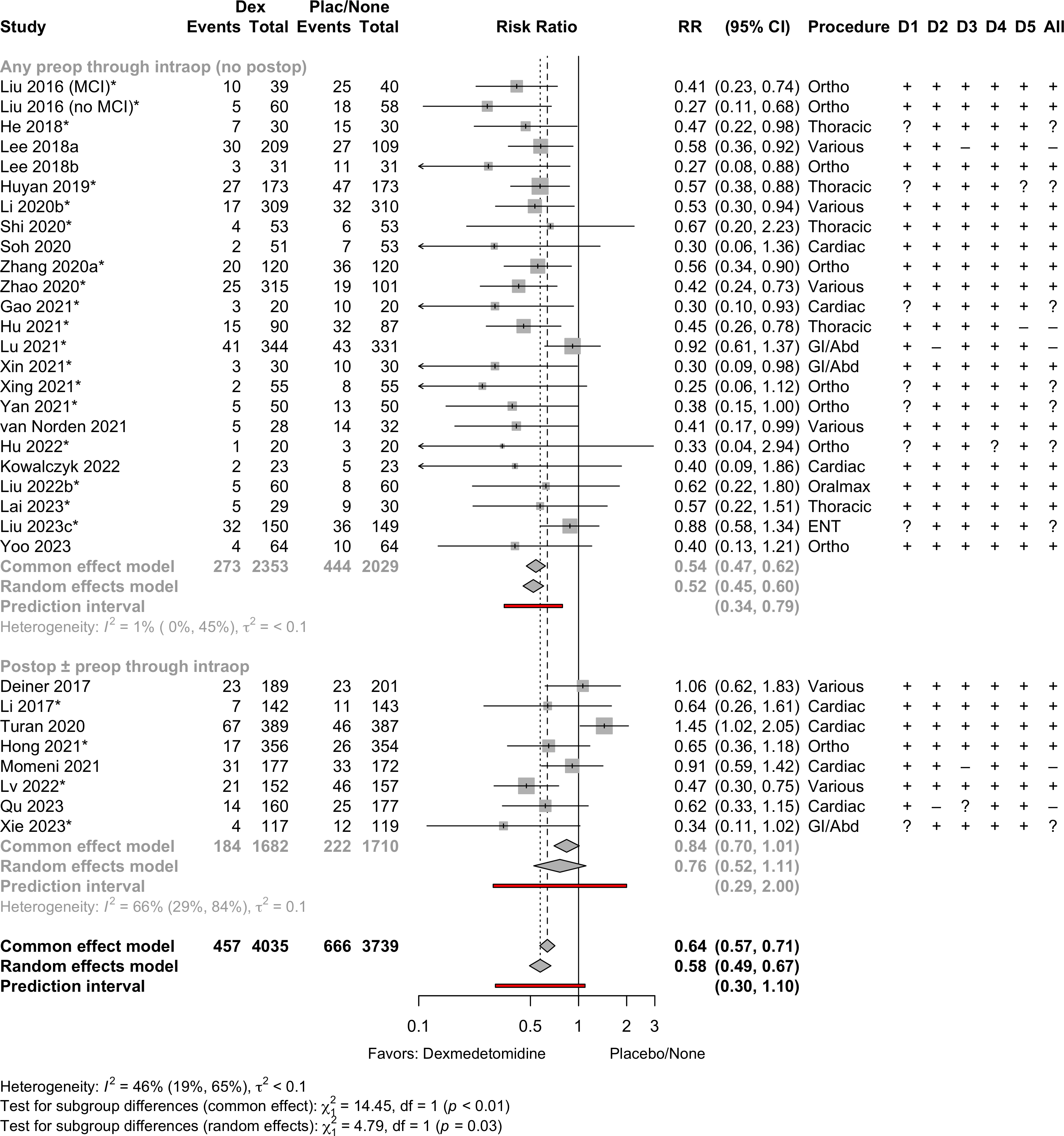
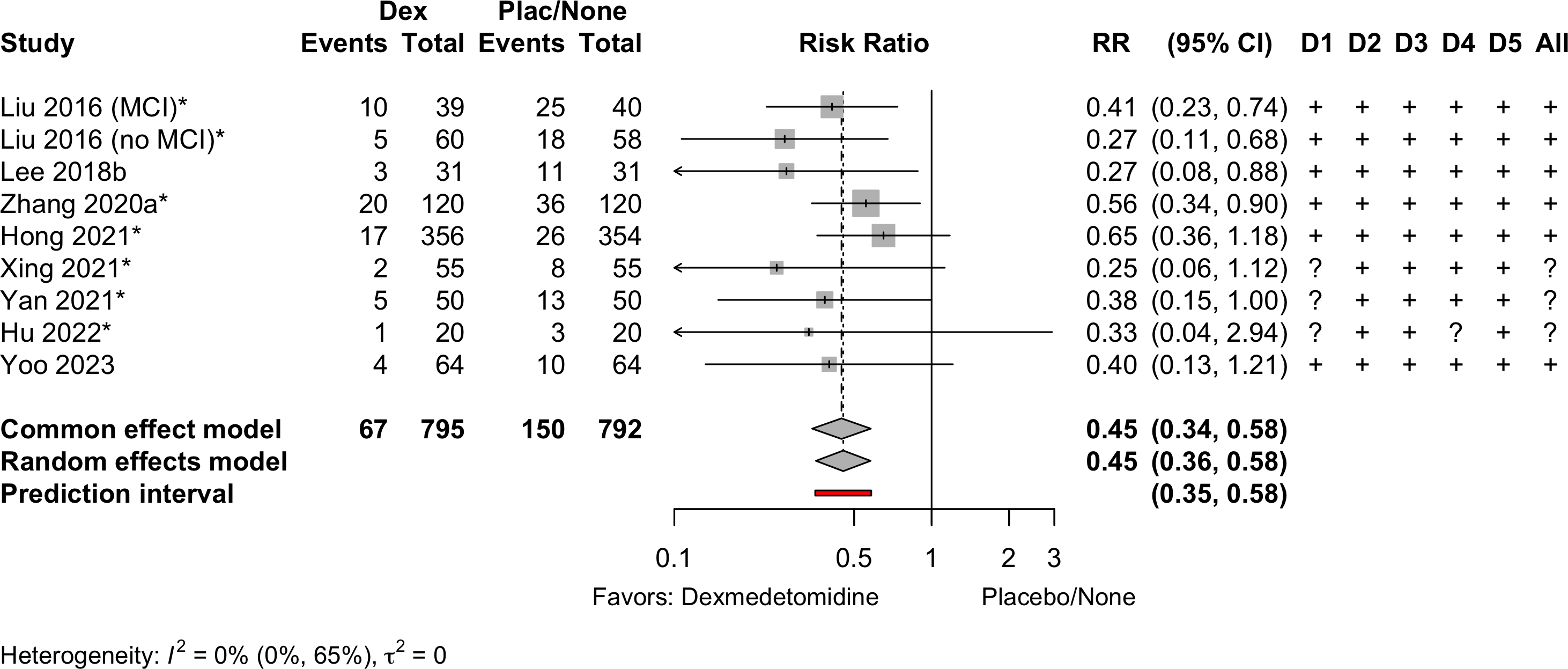
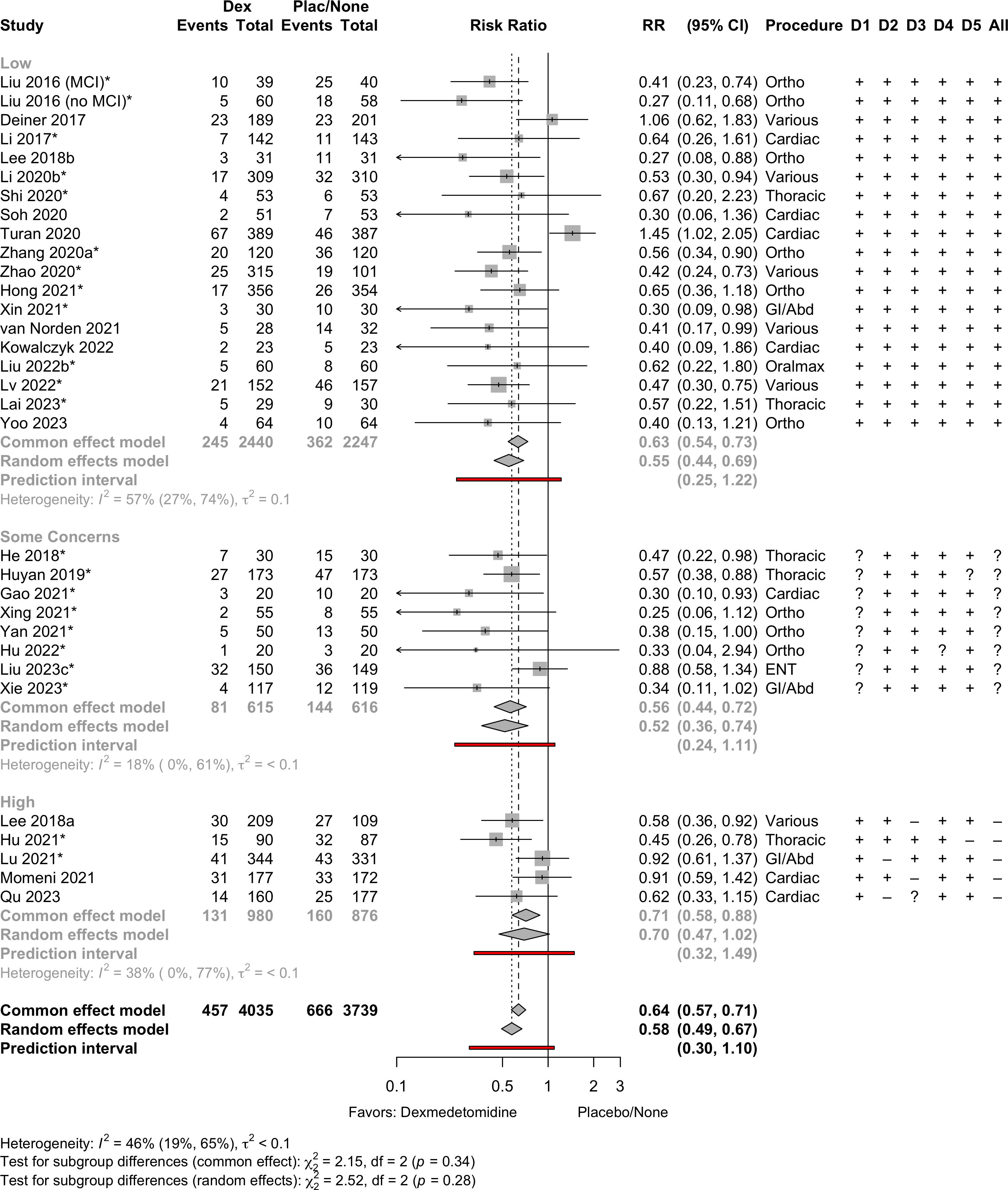
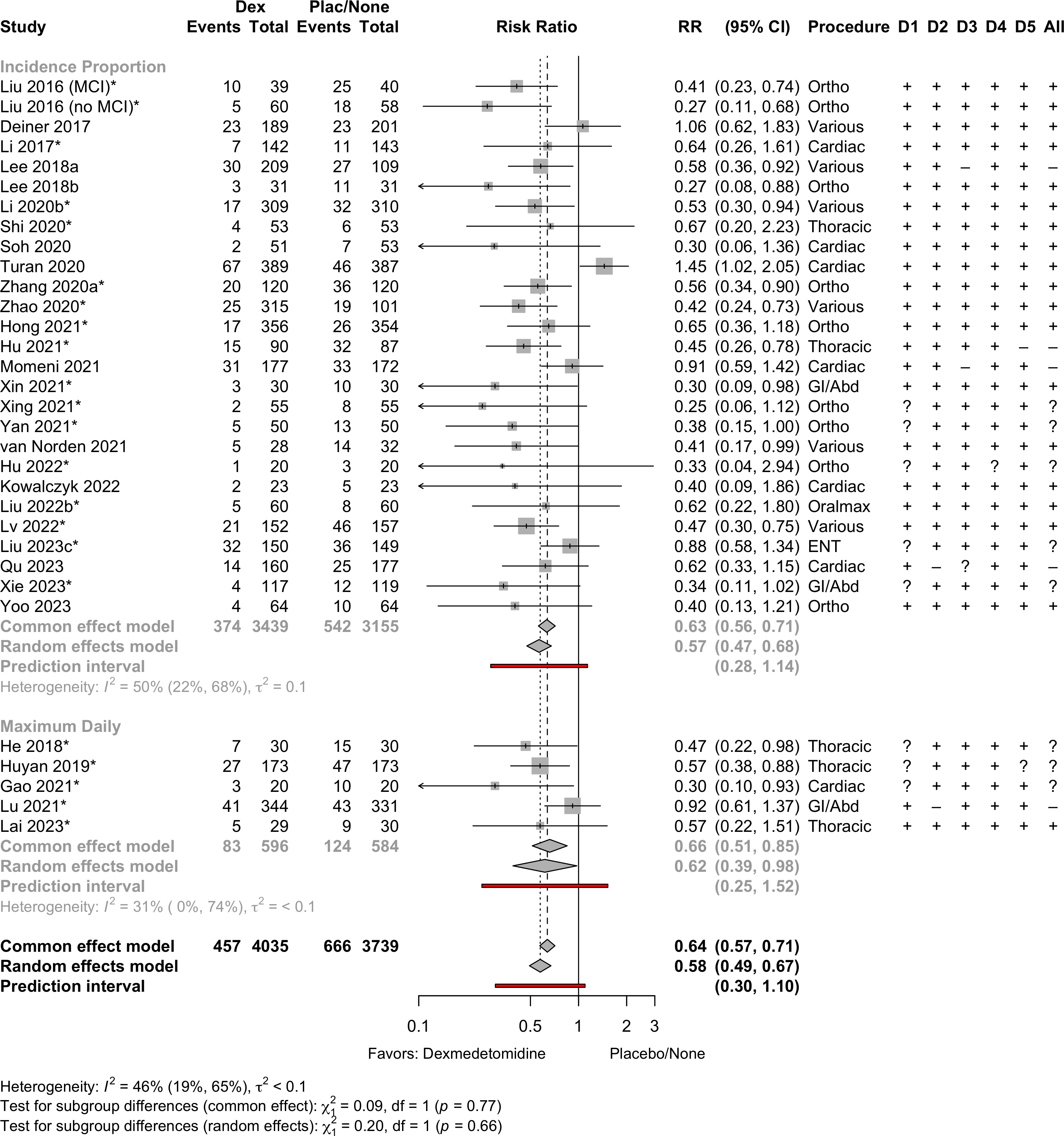
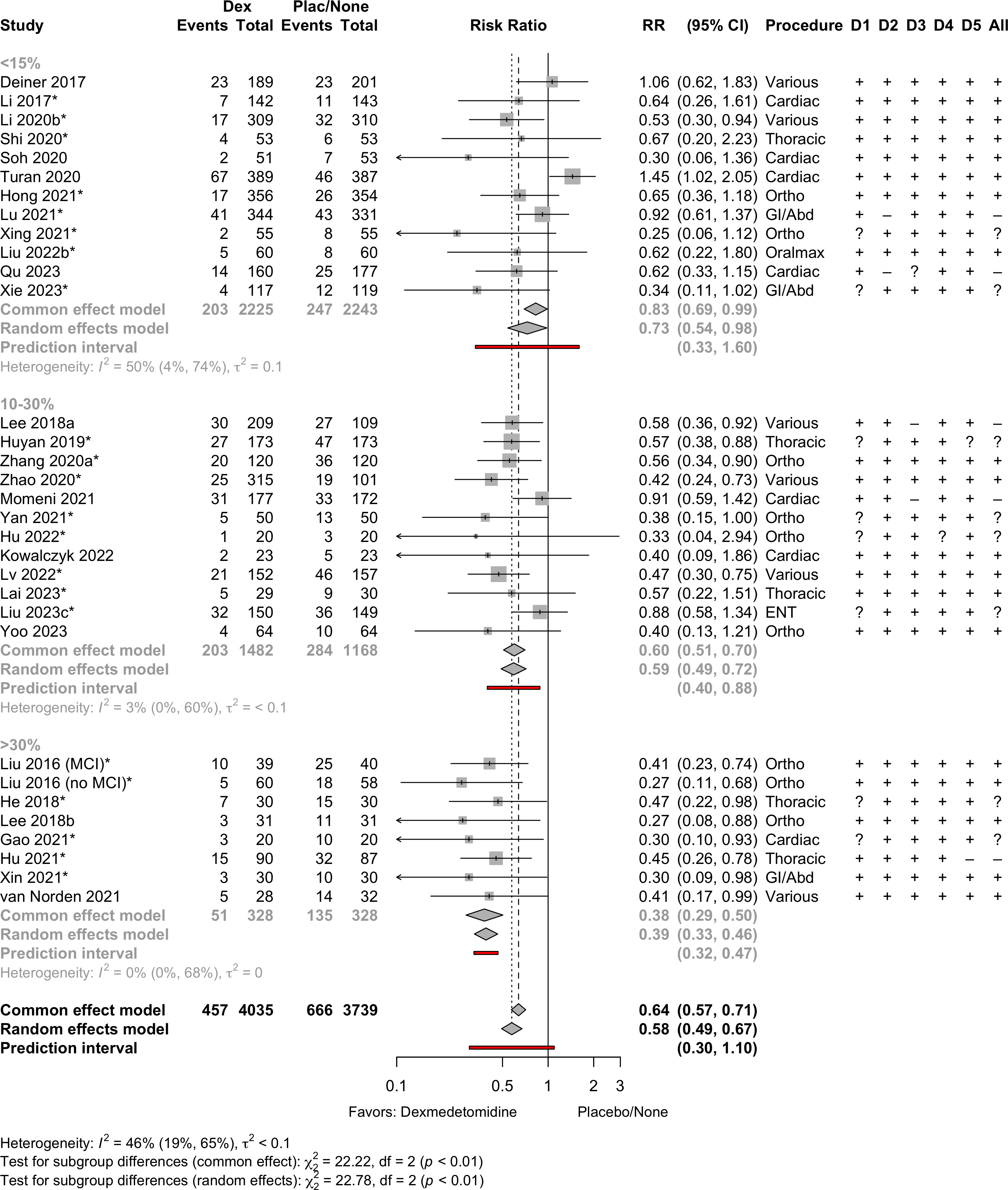
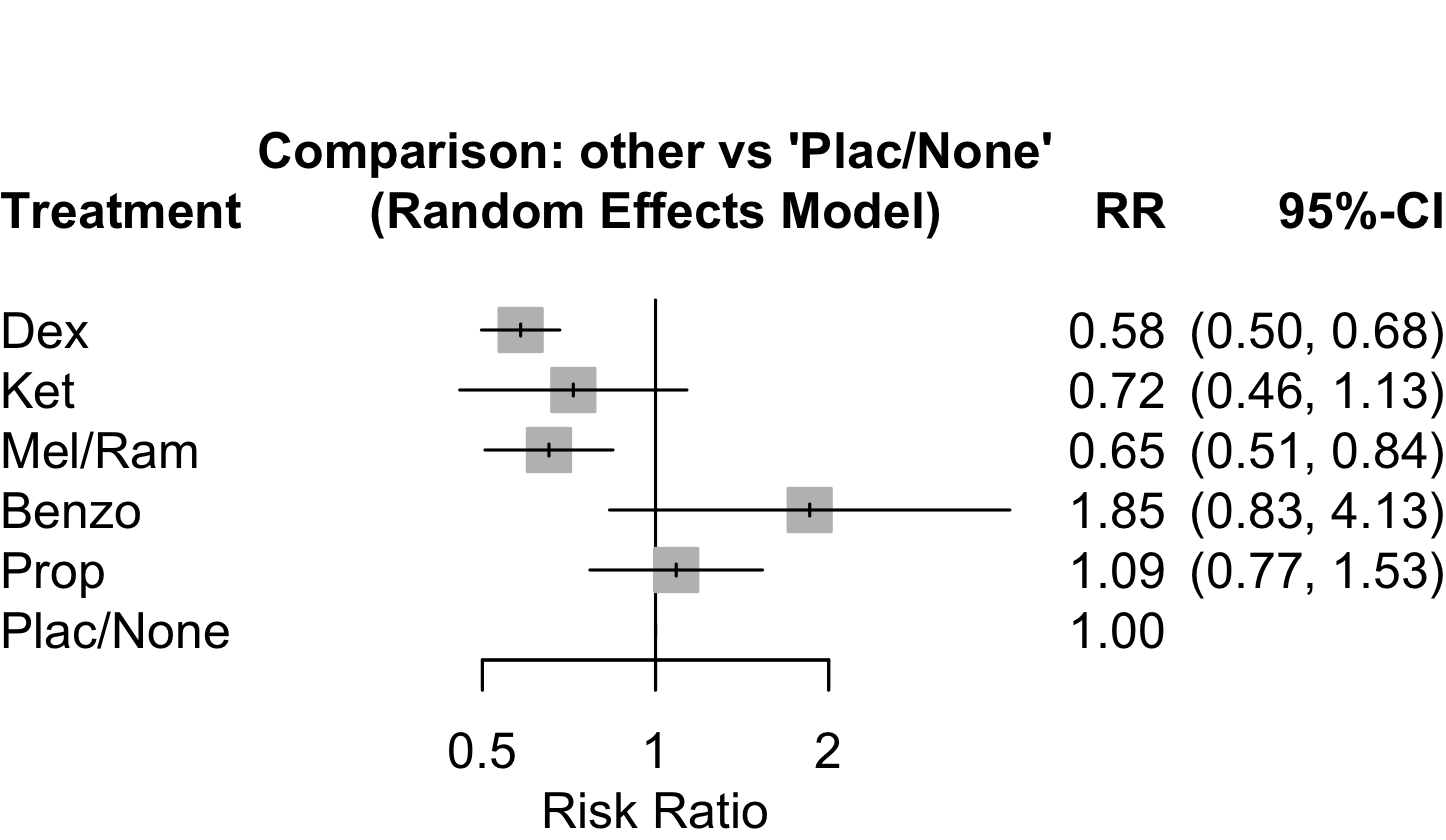
| Delirium | 31 | 457 (4,035) | 666 (3,739) | RR | 0.58 (0.49–0.67) | 46% |
(0.30–1.10) | ||
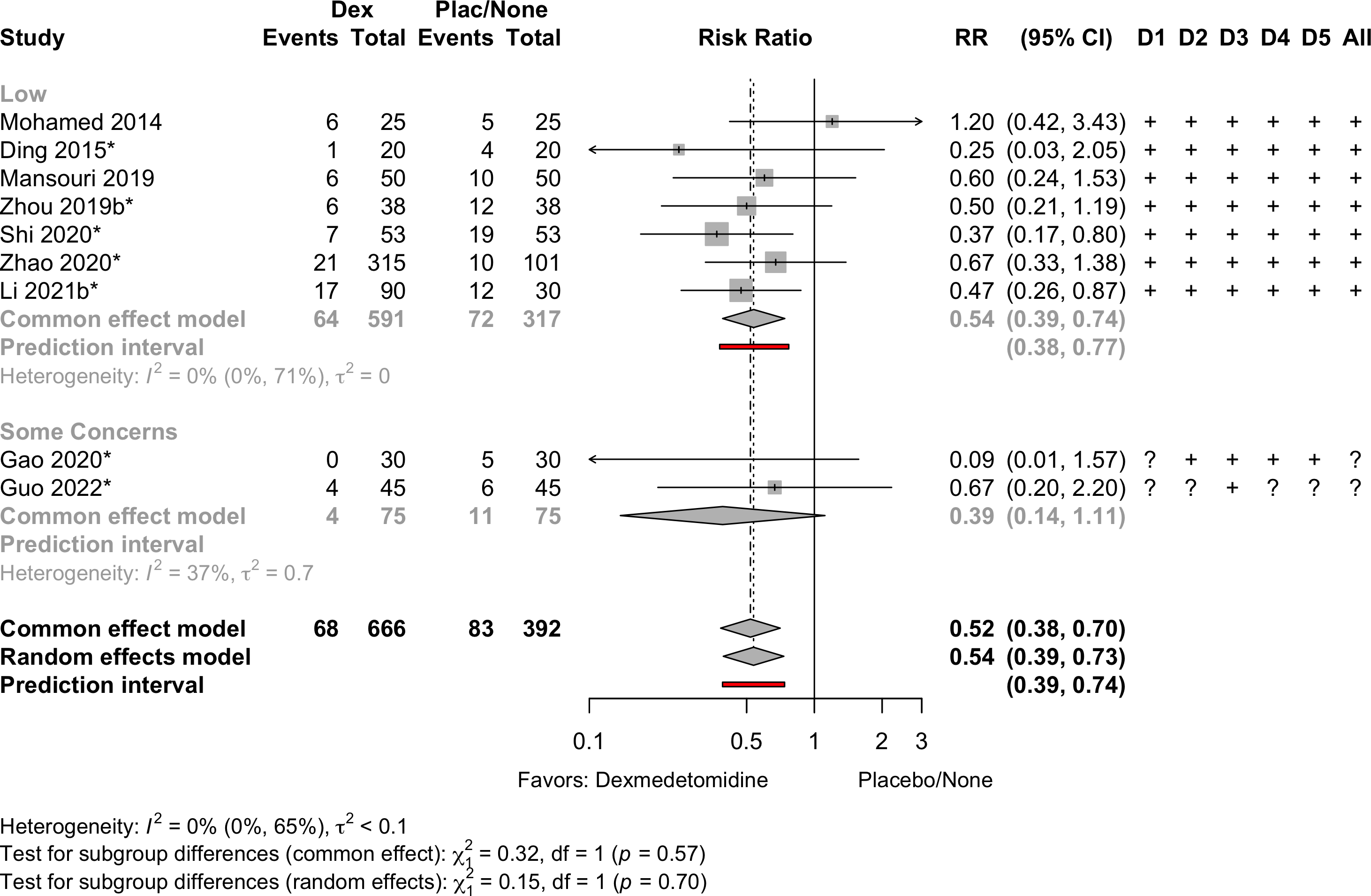
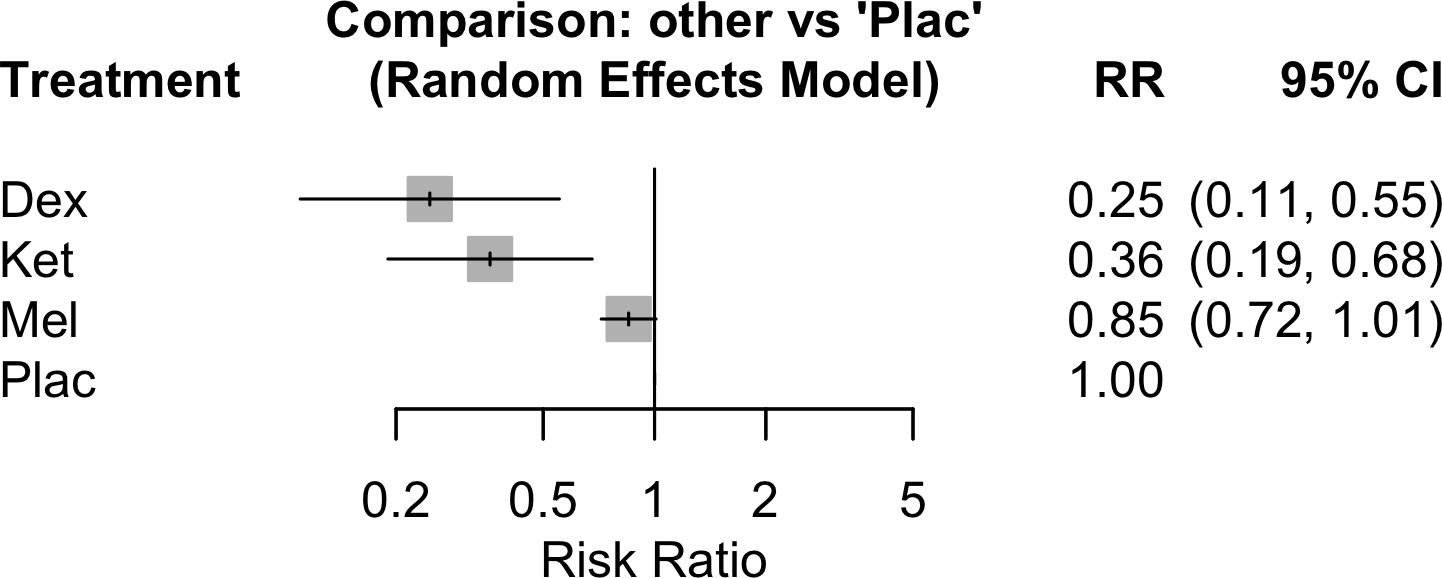
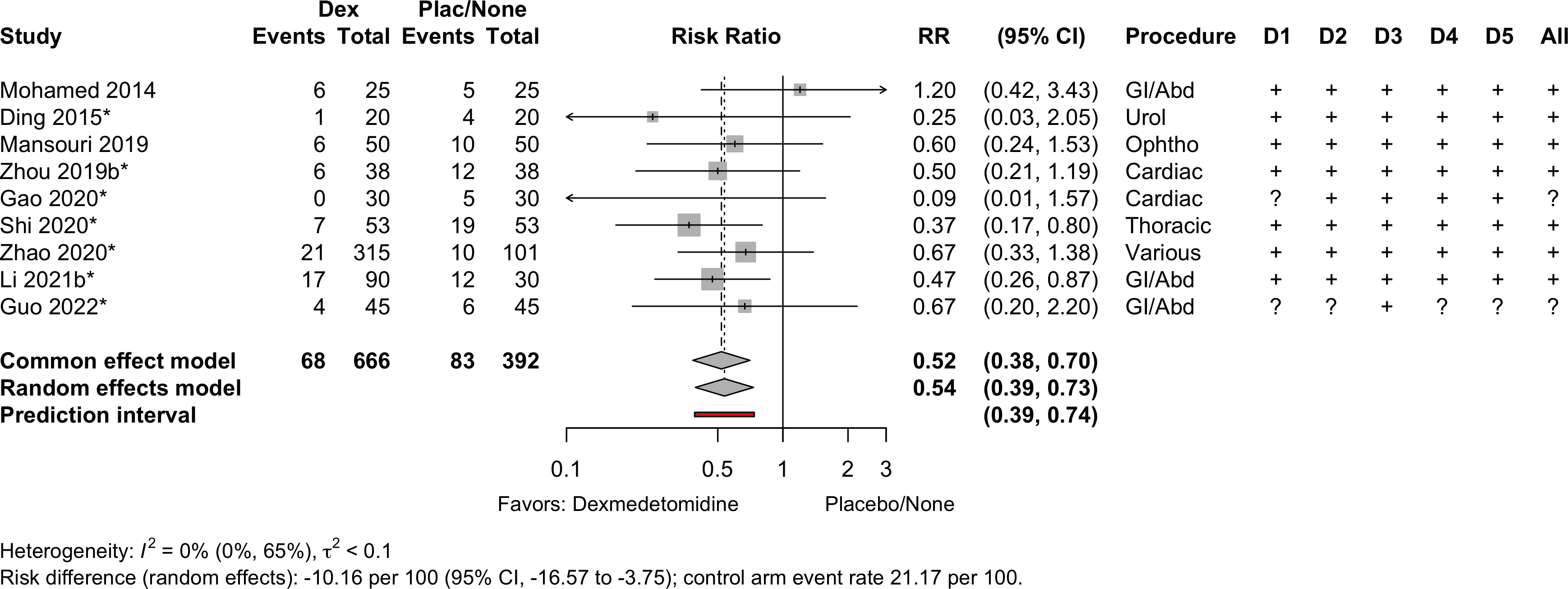
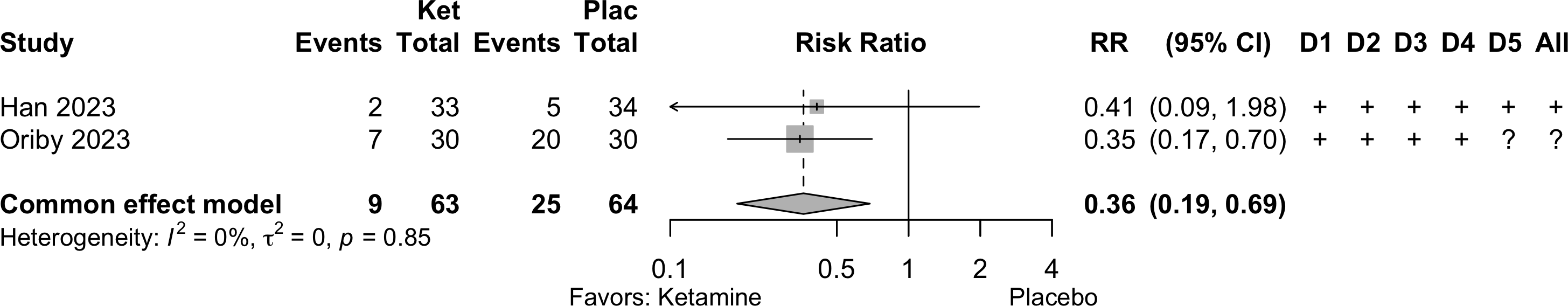
| Neurocognitive disorder <30 days | 9 | 68 (666) | 83 (392) | RR | 0.54 (0.39–0.73) | 0% |
(0.39–0.74) | ||
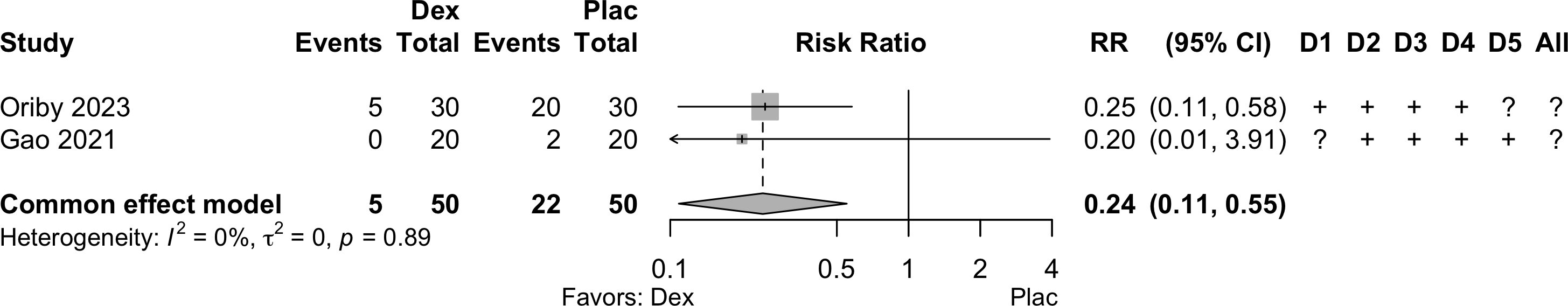
| Neurocognitive disorder 30 days to 1 yr | 2 | 5 (50) | 22 (50) | RR | 0.24 (0.11–0.55) | 0% |
‡ | ||
| Physical function | 1 | (30) | (31) | SMD | 0.39 (-1.57 to 2.34) | ‡ | |||
| Bradycardia | 17 | 236 (2,031) | 129 (1,755) | RR | 1.52 (1.22–1.88) | 0% |
(0.97–2.37) | ||
| 18 | 236 (2,121) | 129 (1,842) | RD/100 | 2.0 (-0.4 to 4.4) | 57% |
(-2.2 to 6.2) | |||
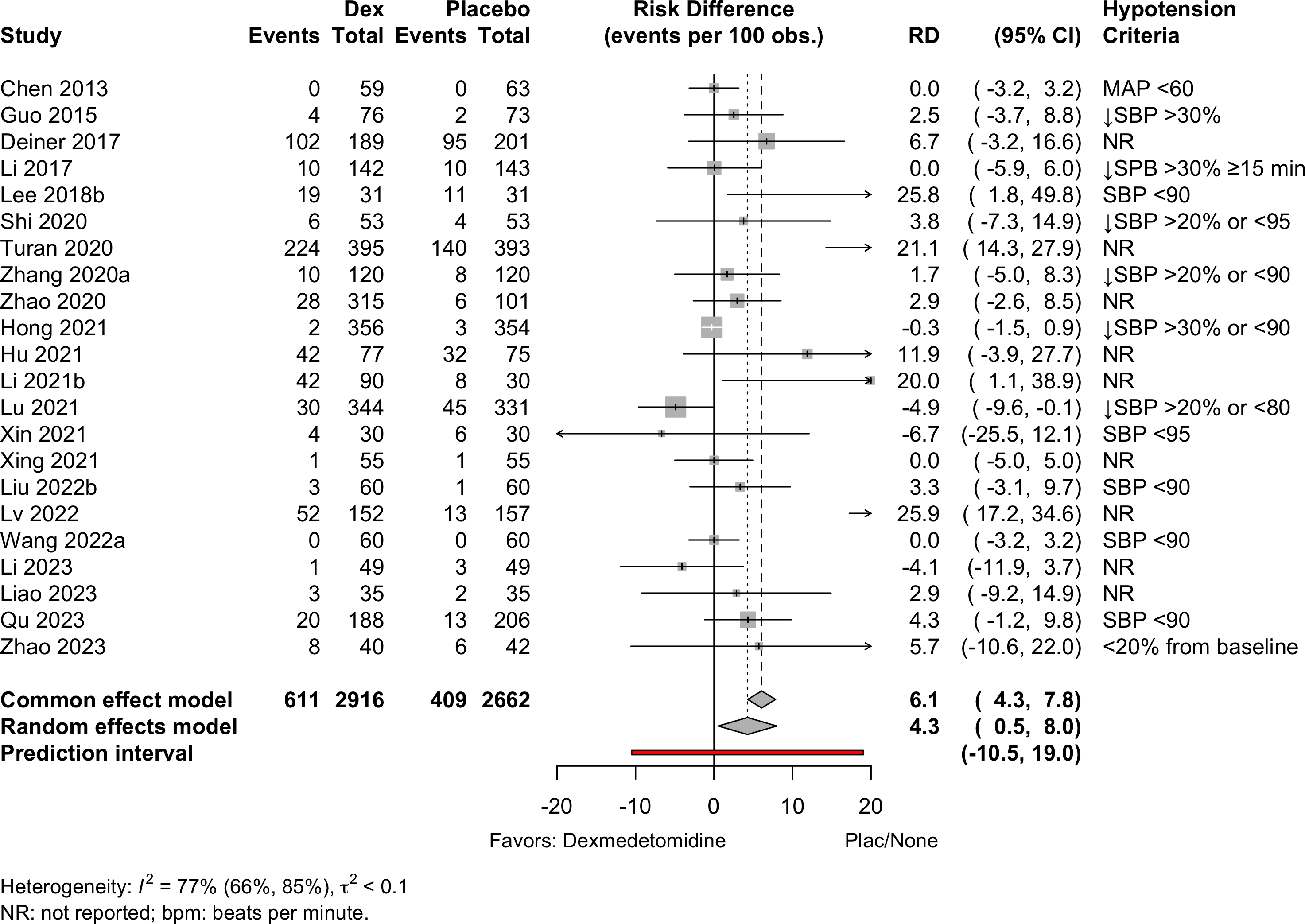
| Hypotension | 20 | 611 (2,797) | 409 (2,539) | RR | 1.38 (1.10–1.72) | 52% |
(0.65–2.91) | ||
| 22 | 611 (2,916) | 409 (2,662) | RD/100 | 4.3 (0.5 to 8.0) | 77% |
(-10.5 to 19.0) | |||
| Other complications | 27 | 3 | see below | ||||||
| Length of stay (days) | 20 | (3,051) | (3,075) | MD | -0.8 (-1.3 to -0.2)§ | 95% |
(-3.3 to 1.7) | ||
| Mortality, in-hospital and 30-day | 11 | 17 (2,123) | 31 (2,141) | RR | 0.64 (0.35–1.16) | 0% |
(0.31–1.32) | ||
| 12 | 17 (2,479) | 31 (2,495) | RD/1000 | -0.8 (-4.7 to 3.1) | 17% |
(-4.7 to 3.2) | |||
| RCT: randomized clinical trial; NRSI: nonrandomized studies of interventions; GRADE: Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation; PI: prediction interval; RR: risk ratio; SMD: standardized mean difference; RD: risk difference; MD: mean difference. | |||||||||
| * In some studies (randomized or not) the control incorporated neither placebo or prophylaxis. | |||||||||
| † Very low: ⨁◯◯◯; Low: ⨁⨁◯◯; Moderate: ⨁⨁⨁◯; High: ⨁⨁⨁⨁. | |||||||||
| ‡ Insufficient data to estimate a valid prediction interval. | |||||||||
| § With Hartung-Knapp adjustment MD -0.8 (-1.5 to -0.08). | |||||||||
Delirium Prophylaxis
Key Question
Among older patients undergoing surgery and anesthesia, does dexmedetomidine administered during the perioperative period decrease the risk of postoperative delirium or other adverse cognitive outcomes?
(The original question included ketamine, ramelteon, and melatonin. These unGRADEd results are included here but not in the advisory.)
Balance Tables
Dexmedetomidine
Other complications and strength of evidence (GRADE) for dexmedetomidine versus placebo or no delirium prophylaxis.
| Outcome | RCT | NRSI | Dexmedetomidine | Placebo* | GRADE† | Effect | Estimate (95% CI) | I 2 | (95% PI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (Total) | N (Total) | ||||||||
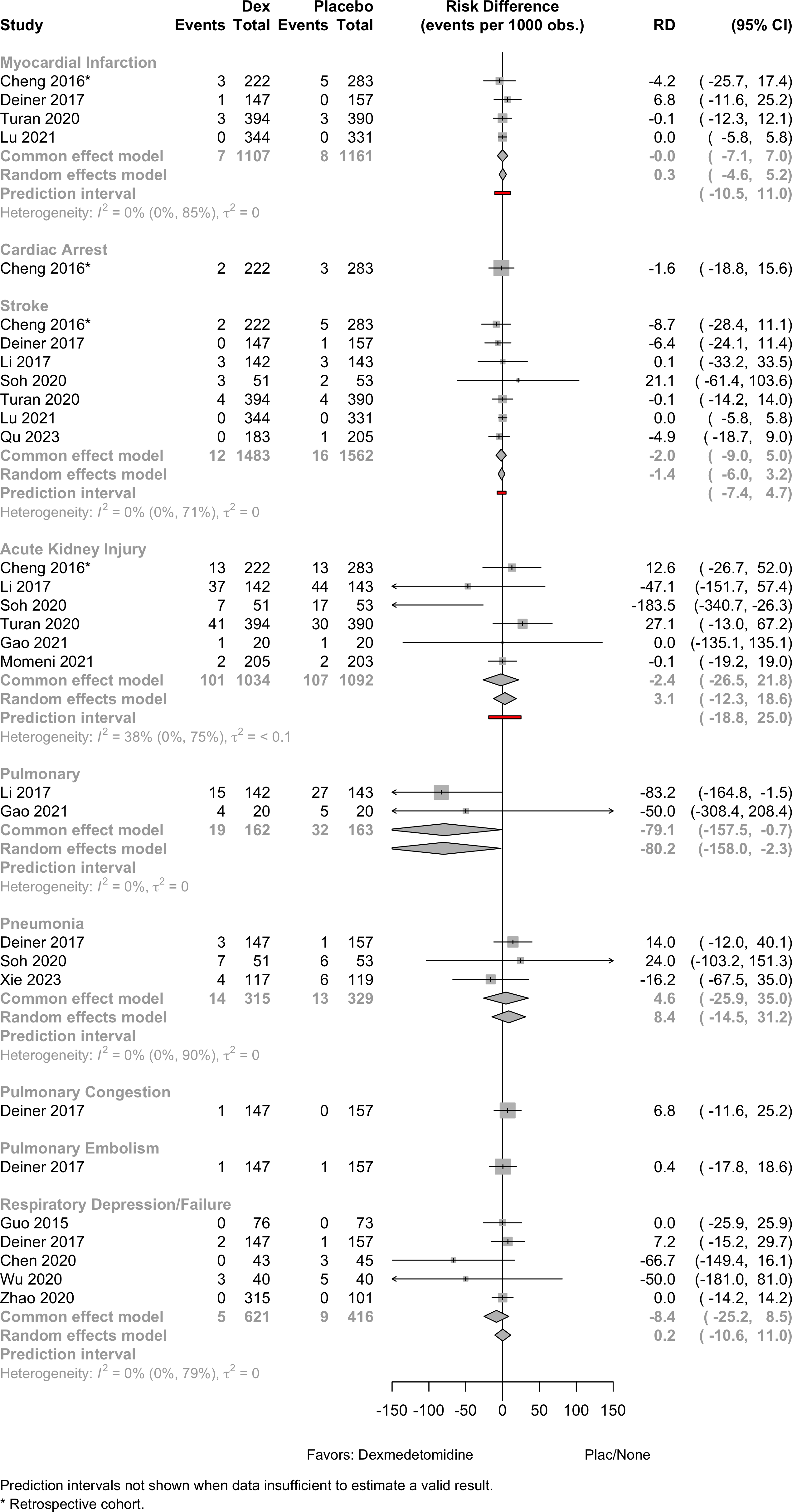
| Myocardial infarction | 2 | 1 | 7 (763) | 8 (830) | RR | 0.98 (0.36–2.67) | 0% |
‡ | |
| 3 | 1 | 7 (1,107) | 8 (1,161) | RD/1000 | 0.3 (-4.6 to 5.2) | 0% |
(-10.5 to 11.0) | ||
| Cardiac arrest | 1 | 2 (222) | 1 (283) | RR | 0.85 (0.14–5.04) | ‡ | |||
| 1 | 2 (222) | 1 (283) | RD/1000 | -1.6 (-18.8 to 15.6) | ‡ | ||||
| Stroke | 5 | 1 | 12 (1,139) | 16 (1,231) | RR | 0.84 (0.40–1.77) | 0% |
(0.30–2.41) | |
| 6 | 1 | 12 (1,483) | 16 (1,562) | RD/1000 | -1.4 (-6.0 to 3.2) | 0% |
(-7.4 to 4.7) | ||
| Acute kidney injury | 5 | 1 | 101 (1,034) | 107 (1,092) | RR | 1.05 (0.69–1.59) | 31% |
(0.35–2.56) | |
| 5 | 1 | 101 (1,034) | 107 (1,092) | RD/1000 | 3.1 (-12.3 to 18.6) | 38% |
(-18.8 to 25.0) | ||
| Pneumonia | 3 | 14 (315) | 13 (329) | RR | 1.09 ( 0.52–2.30) | 0% |
‡ | ||
| 3 | 14 (315) | 13 (329) | RD/1000 | 8.4 (-14.5 to 31.2) | 0% |
‡ | |||
| Pulmonary congestion | 1 | 1 (147) | 0 (157) | RR | 3.20 (0.13–78.02) | ||||
| 1 | 1 (147) | 0 (157) | RD/1000 | 6.8 (-11.6 to 25.2) | |||||
| Pulmonary embolism | 1 | 1 (147) | 1 (157) | RR | 1.07 (0.07–16.92) | ||||
| 1 | 1 (147) | 1 (157) | RD/1000 | 0.4 (-17.8 to 18.6) | |||||
| Respiratory Depression/Failure | 3 | 5 (230) | 9 (242) | RR | 0.65 (0.22–1.94) | 0% |
‡ | ||
| 5 | 5 (621) | 9 (416) | RD/1000 | 0.2 (-10.6 to 11.0) | 0% |
(-17.3 to 17.7) | |||
| RCT: randomized clinical trial; GRADE: Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation; RR: risk ratio; RD: risk difference. | |||||||||
| * In some studies (randomized or not) the control incorporated neither placebo or prophylaxis. | |||||||||
| † Very low: ⨁◯◯◯; Low: ⨁⨁◯◯; Moderate: ⨁⨁⨁◯; High: ⨁⨁⨁⨁. | |||||||||
| ‡ Insufficient data to estimate a valid prediction interval. | |||||||||
Outcomes Reported
Included Studies
See Appendix for detailed summary study and patient characteristics including primary outcomes.
| Dexmedetomidine | |
| Design | Studies |
|---|---|
| Randomized Clinical Trial | 71 |
| Nonrandomized Trial | 6 |
| Prospective Cohort | 1 |
| Retrospective Cohort | 6 |
| Total | 84 |
| Studies with multiple publications counted only once (applied to 1 trial with 2 publications). | |
| Ketamine | |
| Design | Studies |
|---|---|
| Randomized Clinical Trial | 12 |
| Prospective Cohort | 3 |
| Retrospective Cohort | 4 |
| Total | 19 |
| Melatonin or Ramelteon | |
| Design | Studies |
|---|---|
| Randomized Clinical Trial | 16 |
| Nonrandomized Trial | 2 |
| Before-After/Time Series | 2 |
| Retrospective Cohort | 1 |
| Total | 21 |
Design, centers, country, and surgery
| ID | Studya | Centers | Enrolled | Countryb | Surgery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dexmedetomidine - Nonrandomized Trial | |||||
| 13361 | 1 | 110 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 5183 | 1 | 96 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 5052 | 1 | 140 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 120 | 1 | 140 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 13368 | 1 | 165 | Chinab | Spine | |
| 13301 | 1 | 87 | Chinab | Thoracic | |
| Dexmedetomidine - Prospective Cohort | |||||
| 18819 | 1 | 676 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| Dexmedetomidine - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||
| 13579 | 1 | 70 | Egyptb | Cardiac | |
| 7240 | 1 | 70 | Canada | Cardiac | |
| 2288 | 1 | 185 | Canada | Cardiac | |
| 1819 | 1 | 60 | Chinab | Cardiac | |
| 5269 | 1 | 40 | Chinab | Cardiac | |
| 13777 | 1 | 50 | Chinab | Cardiac | |
| 17683 | 1 | 49 | Poland | Cardiac | |
| 24 | 2 | 285 | Chinab | Cardiac | |
| 2173 | 1 | 420 | Belgium | Cardiac | |
| 17019 | 1 | 469 | USA | Cardiac | |
| 18870 | 1 | 78 | Slovenia | Cardiac | |
| 20454 | 1 | 108 | South Korea | Cardiac | |
| 2624 | 1 | 140 | USA | Cardiac | |
| 16008 | 6 | 798 | USA | Cardiac | |
| 16023 | 1 | 80 | Chinab | Cardiac | |
| 13406 | 1 | 156 | Chinab | Cardiac | |
| 335 | 1 | 63 | Germany | Cardiac|GI/Abdominal | |
| 18597 | 1 | 304 | Chinab | ENT | |
| 5436 | 1 | 126 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 889 | 1 | 88 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 1288 | 1 | 87 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 17531 | 1 | 90 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 5024 | 1 | 100 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 4914 | 1 | 120 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 18582 | 1 | 104 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 13941 | 1 | 58 | Egyptb | GI/Abdominal | |
| 12900 | 1 | 100 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 18909 | 1 | 240 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 1919 | 1 | 60 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 8558 | 13 | 808 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal|Hepatic | |
| 5480 | 1 | 174 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal|Neuro|Urol | |
| 13483 | 1 | 198 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal|Ortho|Thoracic | |
| 261 | 1 | 354 | South Korea | GI/Abdominal|Urol | |
| 328 | 1 | 120 | Chinab | Headneck | |
| 1117 | 1 | 150 | Iranb | Ophtho | |
| 18690 | 1 | 90 | Egyptb | Ophtho | |
| 5452 | 1 | 184 | Chinab | Oralmax | |
| 16845 | 1 | 120 | Chinab | Oralmax | |
| 1625 | 1 | 44 | Chinab | Oralmax | |
| 18346 | 2 | 108 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 17503 | 1 | 95 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 5240 | 2 | 712 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 17575 | 1 | 60 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 2748 | 1 | 132 | South Korea | Ortho | |
| 742 | 1 | 164 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 18575 | 1 | 98 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 1419 | 1 | 200 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 3130 | 1 | 152 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 1735 | 1 | 336 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 1267 | 1 | 415 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 17001 | 1 | 748 | South Korea | Ortho | |
| 13075 | 1 | 110 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 16303 | 1 | 100 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 18937 | 1 | 128 | South Korea | Ortho | |
| 5147 | 1 | 240 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 18958 | 1 | 88 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 11129 | 1 | 187 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 13568 | 1 | 90 | Chinab | Thoracic | |
| 3046 | 1 | 177 | Chinab | Thoracic | |
| 69 | 1 | 360 | Chinab | Thoracic | |
| 18558 | 1 | 90 | Chinab | Thoracic | |
| 16741 | 1 | 60 | Chinab | Thoracic | |
| 3391 | 1 | 106 | Chinab | Thoracic | |
| 13731 | 1 | 92 | Chinab | Thoracic | |
| 4798 | 1 | 40 | Chinab | Urol | |
| 7151 | 1 | 125 | Chinab | Urol | |
| 5251 | 1 | 87 | Indiab | Variousc | |
| 2022 | 10 | 429 | USA | Variousc | |
| 20465 | 1 | 620 | Chinab | Variousc | |
| 16718 | 1 | 327 | Chinab | Variousc | |
| 16734 | 1 | 100 | Chinab | Variousc | |
| 3716 | 1 | 432 | Chinab | Variousc | |
| Dexmedetomidine - Retrospective Cohort | |||||
| 2517 | 1 | 505 | USA | Cardiac | |
| 103 | 1 | 278 | USA | Cardiac | |
| 5066 | 1 | 714 | South Korea | Ortho | |
| 16830 | 1 | 60 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 13367 | 1 | 120 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 17150 | 1 | 195 | Chinab | Urol | |
| Ketamine - Prospective Cohort | |||||
| 1140 | 1 | 187 | Norway | Ortho | |
| 17147 | 4 | 98 | Singapore | Other | |
| 9616 | 1 | 98 | USA | Spine | |
| Ketamine - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||
| 181 | 1 | 78 | USA | Cardiac | |
| 1847 | 1 | 58 | USA | Cardiac | |
| 5189 | 1 | 75 | Thailand | Cardiac | |
| 18435 | 1 | 84 | Chinab | GI/Abdominal | |
| 18610 | 1 | 68 | China | GI/Abdominal | |
| 15285 | 1 | 60 | Austria | GI/Abdominal|Hepatic | |
| 18690 | 1 | 90 | Egyptb | Ophtho | |
| 2217 | 1 | 80 | Mexicob | Ophtho | |
| 2578 | 1 | 56 | South Korea | Ortho | |
| 3788 | 1 | 160 | France | Ortho | |
| 13184 | 1 | 80 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 2866 | 5 | 672 | USA | Variousc | |
| 1937 | 2 | 143 | Switzerland | Variousc | |
| Ketamine - Retrospective Cohort | |||||
| 17130 | 4,400 | 564,226 | USA | Orthod | |
| 17136 | 4,400 | 1,130,569 | USA | Orthoe | |
| 18978 | 527,254 | USA | Ortho | ||
| 17144 | 1 | 41,766 | USA | Orthof | |
| 17145 | 1 | 41,766 | USA | Ortho | |
| 17149 | 1 | 84 | USA | Thoracic | |
| Melatonin - Nonrandomized Trial | |||||
| 16537 | 1 | 500 | Slovakia | Cardiac | |
| 13824 | 1 | 500 | Slovakia | Cardiac | |
| Melatonin - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||
| 17055 | 1 | 145 | Iranb | Cardiac | |
| 17057 | 1 | 50 | Egyptb | Cardiac | |
| 16558 | 2 | 210 | Australia | Cardiac | |
| 9256 | 1 | 60 | Iranb | Cardiac | |
| 9741 | 1 | 297 | Chinab | Cardiac | |
| 17152 | 1 | 150 | Iranb | General|Neuro|Ortho | |
| 602 | 1 | 148 | Chinab | Ortho | |
| 17153 | 1 | 80 | Iranb | Ortho | |
| 17154 | 1 | 80 | Egyptb | Ortho | |
| 5164 | 1 | 152 | Egyptb | Ortho | |
| 16552 | 3 | 452 | Netherlands | Ortho | |
| Ramelteon - Before-After/Time Series | |||||
| 693 | 1 | 309 | Japan | Hepatic | |
| 2997 | 1 | 82 | Japan | Thoracic | |
| Ramelteon - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||
| 17084 | 1 | 112 | Japan | GI/Abdominal|Hepatic | |
| 18530 | 1 | 108 | Japan | General|Thoracic|Urol|Vasc | |
| 3841 | 1 | 80 | USA | Ortho | |
| 4150 | 1 | 120 | USA | Thoracic | |
| 13512 | 1 | 100 | Indiab | Variousc | |
| Ramelteon - Retrospective Cohort | |||||
| 20438 | 1 | 69 | Japan | Headneck | |
| GI: gastrointestinal; Ortho: orthopedic; Neuro: neurological; Oralmax: oral maxillofacial; Vasc: vascular; ENT: ear nose and throat. | |||||
| a Studies examining drugs not directly relevant to recommendations but potentially to the evidence space (eg, a connected network including indirect evidence) are included here. | |||||
| b Non very-high Human Development Index country. | |||||
| c Described as various or more than 4 different types of surgery. | |||||
| d Hip arthroplasty. | |||||
| e Knee arthroplasty. | |||||
| f Intraoperative ketamine. | |||||
Country Summary
| N = 98a | |
|---|---|
| Country | |
| China | 56 (57%) |
| USA | 8 (8.2%) |
| Egypt | 6 (6.1%) |
| South Korea | 6 (6.1%) |
| Iran | 5 (5.1%) |
| Canada | 2 (2.0%) |
| India | 2 (2.0%) |
| Japan | 2 (2.0%) |
| Australia | 1 (1.0%) |
| Austria | 1 (1.0%) |
| Belgium | 1 (1.0%) |
| France | 1 (1.0%) |
| Germany | 1 (1.0%) |
| Mexico | 1 (1.0%) |
| Netherlands | 1 (1.0%) |
| Poland | 1 (1.0%) |
| Slovenia | 1 (1.0%) |
| Switzerland | 1 (1.0%) |
| Thailand | 1 (1.0%) |
| a n (%) | |
Interventions & Comparators
Dexmedetomidine
| Study | N | Arm | ASA | Anesthetic | Ageb | MMSEc,b | Dexmedetomidine mcg/kg | Timinge | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSa | Vol | TIVA | Reg | Sed | Load | Maint/hrd | Postop | ||||||
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 92 | Prop | NR | ✓ | 72.4 (6.2) |
|||||||||
| 91 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 72.7 (6.4) |
0.4 | (0.2–0.7) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 24 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 72.0 (4.0) |
26.9 (0.8) |
||||||||
| 24 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.0 (3.0) |
27.2 (0.9) |
0.3 | 0.3 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 143 | Plac | 234 | ✓ | ✓ | 67.5 (5.3) |
29 [28-30] |
|||||||
| 142 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 66.4 (5.4) |
29 [28-30] |
0.6 | 0.4 | 0.1 | ▁▁▆▆ | ||
| 30 | Mid | NR | ✓ | 66.7 (5.6) |
|||||||||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 65.3 (4.8) |
(0.4–0.7) | ▁▁▁▆ | |||||
| 61 | Prop | NR | 70.0 {64-79} |
||||||||||
| 59 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 66.5 {63-74} |
0.5 | (0.1–0.4) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 38 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | ✓ | 70.0 (4.9) |
||||||||
| 39 | Ulin | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.6 (4.4) |
|||||||
| 39 | Dex/Ulin | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.6 (5.0) |
0.4 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||
| 38 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.8 (5.1) |
0.4 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||
| 30 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 70.4 (4.2) |
|||||||||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.5 (5.1) |
1.0 | (0.3–0.5) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 54 | Plac | NR | ✓ | ✓ | 65.0 [37-83] |
||||||||
| 54 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 65.0 [23-82] |
▁▁▆▁ | ||||||
| 396 | Plac | 1234 | ✓ | ✓ | 62.0 (12.0) |
||||||||
| 398 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 63.0 (11.0) |
0.1 | 0.4 | ▁▆▆▆ | ||||
| 40 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 67.7 (8.8) |
28.2 |
||||||||
| 40 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.2 (8.6) |
28.1 |
0.5 | 0.6 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 20 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 71.4 (4.5) |
28.4 (1.3) |
||||||||
| 20 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.4 (4.5) |
28.5 (1.4) |
0.6 | 0.2 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 203 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 70.0 {59-81} |
28 {26-29} |
||||||||
| 205 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.0 {61-81} |
28 {26-29} |
0.4 | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 33 | Prop | NR | ✓ | 78.8 |
30.2 |
||||||||
| 34 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 78.7 |
30.1 |
0.5 (0–1.5) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 23 | None | 23 | ✓ | 66.0 (5.0) |
|||||||||
| 23 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 67.0 (10.0) |
0.5 | 0.25 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 206 | Plac | NR | 70.0 {65-75} |
||||||||||
| 188 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 67.5 {63-73} |
1 | ▁▁▁▆ | |||||
| 34 | Prop | NR | ✓ | 83.5 {79-87} |
26 {25-28} |
||||||||
| 37 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 83.0 {77-85} |
27 {25-28} |
0.5 | (0.2–1) | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 40 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 75.2 (7.8) |
22.4 (2.6) |
||||||||
| 39 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 72.8 (8.2) |
23.3 (2.7) |
(0.2–0.4) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 58 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 72.8 (9.2) |
25.4 (2.4) |
||||||||
| 60 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.2 (8.1) |
26.2 (3.5) |
(0.2–0.4) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 76 | Dex | 23 | ✓ | ✓ | 65.0 (5.8) |
28.3 (1.3) |
0.5 | 0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 75 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 65.5 (5.3) |
28.5 (1.2) |
0.5 | 0.5 | 0.06 | ▁▆▆▆ | ||
| 31 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 67.2 (5.0) |
|||||||||
| 33 | Preg | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.4 (5.1) |
|||||||
| 29 | Dex/Preg | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 65.4 (9.7) |
0.5 | 0.5 | |||||
| 31 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.8 (5.9) |
0.5 | 0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 148 | Prop | 23 | ✓ | 74.0 (6.0) |
25.7 (1.7) |
||||||||
| 148 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 76.0 (7.0) |
26.2 (2.1) |
0.9 | (0.1–0.5) | ▁▆▁▁ | |||
| 55 | Prop | 123 | ✓ | 68.2 (6.4) |
|||||||||
| 54 | Mid | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 66.9 (6.6) |
|||||||
| 55 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.3 (7.1) |
▁▁▆▁ | ||||||
| 183 | Prop | NR | ✓ | 73.0 (11.0) |
27.1 (1.4) |
||||||||
| 183 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 72.0 (9.0) |
26.6 (2.9) |
0.9 | (0.1–0.5) | ▁▁▆▁ | |||
| 120 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 79.0 (6.8) |
|||||||||
| 120 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 78.1 (6.4) |
0.5 | 0.3 | ▆▁▆▁ | ||||
| 354 | Plac | 1234 | ✓ | ✓ | 71.0 (5.0) |
26.1 (3.0) |
|||||||
| 356 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.0 (5.0) |
26.1 (2.9) |
0.03 | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 55 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 69.2 (3.8) |
|||||||||
| 55 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.3 (3.9) |
0.5 | ▁▆▁▁ | |||||
| 50 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 72.7 (4.3) |
29.2 (0.3) |
||||||||
| 50 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 73.2 (5.8) |
29.5 (0.2) |
0.3 | ▁▆▁▁ | ||||
| 92 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 75.2 (6.1) |
28.6 (0.9) |
||||||||
| 95 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 74.1 (4.4) |
28.9 (0.8) |
1.0 | 0.5 | ▆▁▆▁ | |||
| 48 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 67.2 (5.2) |
|||||||||
| 47 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.2 (6.0) |
1.0 | 0.4 | 2 | ▁▆▆▆ | |||
| 20 | None | NR | ✓ | 68.9 (4.3) |
|||||||||
| 20 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.2 (5.0) |
0.4 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||||
| 52 | Dex | 23 | ✓ | 70.8 (4.4) |
|||||||||
| 53 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.8 (5.5) |
(0.2–0.7) | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||
| 49 | None | NR | ✓ | 68.5 (2.2) |
|||||||||
| 49 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 67.7 (2.8) |
4 | 0.2 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 366 | Prop | 12 | ✓ | 71.0 {67-75} |
|||||||||
| 366 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 72.0 {68-76} |
1.0 | (0.1–0.5) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 64 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 74.2 (6.2) |
|||||||||
| 64 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 74.4 (6.0) |
1.0 | 0.2 | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 42 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 69.7 (7.2) |
25.8 (0.6) |
||||||||
| 40 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.9 (7.2) |
25.9 (0.4) |
200 | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| GI/Abd - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 63 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 67.9 (6.6) |
28.5 (1.1) |
||||||||
| 59 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 66.2 (7.5) |
28.2 (0.8) |
1.0 | 0.4 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 25 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | ✓ | 67.8 (5.4) |
||||||||
| 25 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 63.9 (5.0) |
0.17 | 0.4 | ▆▆▆▁ | ||||
| 50 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 70.0 (6.0) |
28.3 (1.4) |
||||||||
| 50 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.0 (5.0) |
28.4 (1.3) |
1.0 | 0.4 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 20 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 68.7 (13.5) |
26.8 (1.5) |
||||||||
| 20 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.3 (12.5) |
26.5 (1.7) |
0.6 | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 45 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 65.4 (11.7) |
29.3 (0.4) |
||||||||
| 43 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 64.9 (11.4) |
29.4 (0.5) |
0.3 | 1 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||
| 30 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 73.4 (5.1) |
28.7 (2.1) |
||||||||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 74.7 (2.6) |
27.6 (3.2) |
0.3 | 0.2 | ▆▁▆▁ | |||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.2 (3.5) |
28.0 (1.7) |
0.3 | 0.5 | ▆▁▆▁ | |||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.8 (4.3) |
28.4 (2.6) |
0.3 | 0.8 | ▆▁▆▁ | |||
| 331 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 70.4 (6.5) |
|||||||||
| 344 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.1 (5.8) |
0.5 | 0.2 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 50 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | ✓ | 70.7 (6.5) |
||||||||
| 50 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.7 (6.6) |
0.5 | 0.4 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 30 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 68.0 [66-71] |
|||||||||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.0 [67-70] |
0.5 | 0.4 | ▆▁▆▁ | ||||
| 45 | None | 23 | ✓ | 68.5 (3.8) |
|||||||||
| 45 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.5 (3.8) |
1.0 | 0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 35 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 69.7 (2.5) |
27.7 (1.9) |
||||||||
| 34 | Rem | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.1 (3.6) |
27.7 (1.7) |
||||||
| 35 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.3 (3.6) |
27.8 (2.1) |
0.5 | (0.3–0.5) | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 119 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 68.6 (5.5) |
|||||||||
| 117 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 67.9 (5.6) |
3 | ▁▁▁▆ | |||||
| Various - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 201 | Plac | 1234 | ✓ | ✓ | 74.0 {71-78} |
||||||||
| 189 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 74.0 {71-78} |
0.5 | ▁▁▆▆ | |||||
| 109 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 73.1 (6.1) |
|||||||||
| 95 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 72.2 (5.4) |
1.0 | (0.2–0.7) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 114 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 73.1 (6.4) |
1.0 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||
| 100 | Mid | 123 | ✓ | 69.4 (4.5) |
25.0 (3.3) |
||||||||
| 98 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.5 (5.0) |
24.9 (3.9) |
0.5 | ▆▁▁▁ | ||||
| 40 | Prop | 123 | ✓ | 64.7 (5.9) |
26.4 (1.3) |
||||||||
| 40 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 66.2 (6.6) |
26.1 (1.2) |
(0.5–0.7) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 310 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | ✓ | 69.0 (6.4) |
27.4 (2.7) |
|||||||
| 309 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.0 (6.6) |
27.4 (2.6) |
0.6 | 0.5 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||
| 101 | None | 23 | ✓ | 69.2 (4.1) |
27 {24-30} |
||||||||
| 108 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.0 (4.5) |
27 {24-30} |
1.0 | 100f | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 105 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.4 (3.9) |
27 {24-30} |
1.0 | 200f | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 102 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.3 (4.1) |
27 {24-30} |
1.0 | 400f | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 87 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 71.4 (4.9) |
25.8 (0.8) |
||||||||
| 87 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.6 (4.2) |
26.1 (0.7) |
1.0 | 0.4 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 32 | Plac | 1234 | ✓ | ✓ | 70.5 (6.2) |
||||||||
| 28 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.4 (7.1) |
0.7 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||
| 157 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 68.4 (6.6) |
|||||||||
| 152 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 67.9 (5.9) |
▁▁▁▆ | ||||||
| 40 | None | 123 | ✓ | 71.0 (7.1) |
27 {23-30} |
||||||||
| 42 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.4 (6.8) |
27 {23-30} |
0.6 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| Thoracic - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 46 | Mid | 12 | ✓ | 69.1 (4.9) |
29.8 (0.7) |
||||||||
| 46 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.7 (4.3) |
29.8 (0.7) |
0.2 | 0.5 (0.2–0.7) | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 30 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | ✓ | 83.2 (5.1) |
||||||||
| 30 | Mid | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 81.9 (6.2) |
|||||||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 82.5 (5.4) |
0.5 | 0.4 | ▆▆▆▁ | ||||
| 173 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 71.0 (6.0) |
|||||||||
| 173 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.0 (5.0) |
0.5 | 0.1 | ▆▁▆▁ | ||||
| 53 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | ✓ | 68.7 (3.4) |
28.0 (0.9) |
|||||||
| 53 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.7 (4.6) |
27.9 (0.9) |
0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 87 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 69.1 (5.1) |
|||||||||
| 90 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.6 (4.5) |
0.4 | 0.1 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 31 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 68.5 (2.3) |
|||||||||
| 29 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.1 (2.6) |
1.0 | ▁▆▁▁ | |||||
| 30 | None | 23 | ✓ | 71.2 (5.1) |
|||||||||
| 29 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.6 (5.3) |
1.0 | 0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| Oralmax - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 73 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 71.3 (5.1) |
28.0 (1.6) |
||||||||
| 76 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.7 (5.2) |
28.2 (1.6) |
0.2 | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 20 | Mid | NR | ✓ | 60.5 (8.2) |
|||||||||
| 20 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 60.0 (10.1) |
1.0 | (0.2–0.7) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 60 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 72.1 (5.9) |
|||||||||
| 60 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.3 (6.7) |
0.5 | 0.4 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| Urol - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 20 | Plac | NR | ✓ | ||||||||||
| 20 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 2 | ▁▆▁▁ | ||||||
| 60 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 66.7 (4.1) |
25.4 (2.2) |
||||||||
| 60 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 65.6 (3.4) |
25.5 (2.5) |
0.4 | ▁▆▁▁ | ||||
| Headneck - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 30 | Mid/Prop | NR | ✓ | 69.9 (2.8) |
28.5 (1.2) |
||||||||
| 30 | Mid/Sevo | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.1 (3.2) |
28.6 (1.2) |
||||||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.8 (3.0) |
29.0 (0.9) |
1.0 | 0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.3 (3.1) |
28.8 (1.1) |
1.0 | 0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| ENT - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 149 | Plac | NR | ✓ | ✓ | 70.1 (4.2) |
23.9 (4.9) |
|||||||
| 150 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 70.4 (5.0) |
24.3 (4.8) |
0.5 | 0.2 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||
| Ortho - Nonrandomized Trial | |||||||||||||
| 70 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 69.7 (5.3) |
27.3 (0.7) |
||||||||
| 70 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.2 (5.6) |
27.6 (0.5) |
0.5 | 0.4 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| Spine - Nonrandomized Trial | |||||||||||||
| 46 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 70.6 (6.1) |
25.6 (4.8) |
||||||||
| 57 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.4 (6.7) |
24.1 (4.6) |
0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 62 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 72.5 (7.2) |
25.8 (4.5) |
1 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| Ophtho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||||
| 50 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 64.0 (7.2) |
|||||||||
| 50 | Mid | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 63.6 (8.3) |
|||||||
| 50 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 66.5 (1.6) |
1 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||
| 30 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 70.6 (5.6) |
|||||||||
| 30 | Ket | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 72.8 (5.3) |
▁▆▆▁ | ||||||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 73.3 (5.1) |
0.5 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||||
| GI/Abd - Nonrandomized Trial | |||||||||||||
| 48 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 72.1 (32.2) |
|||||||||
| 48 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 71.9 (31.4) |
0.5 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||
| 60 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 74.1 (13.9) |
28.9 (1.2) |
||||||||
| 80 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 73.8 (14.5) |
28.9 (1.2) |
1.0 | (0.2–0.7) | ▁▁▆▁ | |||
| 50 | Plac | NR | ✓ | ✓ | 68.3 (2.1) |
28.5 (4.2) |
|||||||
| 60 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.4 (3.3) |
28.5 (4.3) |
0.5 | 0.4 | ▆▁▁▁ | |||
| Thoracic - Nonrandomized Trial | |||||||||||||
| 46 | None | NR | ✓ | 67.3 (2.1) |
28.5 (4.2) |
||||||||
| 41 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 67.4 (3.3) |
28.5 (4.3) |
0.5 | 0.1 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||
| GI/Abd - Prospective Cohort | |||||||||||||
| 289 | None | 123 | 69.3 (5.1) |
||||||||||
| 354 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 69.3 (5.1) |
Unspecified | ||||||
| Cardiac - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||||||||
| 283 | None | NR | ✓ | 73.5 (6.2) |
|||||||||
| 222 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 73.6 (6.1) |
(0.24–0.6) | ▁▁▆▆ | |||||
| 209 | Prop | NR | ✓ | 62.0 (13.0) |
|||||||||
| 69 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 63.0 (13.0) |
0.19 (0.08–0.31) | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||
| Ortho - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||||||||
| 58 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 72.1 (0.2) |
28.7 (1.1) |
||||||||
| 62 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 72.2 (0.3) |
28.6 (1.3) |
0.5 | 0.4 | ▆▁▆▁ | |||
| 357 | Prop | 123 | ✓ | 74.0 {70-78} |
|||||||||
| 357 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 74.0 {70-79} |
1.0 | (0.1–0.5) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 30 | None | NR | ✓ | 67.9 (5.0) |
18.0 (1.5) |
||||||||
| 30 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 67.3 (5.5) |
18.3 (2.0) |
0.5 | 0.4 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||
| Urol - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||||||||
| 35 | None | 1234 | 68.0 [66-72] |
||||||||||
| 160 | Dex | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 68.0 [66-72] |
▁▁▆▁ | ||||||
| GI: gastrointestinal; Abd: abdominal (includes hepatic); Ortho: orthopedic; Various: more that one procedure category; Oralmax: oral and maxillofacial; Ophtho; ophthalmologic; Urol: urologic; Dex: dexmedetomidine; Ulin: ulinastatin; Mid: midazolam; Mid/Prop: midazolam/propofol; Mid/Seve: midazolam/sevoflurane; Preg: pregabalin; Prop: propofol; Plac; placebo; PS: physical status; Vol: volatile; TIVA: total intravenous anesthesia; Reg: regional; Sed: sedation; MMSE: Mini-Mental State Exam. | |||||||||||||
| a ASA Physical Status of patients included (proportions can be found here[link to table add]). | |||||||||||||
| b Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | |||||||||||||
| c No studies reported including cognitively impaired patients except Liu 2016 as indicated. | |||||||||||||
| d Maintenance range if reported in parentheses. | |||||||||||||
| e Bars indicate adminstration times from left to right: preoperative, induction, intraoperative, and postoperative (includes PACU). | |||||||||||||
| f Given as a single dose. | |||||||||||||
Ketamine
| Study | N | Arm | ASA | Anesthetic | Ageb | MMSEb,c | Dose | Maintenance | Timingd | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSa | Vol | TIVA | Reg | (mg/kg) | (mg/kg) | ||||||
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 26 | None | NR | ✓ | 64.0 (7.0) |
|||||||
| 26 | Plac | 67.0 (8.0) |
|||||||||
| 26 | Ket | 68.0 (7.0) |
0.5 | ▁▆▁▁ | |||||||
| 29 | Plac | 34 | ✓ | 60.8 (8.0) |
|||||||
| 29 | Ket | 68.0 (8.0) |
0.5 | ▁▆▁▁ | |||||||
| 32 | Prop | NR | ✓ | ||||||||
| 32 | Ket | 1 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||||||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 75 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 65.0 (14.0) |
|||||||
| 79 | Ket | 64.0 (13.0) |
0.5 | ▁▁▆▆ | |||||||
| 26 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 68.4 (6.5) |
26 {24-28} |
||||||
| 25 | Ket | 68.3 (5.3) |
25 {24-28} |
0.5 | ▁▆▁▁ | ||||||
| 40 | Suf | 123 | ✓ | 65.3 (5.2) |
|||||||
| 40 | Kete | 66.0 (5.3) |
0.5 | ▁▆▁▁ | |||||||
| GI/Abd - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 19 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | ✓ | 61.0 (12.4) |
||||||
| 19 | Kete | 58.4 (8.1) |
0.01 | ▁▁▆▆ | |||||||
| 18 | Kete | 62.2 (9.8) |
0.25 | 0.12 | ▁▁▆▆ | ||||||
| 34 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 70.0 (6.2) |
27.9 (1.6) |
||||||
| 33 | Ket | 70.6 (7.6) |
28.6 (1.1) |
0.15 | ▁▆▁▁ | ||||||
| 31 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 70.5 (4.2) |
|||||||
| 31 | Ket | 69.5 (4.3) |
0.25 | 0.12 | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||||
| Various - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 222 | Plac | NR | 70.0 (6.9) |
||||||||
| 227 | Ket | 70.0 (7.2) |
0.5 | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||||
| 223 | Ket | 70.0 (7.3) |
1 | ||||||||
| 44 | Plac | NR | 74.8 (6.6) |
28.3 (2.3) |
|||||||
| 45 | Hal | 73.4 (6.3) |
28.0 (1.3) |
||||||||
| 47 | Ket | 73.4 (6.1) |
27.7 (1.7) |
1 | ▆▁▁▁ | ||||||
| Ophtho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 32 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 70.5 (4.7) |
|||||||
| 33 | Ket | 68.7 (7.1) |
0.3 | ||||||||
| 30 | Plac | 23 | ✓ | 70.6 (5.6) |
|||||||
| 30 | Dex | 73.3 (5.1) |
0.3 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||||||
| 30 | Ket | 72.8 (5.3) |
0.3 | ▁▆▆▁ | |||||||
| Ortho - Prospective Cohort | |||||||||||
| 119 | None | NR | ✓ | ||||||||
| 68 | Ket | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||||||
| Spine - Prospective Cohort | |||||||||||
| 38 | None | 123 | 71.0 {68-78} |
||||||||
| 60 | Ket | 70.0 {67-75} |
Unspecified | ||||||||
| Other - Prospective Cohort | |||||||||||
| 92 | None | NR | |||||||||
| 6 | Ket | ▁▁▆▁ | |||||||||
| Ortho - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||||||
| 31,796 | None | NR | ✓ | ||||||||
| 4,070 | Ket | ||||||||||
| 36,852 | None | NR | ✓ | ||||||||
| 99 | Ket | ▁▁▁▆ | |||||||||
| 538,559 | None | NR | |||||||||
| 25,667 | Ket | ▁▁▆▆ | |||||||||
| 1,081,139 | None | NR | |||||||||
| 49,430 | Ket | ▁▁▆▆ | |||||||||
| 468,004 | None | NR | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| 37,148 | Ket | ▆▁▁▆ | |||||||||
| Thoracic - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||||||
| 74 | None | NR | 61.7 (10.5) |
||||||||
| 10 | Ket | 61.7 (10.5) |
▁▁▆▁ | ||||||||
| GI: gastrointestinal; Abd: abdominal (includes hepatic); Ortho: orthopedic; Various: more that one procedure category; Dex: dexmedetomidine; Hal: haloperidol; Suf: sufentanil; Prop: propofol; Plac; placebo; PS: physical status; Vol: volatile; TIVA: total intravenous anesthesia; Reg: regional; MMSE: Mini-Mental State Exam. | |||||||||||
| a ASA Physical Status of patients included (proportions can be found here[link to table add]). | |||||||||||
| b Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | |||||||||||
| c No studies reported including cognitively impaired patients. | |||||||||||
| d Bars indicate adminstration times from left to right: preoperative, induction, intraoperative, and postoperative (includes PACU). | |||||||||||
| e S-Ketamine. | |||||||||||
Melatonin/Ramelteon
| Study | N | Arm | ASA | Anesthetic | Ageb | MMSEb,c | Dosing | Timingd | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSa | Vol | TIVA | Reg | |||||||
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | ||||||||||
| 71 | Oxaz | NR | 61.7 (9.9) |
|||||||
| 66 | Mel | 60.0 (10.2) |
3mg × 10 | ▆▆ | ||||||
| 25 | Plac | 34 | ✓ | 67.9 (4.1) |
29 [28-30] |
|||||
| 25 | Mel | 66.6 (4.8) |
29 [27-30] |
3mg × 5 | ▆▆ | |||||
| 104 | Plac | NR | 67.6 (8.0) |
|||||||
| 98 | Mel | 69.0 (8.3) |
3mg × 7 | ▆▆ | ||||||
| 30 | Plac | NR | ✓ | 62.9 (8.1) |
||||||
| 30 | Mel | 60.3 (9.5) |
3mg × 3 | ▆▆ | ||||||
| 149 | Plac | NR | 71.6 (6.6) |
|||||||
| 148 | Mel | 71.5 (6.7) |
3mg × 7 | ▁▆ | ||||||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | ||||||||||
| 49 | None | 123 | ✓ | 72.3 (6.4) |
||||||
| 50 | Mid | 69.9 (8.2) |
||||||||
| 53 | Mel | 70.4 (7.1) |
5mg × 2 | ▆▁ | ||||||
| 192 | Plac | NR | 83.4 (7.5) |
23 {10-28} |
||||||
| 186 | Mel | 84.1 (8.0) |
23 {12-29} |
3mg × 5 | ▆▆ | |||||
| 70 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | 74.6 (5.4) |
27.1 (0.3) |
|||||
| 69 | Mel | 74.5 (5.7) |
27.3 (0.2) |
1mg × 6 | ▆▆ | |||||
| 39 | Plac | NR | 75.4 (5.0) |
28.2 (1.9) |
||||||
| 41 | Ram | 74.3 (5.5) |
28.6 (1.5) |
8mg × 3 | ▆▆ | |||||
| 36 | Plac | NR | ✓ | |||||||
| 36 | Mel | 5mg × 4 | ▆▆ | |||||||
| 40 | Plac | 123 | ||||||||
| 40 | Mel | 5mg × 2 | ▆▁ | |||||||
| GI/Abd - Randomized Clinical Trial | ||||||||||
| 19 | Plac | NR | 73.7 (5.8) |
|||||||
| 23 | Ram | 72.7 (5.2) |
4mg × 14 | ▆▁ | ||||||
| Thoracic - Randomized Clinical Trial | ||||||||||
| 58 | Plac | NR | 56.1 (15.8) |
|||||||
| 59 | Ram | 58.1 (14.1) |
8mg × 6 | ▆▆ | ||||||
| Various - Randomized Clinical Trial | ||||||||||
| 50 | Plac | 12 | ✓ | 70.6 (3.8) |
||||||
| 50 | Ram | 69.3 (4.0) |
8mg × 2 | ▆▁ | ||||||
| 49 | None | NR | ✓ | ✓ | 73.7 (6.0) |
26.2 (2.2) |
||||
| 51 | Mel | 75.9 (6.1) |
26.4 (2.1) |
5mg × 2 | ▆▁ | |||||
| 49 | Plac | 123 | ✓ | ✓ | 75.4 (5.6) |
|||||
| 54 | Ram | 78.1 (6.9) |
8mg × 6 | ▆▆ | ||||||
| Cardiac - Nonrandomized Trial | ||||||||||
| 250 | None | NR | ✓ | 65.2 (10.3) |
||||||
| 250 | Mel | 64.3 (10.1) |
5mg × 4 | ▆▆ | ||||||
| 250 | None | NR | ✓ | 65.2 (10.3) |
||||||
| 250 | Mel | 64.3 (10.1) |
5mg × 4 | ▆▆ | ||||||
| GI/Abd - Before-After/Time Series | ||||||||||
| 186 | None | 123 | 69.0 [30-88] |
|||||||
| 120 | Ram | 71.0 [34-85] |
8mg × 4 | ▆▆ | ||||||
| Thoracic - Before-After/Time Series | ||||||||||
| 58 | None | NR | ✓ | ✓ | 76.5 [70-87] |
|||||
| 24 | Ram | 79.0 [70-89] |
8mg × 7 | ▁▆ | ||||||
| Headneck - Retrospective Cohort | ||||||||||
| 34 | None | NR | 62.9 (11.9) |
|||||||
| 35 | Ram | 62.9 (11.9) |
NR | ▁▆ | ||||||
| GI: gastrointestinal; Abd: abdominal (includes hepatic); Ortho: orthopedic; Various: more that one procedure category; PS: physical status; Vol: volatile; TIVA: total intravenous anesthesia; Reg: regional; MMSE: Mini-Mental State Exam; Mel: melatonin; Ram: ramelteon; Oxaz: oxazepam; Dex: dexmedetomidine; Mid: midazolam; Plac; placebo; NR: not reported. | ||||||||||
| a ASA Physical Status of patients included (proportions can be found here[link to table add]). | ||||||||||
| b Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | ||||||||||
| c No studies reported including cognitively impaired patients. | ||||||||||
| d Bars indicate adminstration times: preoperative left and postoperative right. | ||||||||||
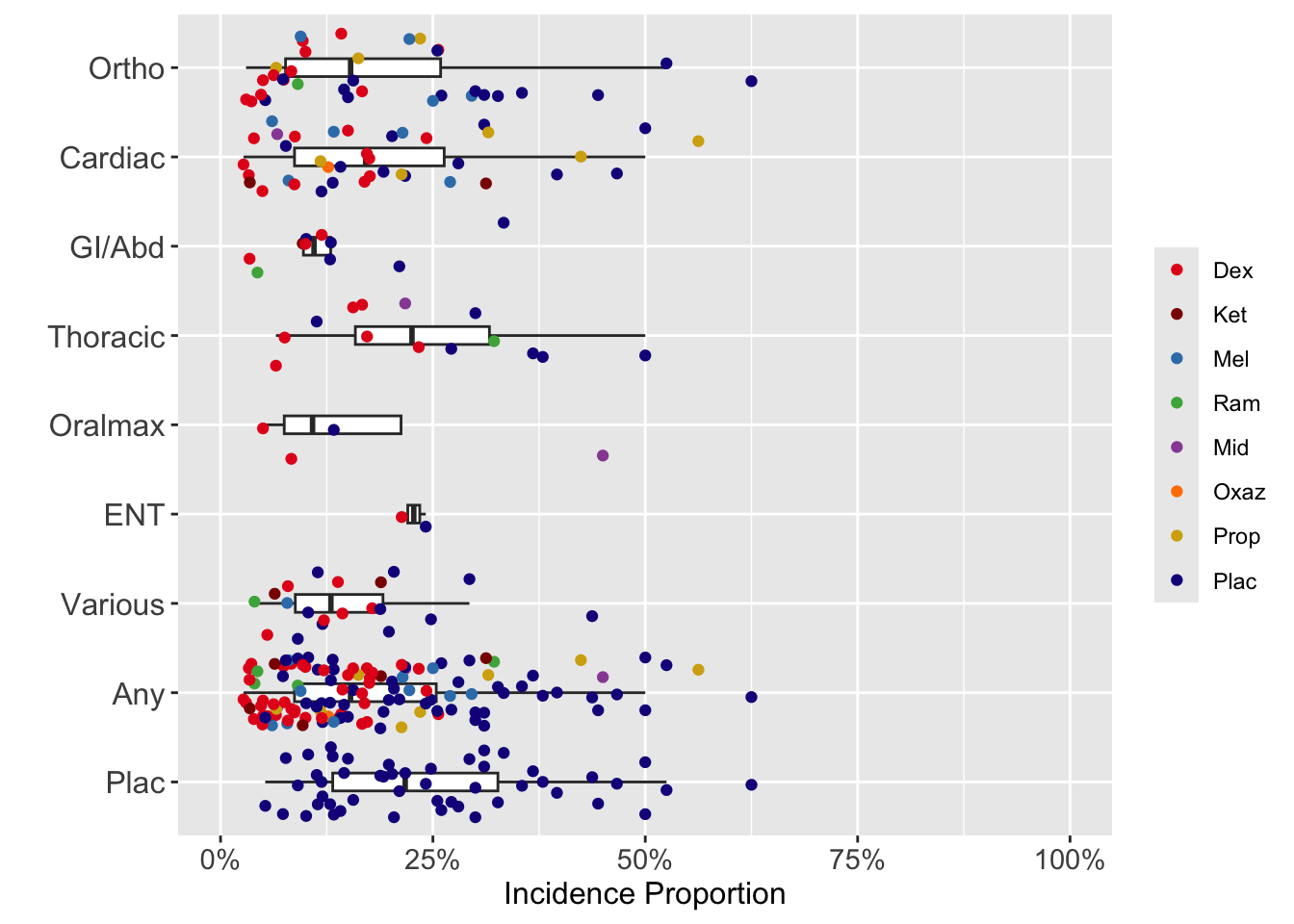
Delirium Incidence
Dexmedetomidine
| Study | N | Arm | Scale | Day(s)a | Incidence Proportion | RR (95% CI) | Timingb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 0 – 100% | |||||||
| Cardiac | ||||||||
| 92 | Prop | CAM | 5 | 29 (31.5) | — | |||
| 91 | Dexc | 16 (17.6) | 0.56 (0.33-0.95) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 143 | Plac | CAM | 5 | 11 (7.7) | — | |||
| 142 | Dex | 7 (4.9) | 0.64 (0.26-1.61) | ▁▁▆▆ | ||||
| 30 | Mid | CAM | 7 | 2 (6.7) | — | |||
| 30 | Dexc | 1 (3.3) | 0.50 (0.05-5.22) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 61 | Prop | CAM | Stay | 13 (21.3) | — | |||
| 59 | Dexc | 10 (16.9) | 0.80 (0.38-1.67) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 54 | Plac | DSM | 7 | 7 (13.0) | — | |||
| 54 | Dex | 2 (3.7) | 0.29 (0.06-1.31) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 396 | Plac | CAM | 5 | 46 (11.6) | — | |||
| 398 | Dex | 67 (16.8) | 1.45 (1.02-2.05) | ▁▆▆▆ | ||||
| 20 | Plac | DSM | Noted | 10 (50.0)e | — | |||
| 20 | Dex | 3 (15.0)e | 0.30 (0.10-0.93) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 203 | Plac | CAM | Stay | 33 (16.3) | — | |||
| 205 | Dexc | 31 (15.1) | 0.93 (0.59-1.46) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 33 | Prop | ICDSC | 5 | 14 (42.4) | — | |||
| 34 | Dexc | 8 (23.5) | 0.55 (0.27-1.14) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 23 | None | NS | Stay | 5 (21.7) | — | |||
| 23 | Dex | 2 (8.7) | 0.40 (0.09-1.86) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 206 | Plac | CAM | 3 | 25 (12.1) | — | |||
| 188 | Dexc | 14 (7.4) | 0.61 (0.33-1.14)f | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 34 | Prop | CAM | 2 | 4 (11.8) | — | |||
| 37 | Dex | 1 (2.7) | 0.23 (0.03-1.96) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| Ortho | ||||||||
| 40 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 25 (62.5) | — | |||
| 39 | Dex | 10 (25.6) | 0.41 (0.23-0.74) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 58 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 18 (31.0) | — | |||
| 60 | Dex | 5 (8.3) | 0.27 (0.11-0.68) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 31 | Plac | Psych | Stay | 11 (35.5) | — | |||
| 33 | Preg | 14 (42.4) | 1.20 (0.64-2.22) | |||||
| 29 | Dex/Preg | 7 (24.1) | 0.68 (0.31-1.52) | |||||
| 31 | Dex | 3 (9.7) | 0.27 (0.08-0.88) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 148 | Prop | CAM | 3 | 24 (16.2) | — | |||
| 148 | Dex | 11 (7.4) | 0.46 (0.23-0.90) | ▁▆▁▁ | ||||
| 183 | Prop | CAM | 7 | 43 (23.5) | — | |||
| 183 | Dex | 26 (14.2) | 0.60 (0.39-0.94) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 120 | Plac | CAM/DSM | 3 | 36 (30.0) | — | |||
| 120 | Dex | 20 (16.7) | 0.56 (0.34-0.90) | ▆▁▆▁ | ||||
| 354 | Plac | CAM | 5 | 26 (7.3) | — | |||
| 356 | Dexc | 17 (4.8) | 0.65 (0.36-1.18) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 55 | Plac | Noteg | 1 | 8 (14.5) | — | |||
| 55 | Dex | 2 (3.6) | 0.25 (0.06-1.12) | ▁▆▁▁ | ||||
| 50 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 13 (26.0) | — | |||
| 50 | Dex | 5 (10.0) | 0.38 (0.15-1.00) | ▁▆▁▁ | ||||
| 20 | None | DOC | 5 | 3 (15.0) | — | |||
| 20 | Dex | 1 (5.0) | 0.33 (0.04-2.94) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 366 | Prop | CAM | 3 | 24 (6.6) | — | |||
| 366 | Dex | 11 (3.0) | 0.46 (0.23-0.92) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 64 | Plac | CAM | Stay | 10 (15.6) | — | |||
| 64 | Dex | 4 (6.2) | 0.40 (0.13-1.21) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| Various | ||||||||
| 201 | Plac | CAM | 5 | 23 (11.4) | — | |||
| 189 | Dex | 23 (12.2) | 1.06 (0.62-1.83) | ▁▁▆▆ | ||||
| 109 | Plac | CAM | 5 | 27 (24.8) | — | |||
| 95 | Dex | 9 (9.5) | 0.38 (0.19-0.77) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 114 | Dex | 21 (18.4) | 0.74 (0.45-1.23) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 310 | Plac | CAM | 5 | 32 (10.3) | — | |||
| 309 | Dex | 17 (5.5) | 0.53 (0.30-0.94) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 101 | None | CAM | 7 | 19 (18.8) | — | |||
| 108 | Dex | 15 (13.9) | 0.74 (0.40-1.37) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 105 | Dex | 5 (4.8) | 0.25 (0.10-0.65) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 102 | Dex | 5 (4.9) | 0.26 (0.10-0.67) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 32 | Plac | CAM/ICDSC | 14 | 14 (43.8) | — | |||
| 28 | Dex | 5 (17.9) | 0.41 (0.17-0.99) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| 157 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 46 (29.3) | — | |||
| 152 | Dexc | 21 (13.8) | 0.47 (0.30-0.75) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| Thoracic | ||||||||
| 46 | Mid | CAM | 3 | 10 (21.7) | — | |||
| 46 | Dex | 3 (6.5) | 0.30 (0.09-1.02) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 30 | Plac | CAM | Noted | 15 (50.0)e | — | |||
| 30 | Mid | 17 (56.7)e | 1.13 (0.70-1.82) | |||||
| 30 | Dex | 7 (23.3)e | 0.47 (0.22-0.98) | ▆▆▆▁ | ||||
| 173 | Plac | ICDSC | Noted | 47 (27.2)e | — | |||
| 173 | Dex | 27 (15.6)e | 0.57 (0.38-0.88) | ▆▁▆▁ | ||||
| 53 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 6 (11.3) | — | |||
| 53 | Dex | 4 (7.5) | 0.67 (0.20-2.23) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 87 | Plac | CAM | 4 | 32 (36.8) | — | |||
| 90 | Dex | 15 (16.7) | 0.45 (0.26-0.78) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 30 | None | CAM | Noted | 9 (30.0)e | — | |||
| 29 | Dex | 5 (17.2)e | 0.57 (0.22-1.51) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| Oralmax | ||||||||
| 20 | Mid | NS | Stay | 9 (45.0) | — | |||
| 20 | Dexc | 1 (5.0) | 0.11 (0.02-0.80) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| 60 | Plac | CAM | 5 | 8 (13.3) | — | |||
| 60 | Dex | 5 (8.3) | 0.62 (0.22-1.80) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| GI/Abd | ||||||||
| 331 | Plac | CAM | Noted | 43 (13.0)e | — | |||
| 344 | Dex | 41 (11.9)e | 0.92 (0.61-1.37) | ▁▆▆▁ | ||||
| 30 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 10 (33.3) | — | |||
| 30 | Dex | 3 (10.0) | 0.30 (0.09-0.98) | ▆▁▆▁ | ||||
| 119 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 12 (10.1) | — | |||
| 117 | Dexc | 4 (3.4) | 0.34 (0.11-1.02) | ▁▁▁▆ | ||||
| ENT | ||||||||
| 149 | Plac | CAM | 5 | 36 (24.2) | — | |||
| 150 | Dex | 32 (21.3) | 0.88 (0.58-1.34) | ▁▁▆▁ | ||||
| GI: gastrointestinal; Abd: abdominal (includes hepatic); Ortho: orthopedic; Various: more that one procedure category; Oralmax: oral and maxillofacial; Ophtho; ophthalmologic; Urol: urologic; RR: risk ratio; Dex: dexmedetomidine; Mid: midazolam; Prop: propofol; Preg: pregabalin; Plac: placebo; DSM: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; ICDSC: Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist; Psych: psychiatrist interview; Nu-DESC: Nursing Delirium Screening Scale; NS: not specified. | ||||||||
| a Day(s) over which incidence proportion assessed. Stay indicates duration of hospitalization. | ||||||||
| b Bars indicate adminstration times from left to right: preoperative, induction, intraoperative, and postoperative (includes PACU). | ||||||||
| c Postoperative dexmedetomidine only. | ||||||||
| d Reported only daily incidence. | ||||||||
| e Maximum of reported daily incidence. | ||||||||
| f Primary outcome was delirium on postoperative day 1 — OR 0.32 (95% CI, 0.10–0.83) | ||||||||
| g Tool reported in the `Chinese Expert Consensus on the Prevention and Treatment of Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients.' | ||||||||
Ketamine
| Study | N | Arm | Scale | Day(s)a | Incidence Proportion | RR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 0 – 100% | ||||||
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 29 | Plac | ICDSC | 5 | 9 (31.0) | — | ||
| 29 | Ket | 1 (3.4) | 0.11 (0.02-0.82) | ||||
| 32 | Prop | CAM | 1 | 18 (56.2) | — | ||
| 32 | Ket | 10 (31.2) | 0.56 (0.31-1.01) | ||||
| Ortho - Prospective Cohort | |||||||
| 119 | None | CAM | 5 | 38 (31.9) | — | ||
| 68 | Ket | 30 (44.1) | 1.38 (0.95-2.01) | ||||
| Various - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 222 | Plac | CAM | 3 | 43 (19.4) | — | ||
| 227 | Ket | 39 (17.2) | 0.89 (0.60-1.31) | ||||
| 223 | Ket | 46 (20.6) | 1.06 (0.73-1.54) | ||||
| 44 | Plac | ICDSC | 3 | 4 (9.1) | — | ||
| 45 | Hal | 5 (11.1) | 1.22 (0.35-4.25) | ||||
| 47 | Ket | 3 (6.4) | 0.70 (0.17-2.96) | ||||
| Ortho - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||
| 31,796 | None | ICD | Stay | 713 (2.2) | — | ||
| 4,070 | Ket | 84 (2.1) | 0.92 (0.74-1.15) | ||||
| 36,852 | None | ICD | Stay | 771 (2.1) | — | ||
| 99 | Ket | 13 (13.1) | 6.28 (3.76-10.47) | ||||
| 538,559 | None | Otherb | Stay | 14,082 (2.6) | — | ||
| 25,667 | Ket | 703 (2.7) | 1.05 (0.97-1.13) | ||||
| 1,081,139 | None | Otherb | Stay | 30,978 (2.9) | — | ||
| 49,430 | Ket | 1,406 (2.8) | 0.99 (0.94-1.05) | ||||
| 468,004 | None | ICD | Stay | 72,998 (15.6) | — | ||
| 37,148 | Ket | 6,549 (17.6) | 1.13 (1.10-1.16) | ||||
| Thoracic - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||
| 74 | None | CAM | Stay | 24 (32.4) | — | ||
| 10 | Ket | 3 (30.0) | 0.92 (0.34-2.52) | ||||
| Spine - Prospective Cohort | |||||||
| 38 | None | CAM/ICDSC | Stay | 7 (18.4) | — | ||
| 60 | Ket | 19 (31.7) | 1.72 (0.80-3.70) | ||||
| Other - Prospective Cohort | |||||||
| 92 | None | Nu-DESC | Stay | 10 (10.9) | — | ||
| 6 | Ket | 1 (16.7) | 1.53 (0.23-10.07) | ||||
| GI/Abd - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 31 | Plac | CAM | NA | 4 (12.9) | — | ||
| 31 | Ket | 3 (9.7) | 0.75 (0.18-3.08) | ||||
| RR: risk ratio; Ket: ketamine; Plac: placebo; Prop: propofol; Hal: haloperidol; ICDSC: Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist; CAM: Confusion Assessment Method; Nu-DESC: Nursing Delirium Screening Scale; ICD: ICD codes. | |||||||
| a Days over which incidence assessed. Stay indicates duration of hospital stay. | |||||||
| b Claims-based algorithm. | |||||||
Melatonin/Ramelteon
| Study | N | Arm | Scale | Day(s)a | Incidence Proportion | RR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 0 – 100% | ||||||
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 71 | Oxaz | Clinical | Stay | 9 (12.7) | — | ||
| 66 | Mel | 4 (6.1) | 0.48 (0.15-1.48) | ||||
| 25 | Plac | ICDSC | 3 | 7 (28.0) | — | ||
| 25 | Mel | 2 (8.0) | 0.29 (0.07-1.24) | ||||
| 104 | Plac | CAM/DSM | 7 | 21 (20.2) | — | ||
| 98 | Mel | 21 (21.4) | 1.06 (0.62-1.82) | ||||
| 30 | Plac | CAM | Noteb | 14 (46.7) | — | ||
| 30 | Mel | 4 (13.3) | 0.29 (0.11-0.77) | ||||
| 149 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 59 (39.6) | — | ||
| 148 | Mel | 40 (27.0) | 0.68 (0.49-0.95) | ||||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 49 | None | AMT | 3 | 16 (32.7) | — | ||
| 50 | Mid | 22 (44.0) | 1.35 (0.81-2.24) | ||||
| 53 | Mel | 5 (9.4) | 0.29 (0.11-0.73) | ||||
| 192 | Plac | DSM | 8 | 49 (25.5) | — | ||
| 186 | Mel | 55 (29.6) | 1.16 (0.83-1.61) | ||||
| 39 | Plac | CAM/DRS/DSM | 2 | 2 (5.1) | — | ||
| 41 | Ram | 3 (7.3) | 1.43 (0.25-8.09) | ||||
| 36 | Plac | AMT | Noteb | 16 (44.4) | — | ||
| 36 | Mel | 8 (22.2) | 0.50 (0.25-1.02) | ||||
| 40 | Plac | AMT | 3 | 21 (52.5) | — | ||
| 40 | Mel | 10 (25.0) | 0.48 (0.26-0.88) | ||||
| Various - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 50 | Plac | CAM | 3 | 6 (12.0) | — | ||
| 50 | Ram | 2 (4.0) | 0.33 (0.07-1.57) | ||||
| 49 | None | AMT | Noteb | 10 (20.4) | — | ||
| 51 | Mel | 4 (7.8) | 0.38 (0.13-1.14) | ||||
| Thoracic - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 58 | Plac | CAM | Stay | 22 (37.9) | — | ||
| 59 | Ram | 19 (32.2) | 0.85 (0.52-1.39) | ||||
| GI/Abd - Before-After/Time Series | |||||||
| 186 | None | DSM | 7 | 28 (15.1) | — | ||
| 120 | Ram | 7 (5.8) | 0.39 (0.17-0.86) | ||||
| Thoracic - Before-After/Time Series | |||||||
| 58 | None | ICDSC | 9 | 5 (8.6) | — | ||
| 24 | Ram | 0 (0) | Not estimated | ||||
| Cardiac - Nonrandomized Trial | |||||||
| 250 | None | CAM | Stay | 52 (20.8) | — | ||
| 250 | Mel | 21 (8.4) | 0.40 (0.25-0.65) | ||||
| 250 | None | CAM | Stay | 52 (20.8) | — | ||
| 250 | Mel | 21 (8.4) | 0.40 (0.25-0.65) | ||||
| Headneck - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||
| 34 | None | DSM | Stay | 12 (35.3) | — | ||
| 35 | Ram | 11 (31.4) | 0.89 (0.46-1.74) | ||||
| GI/Abd - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 19 | Plac | CAM | 7 | 4 (21.1) | — | ||
| 23 | Ram | 1 (4.3) | 0.21 (0.03-1.70) | ||||
| RR: risk ratio; MMSE: Mini-Mental State Examination; Mel: melatonin; Ram: ramelteon; Dex: dexmedetomidine; Oxaz: oxazepam; Mid: midazolam; AMT: Abbreviated Mental Test; DRS: Delirium Rating Scale; DSM: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; CAM: Confusion Assessment Method; ICDSC: Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist. | |||||||
| a Day(s) over which incidence proportion assessed. Stay indicates duration of hospitalization. | |||||||
| b Reported only daily incidence. | |||||||
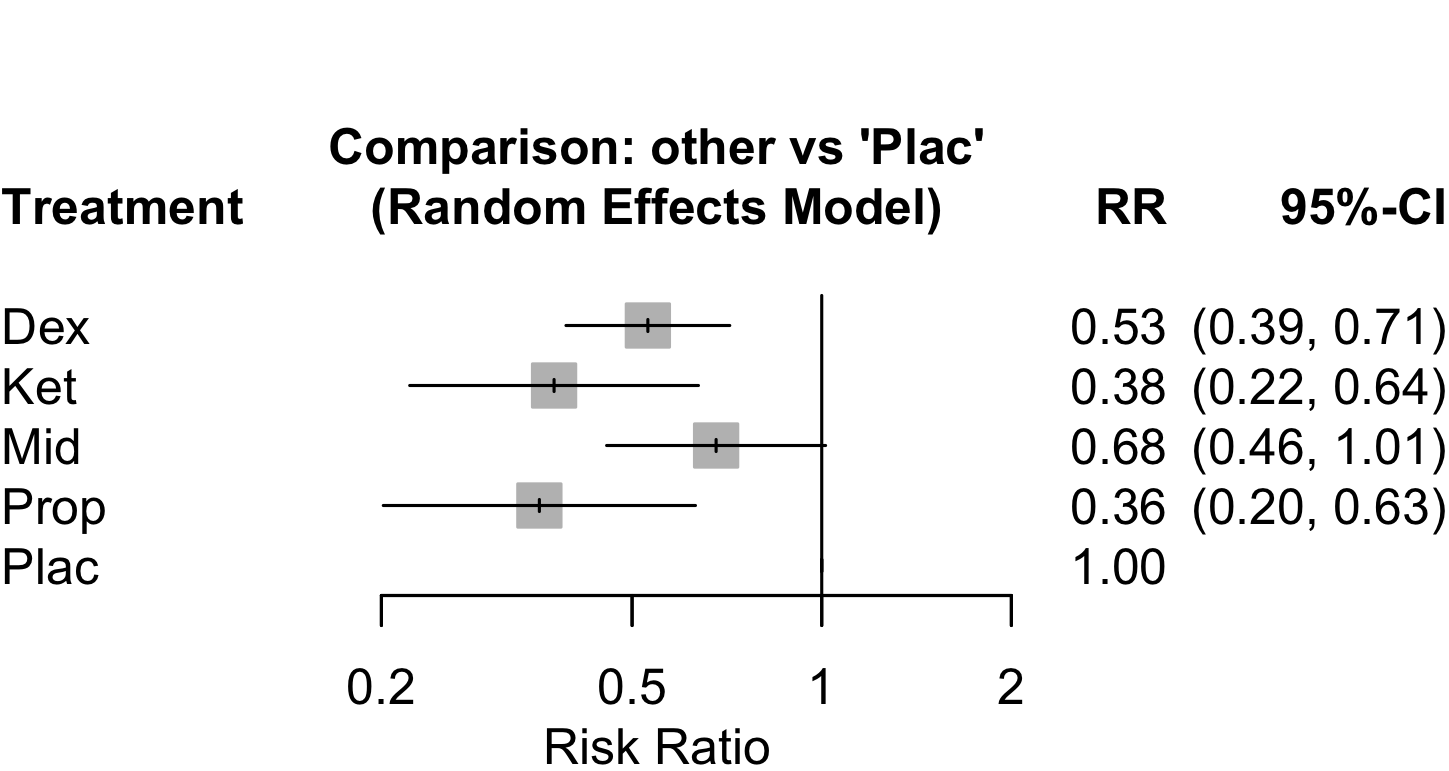
Pooled
Dexmedetomidine
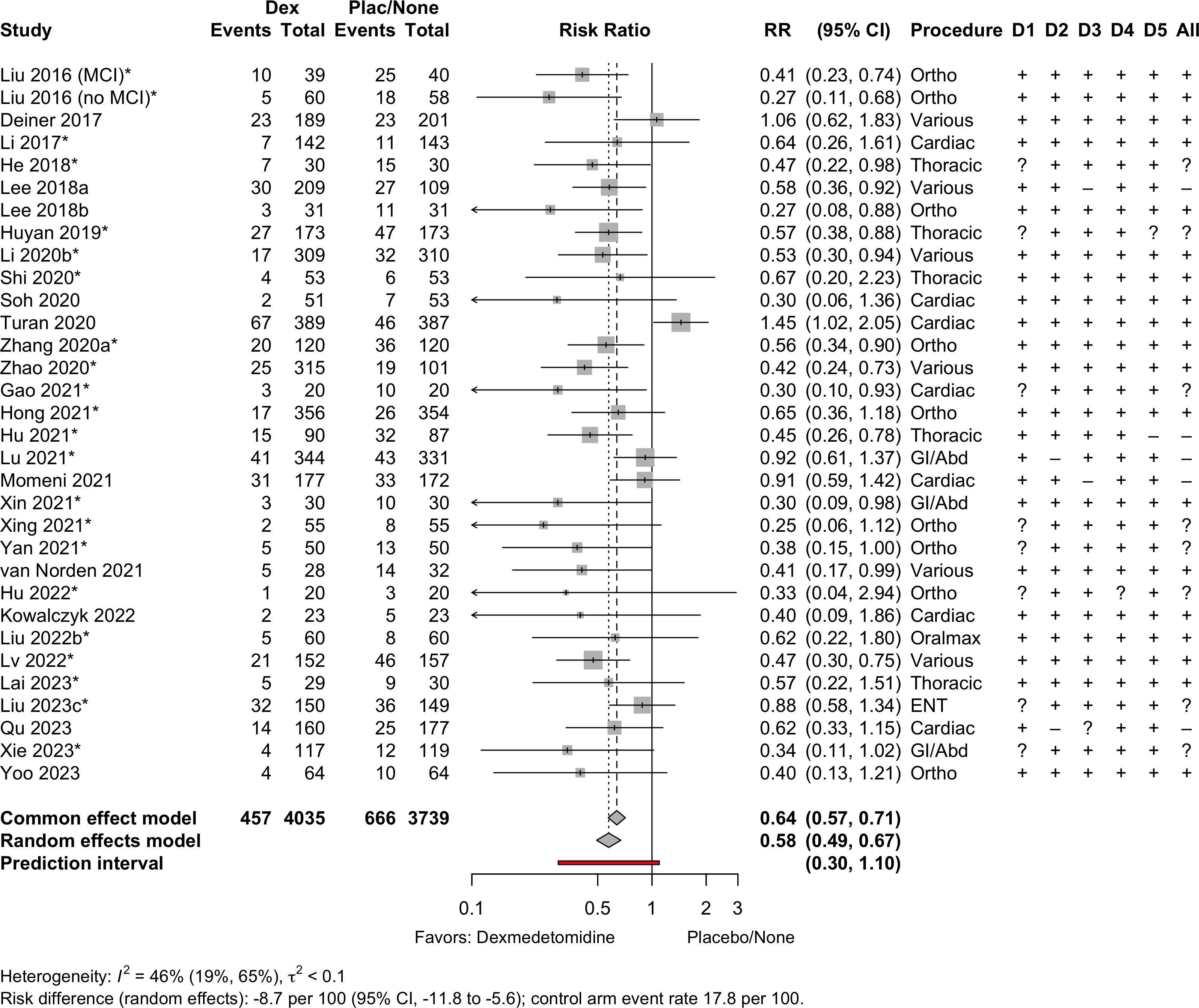
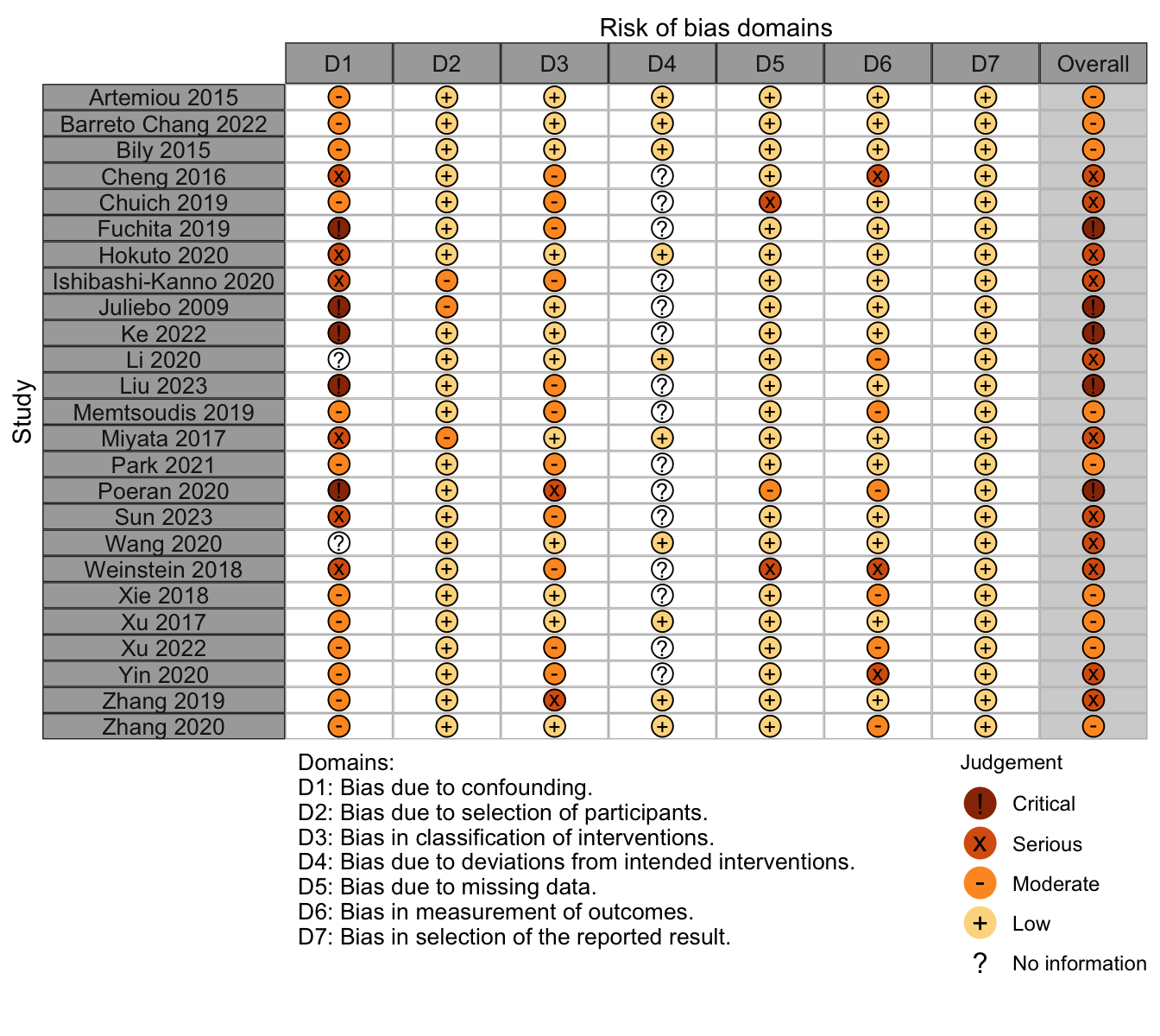
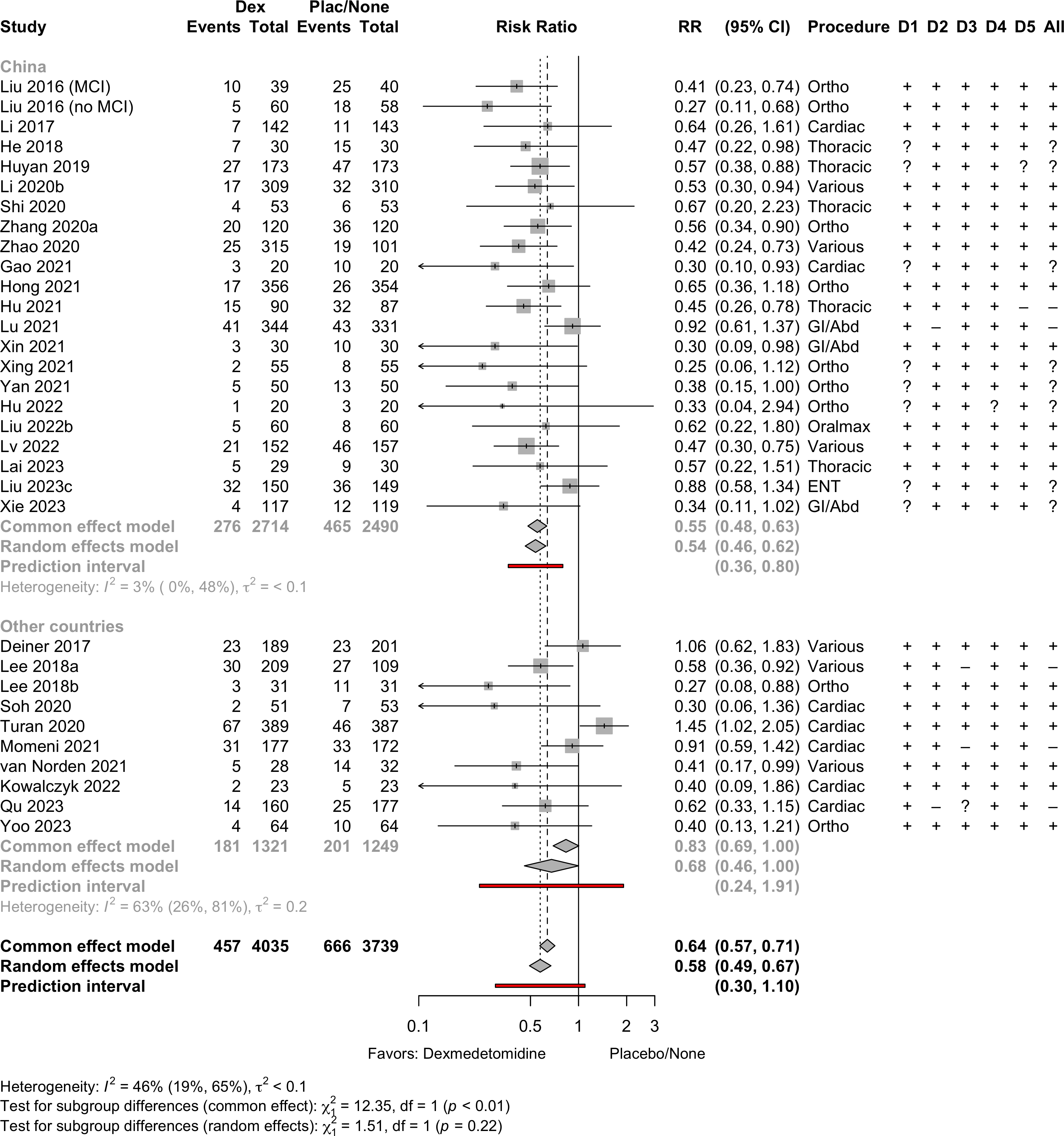
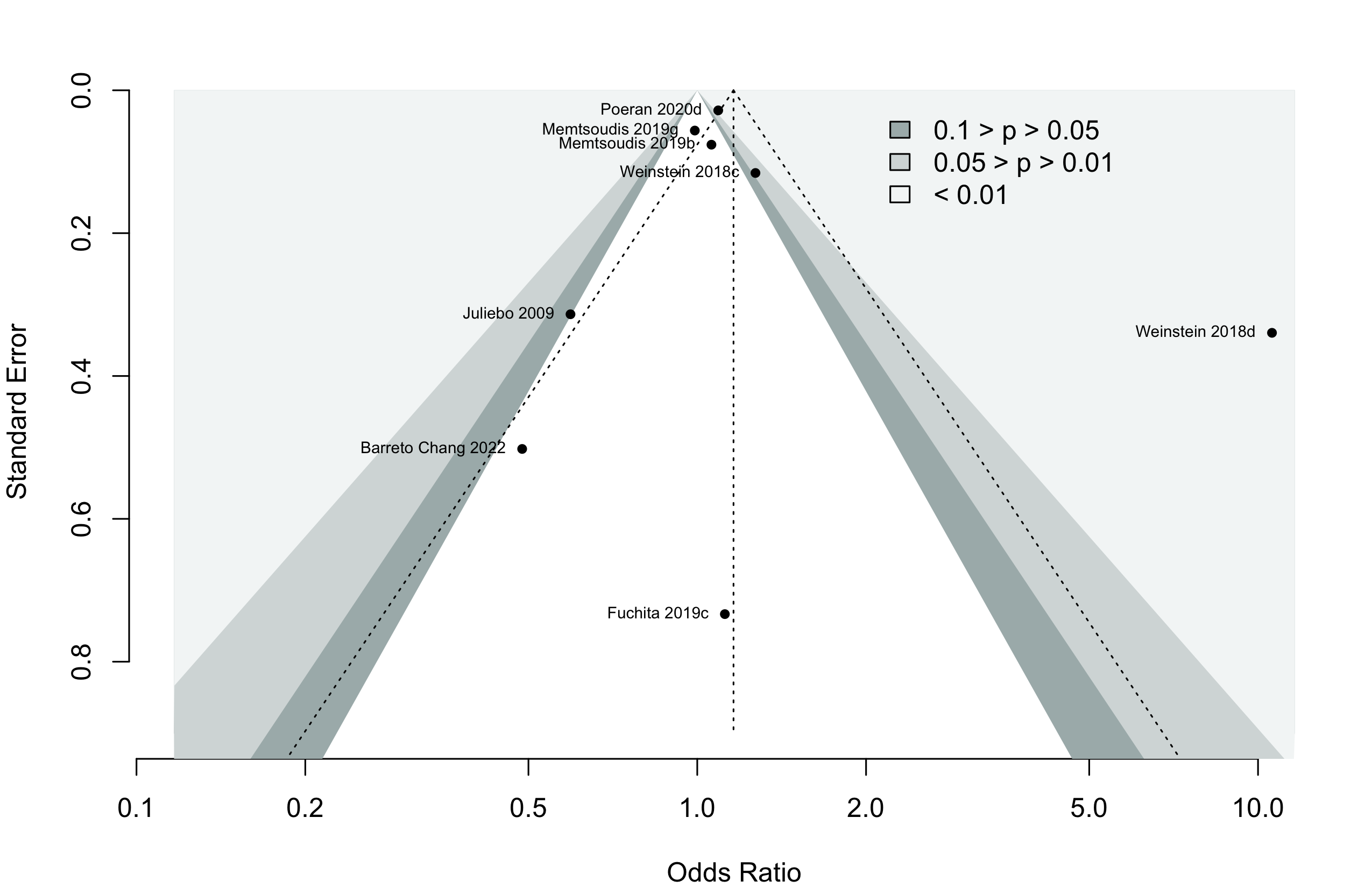
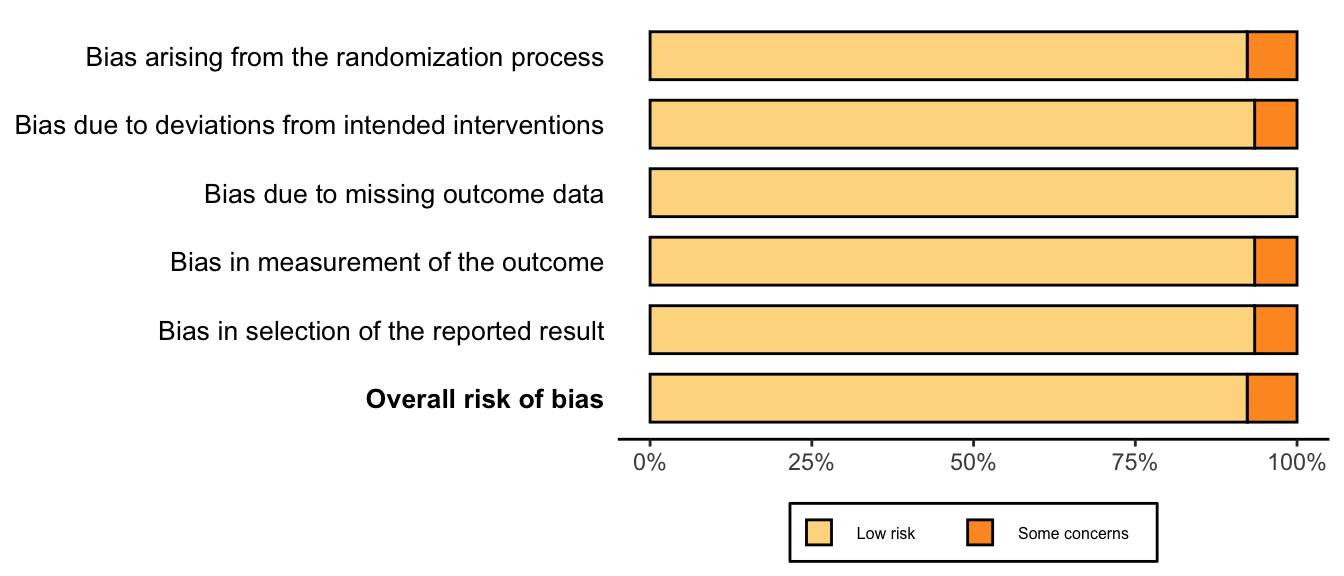
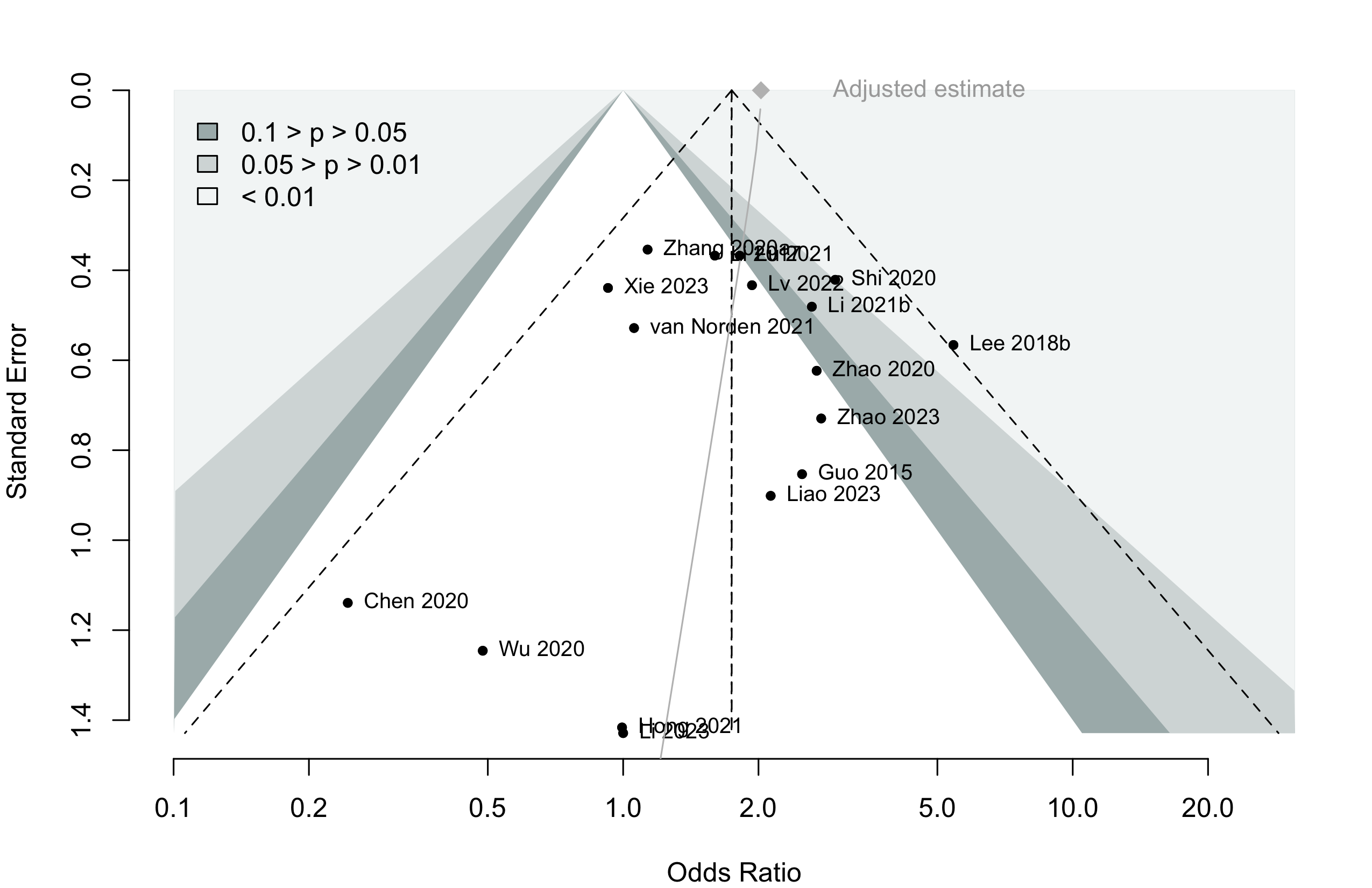
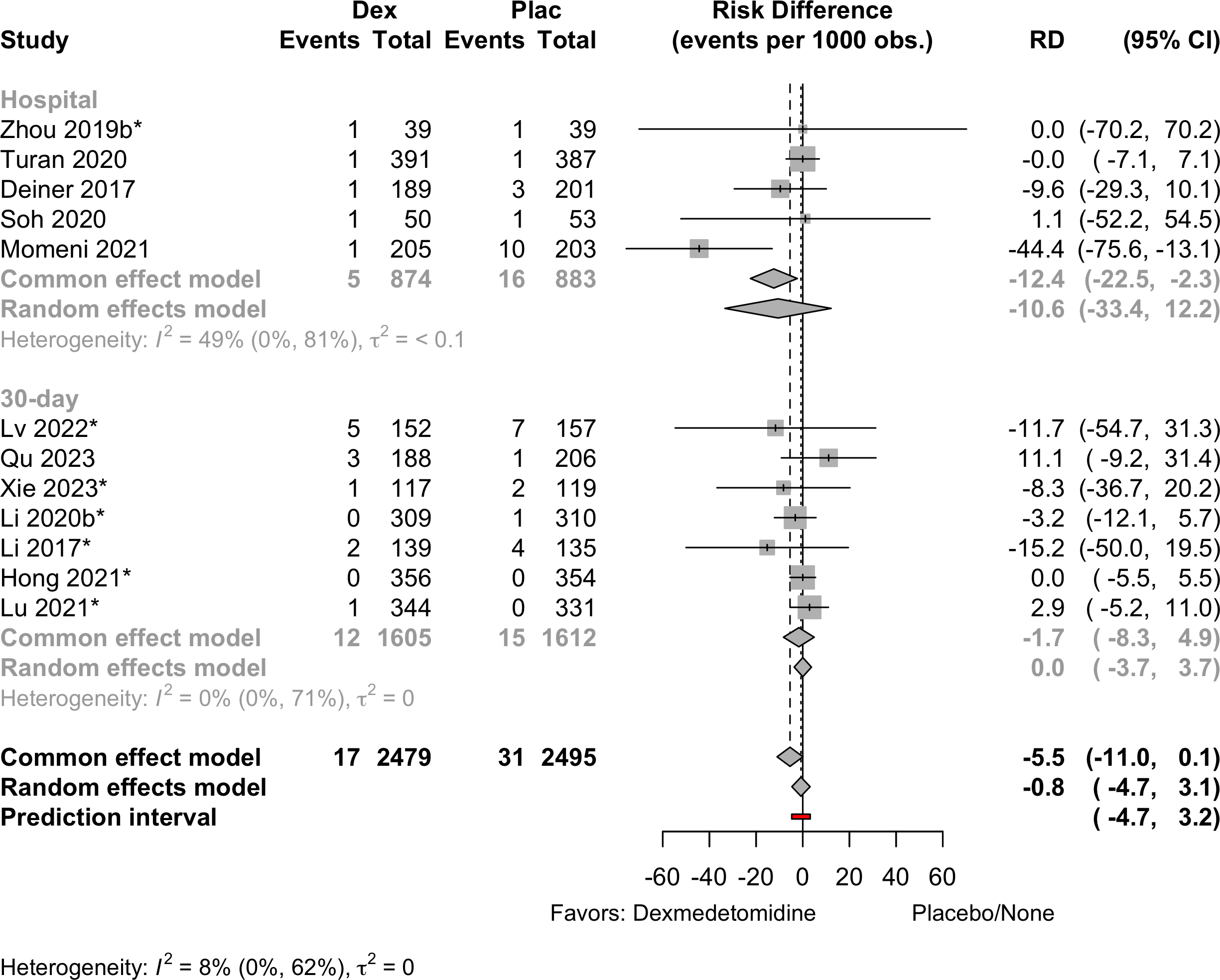
Risk of bias ratings: low +, some concerns ?, high – .
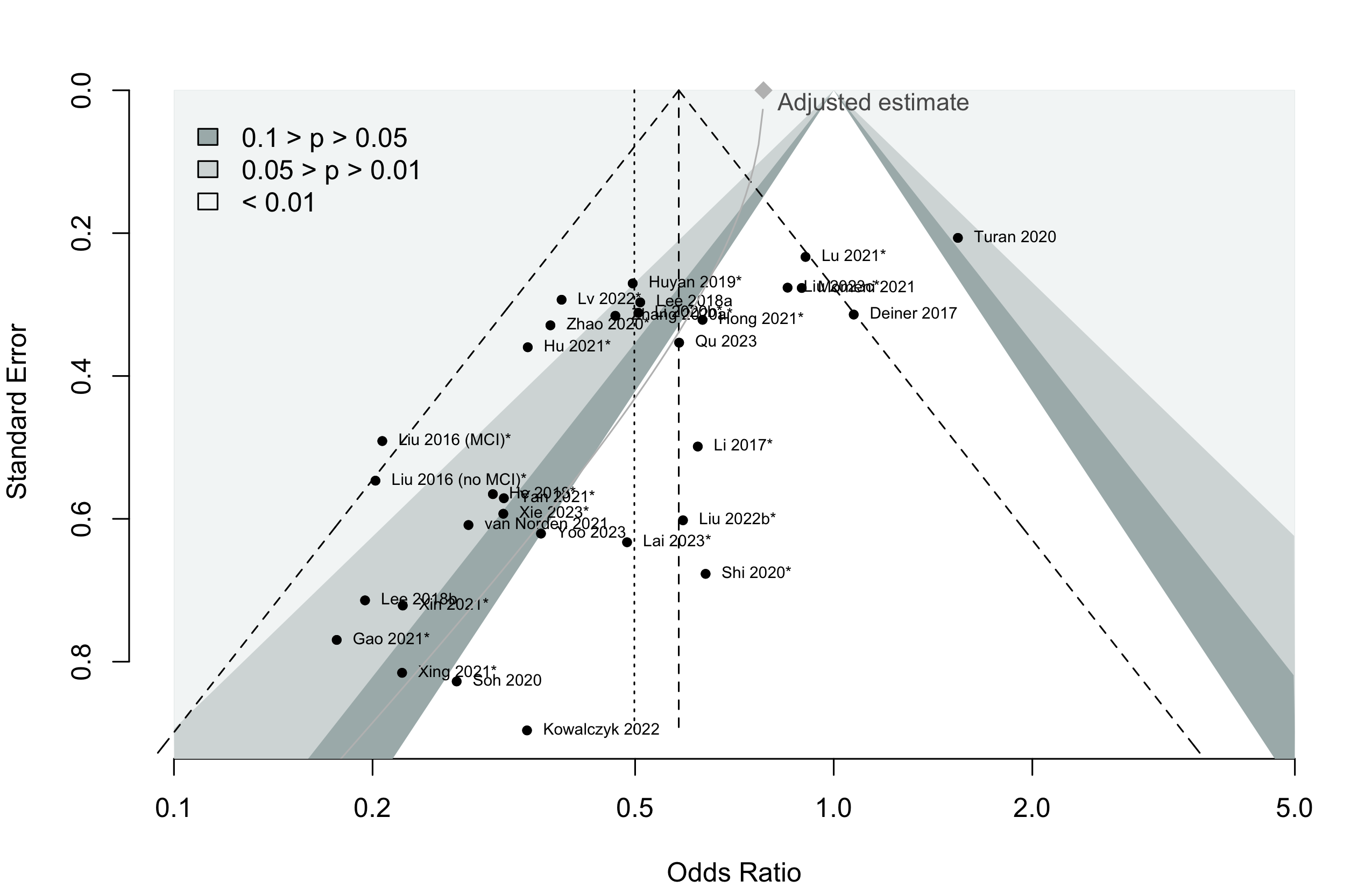
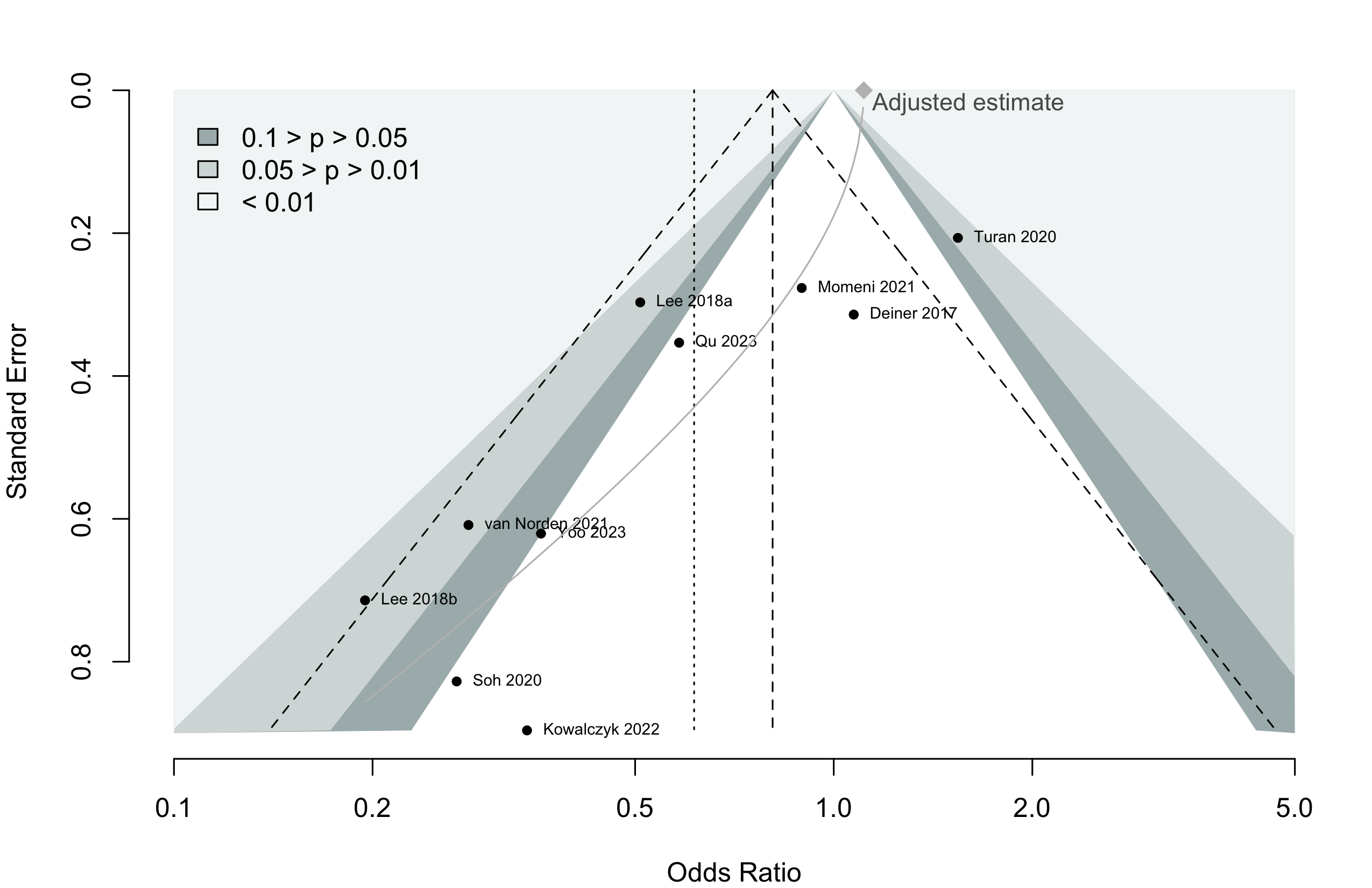
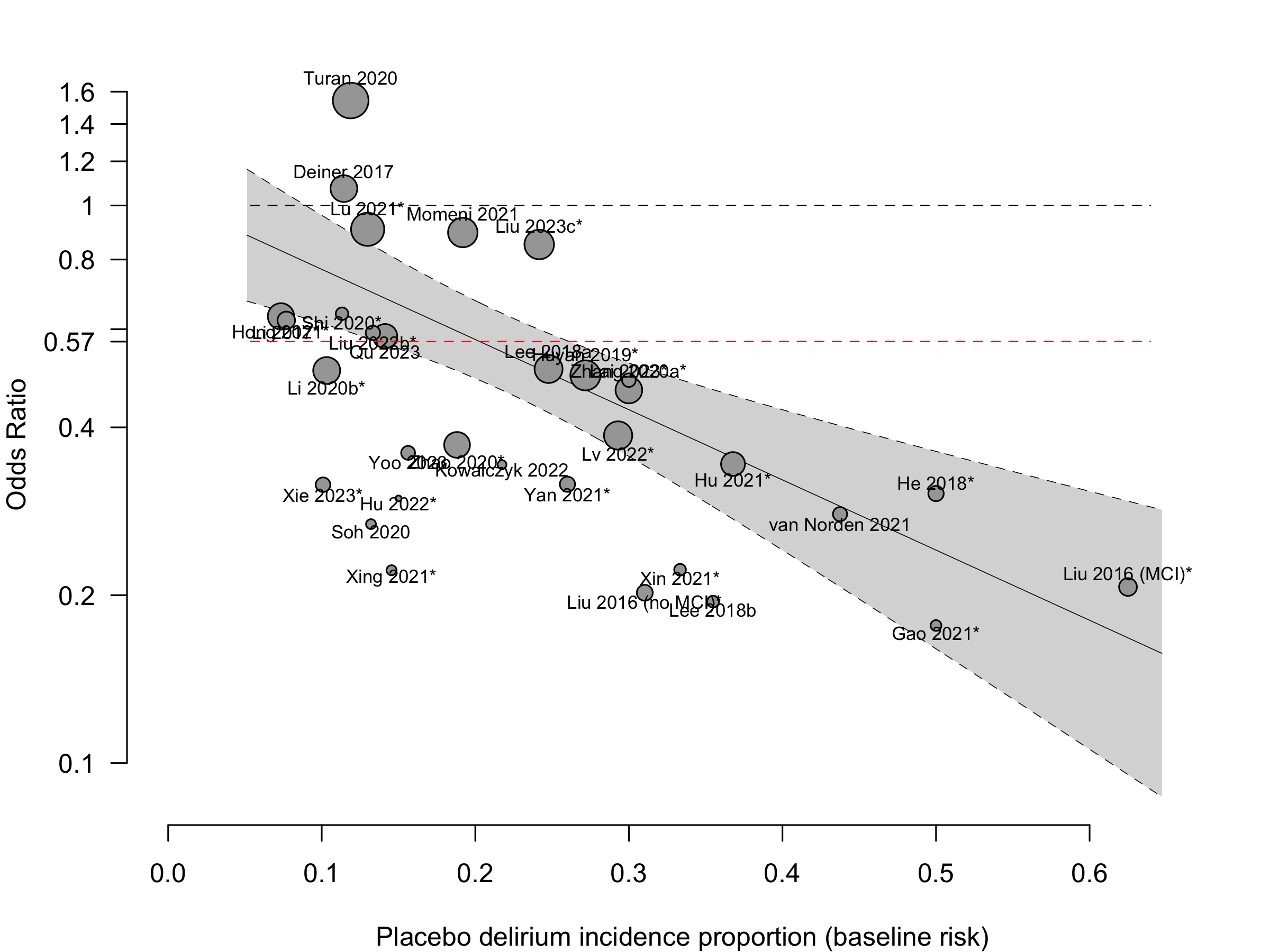
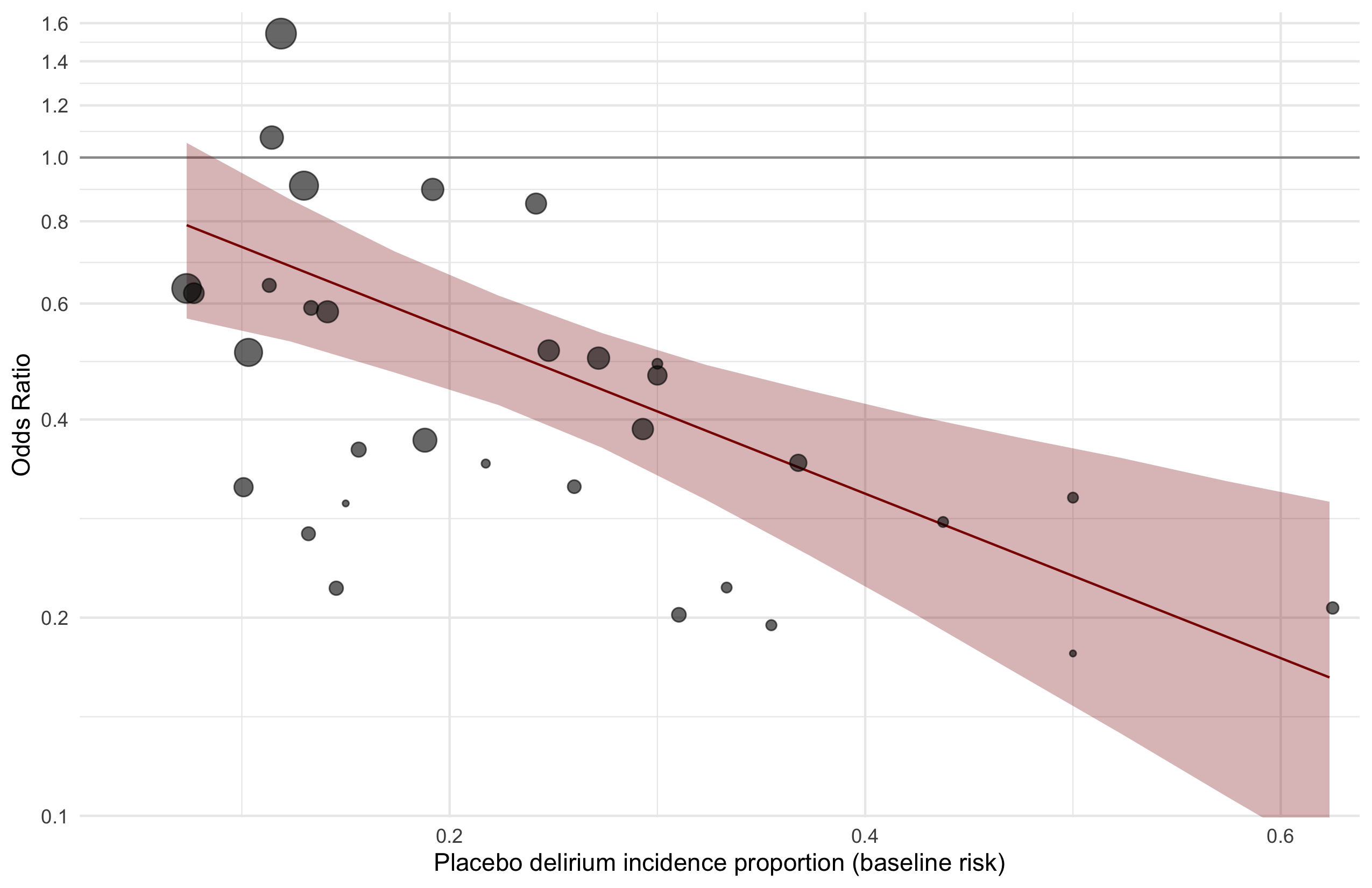
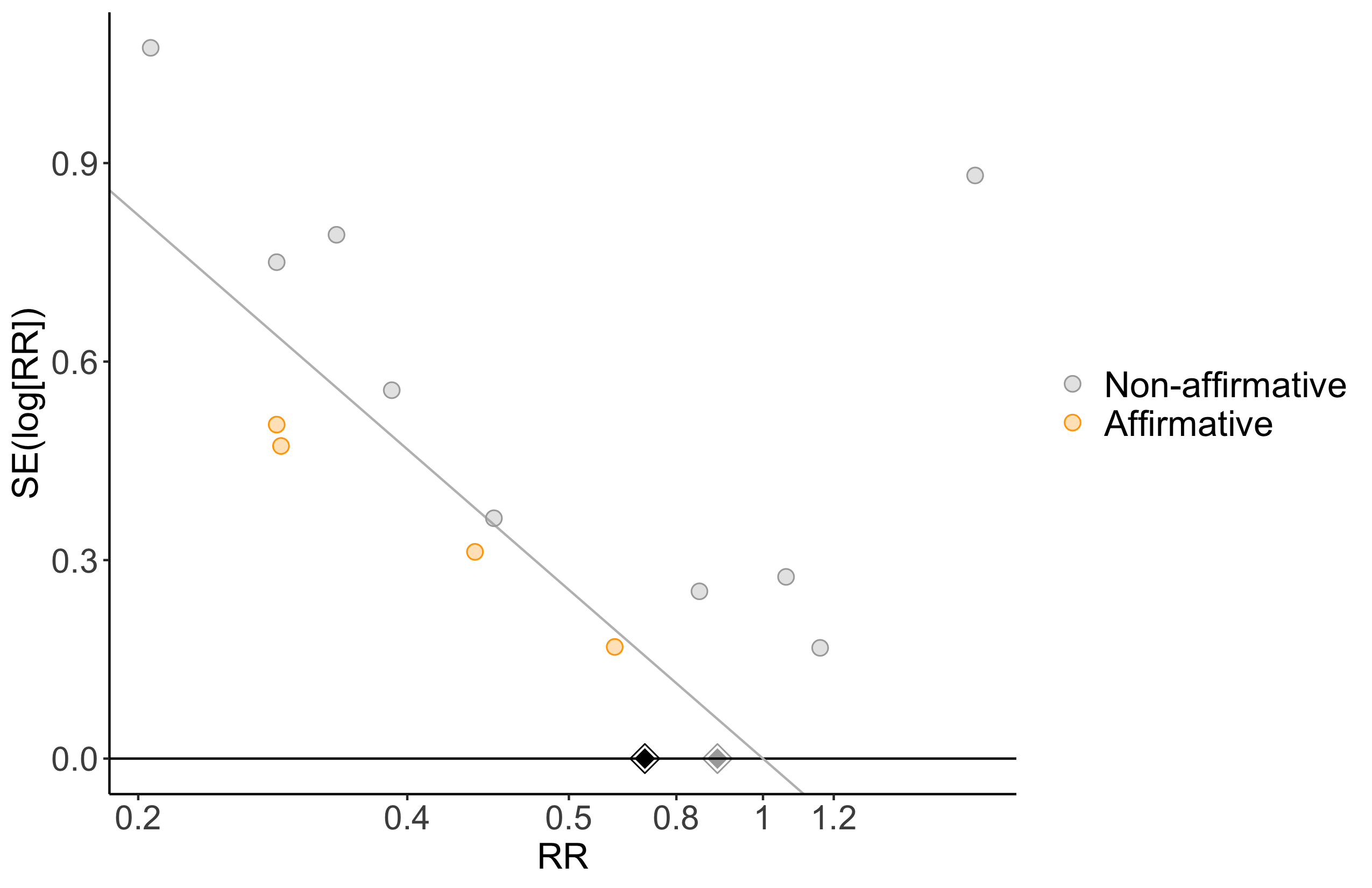
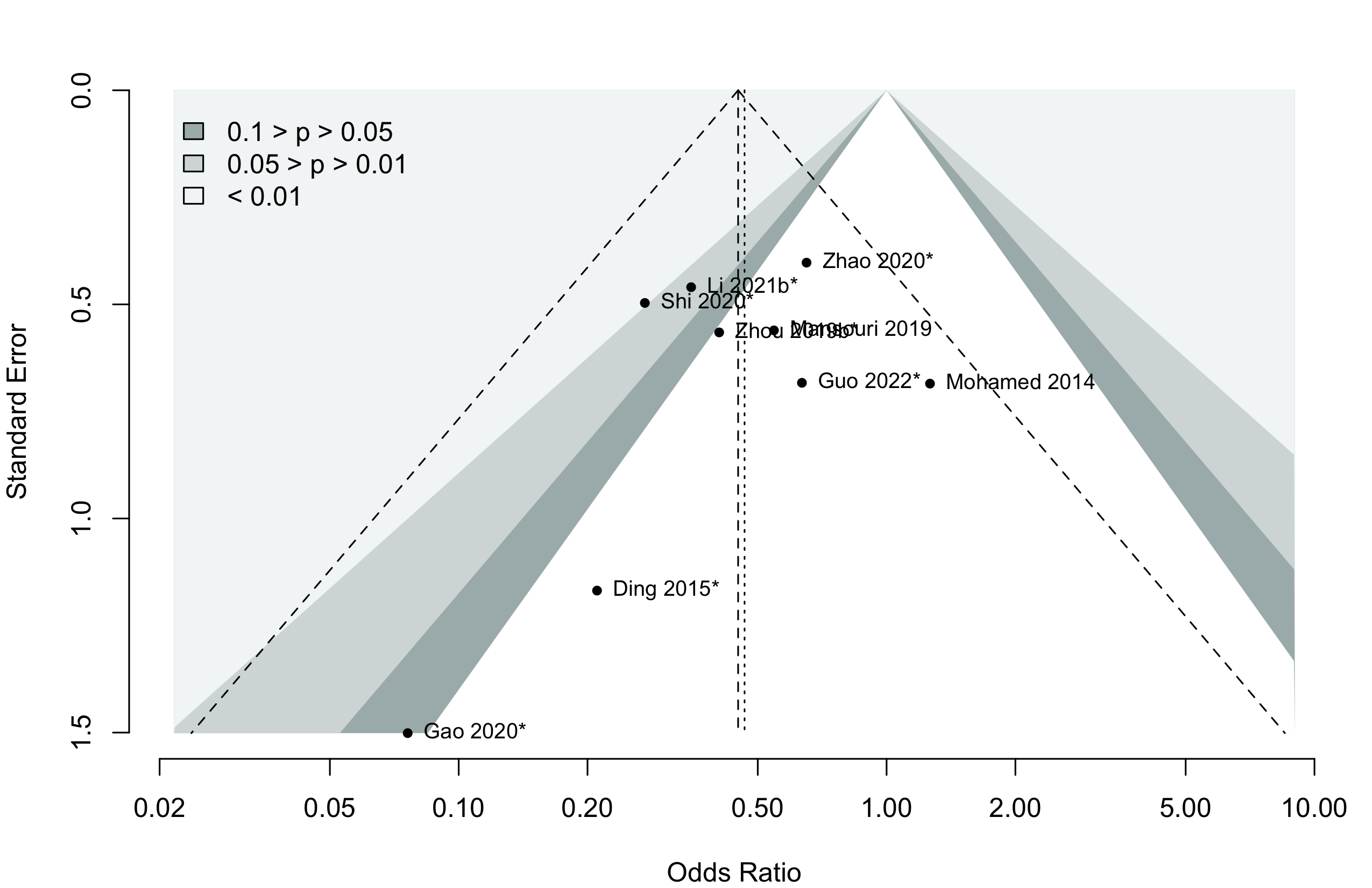
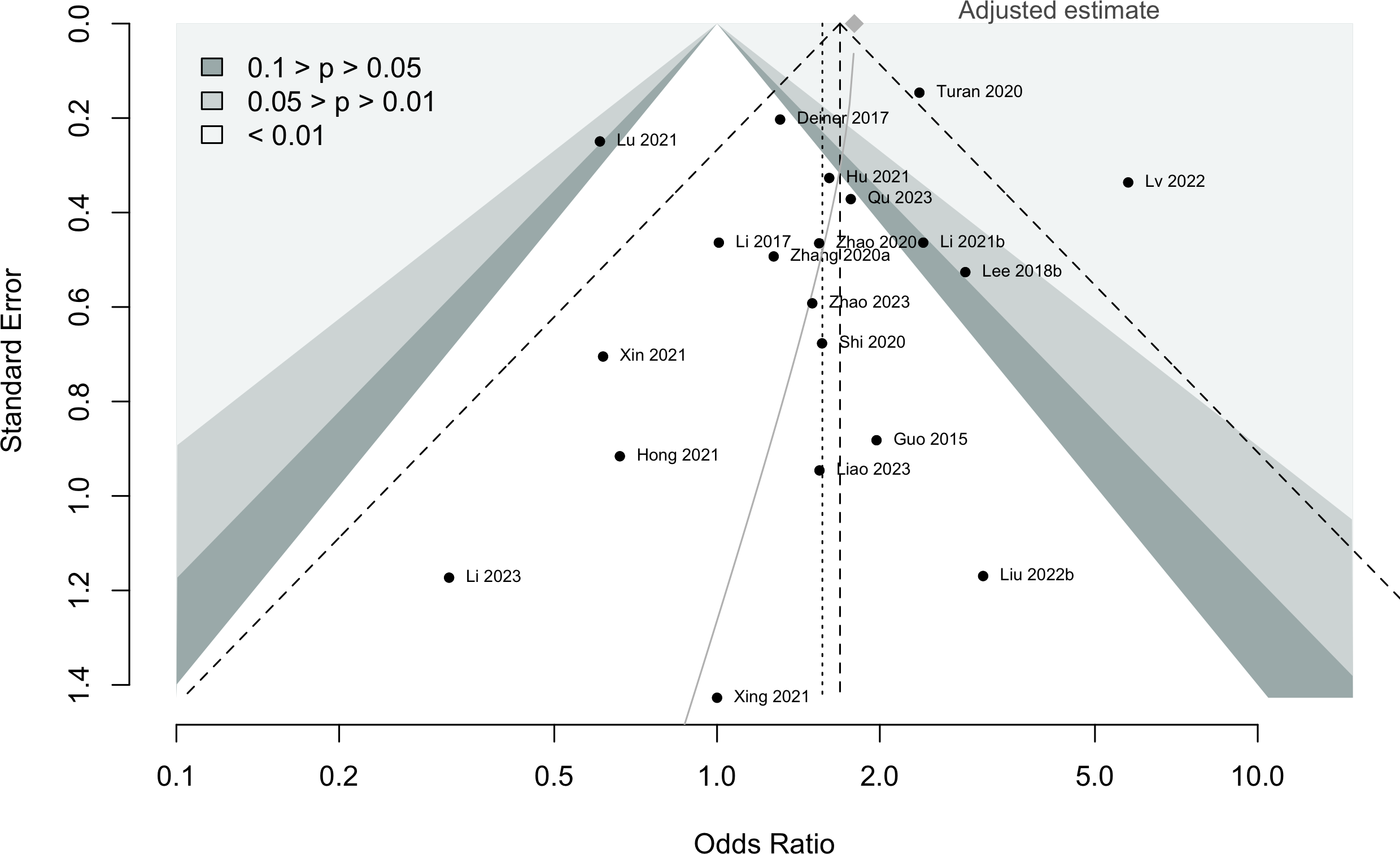
Harbord test for small study effects P = 0.00006.
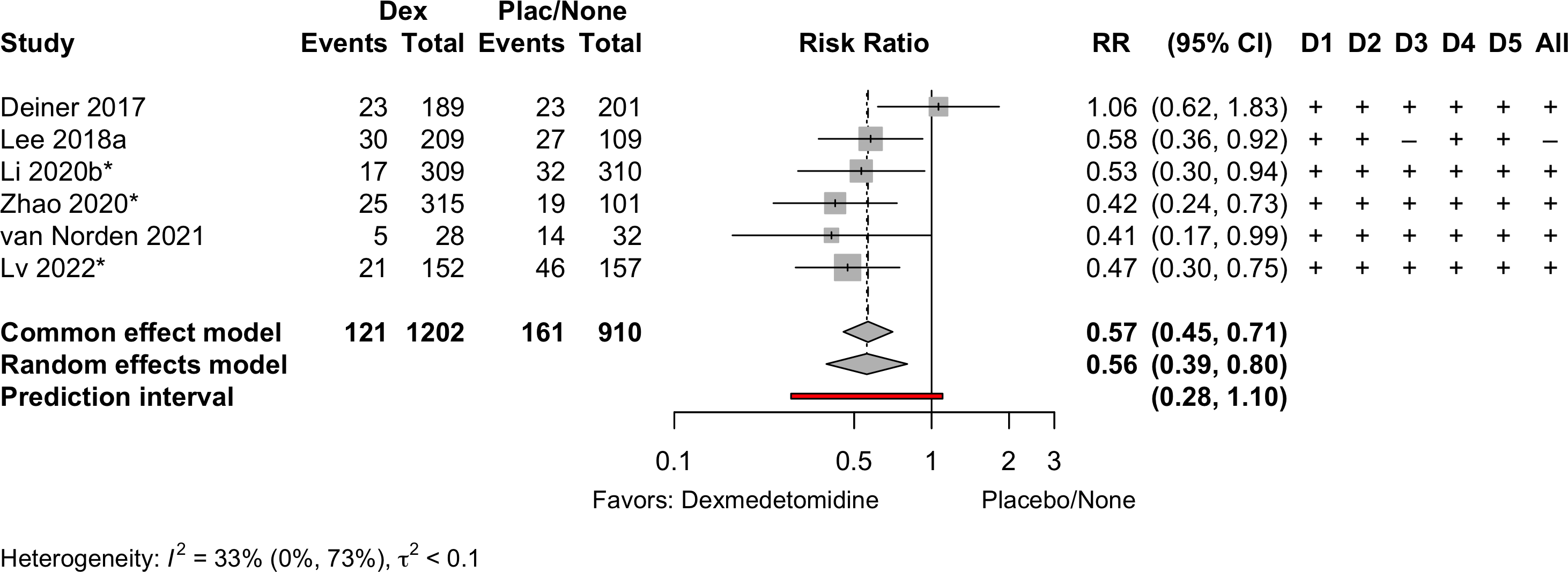
Delirium a designated primary outcome in 71.0%; a secondary outcome in 12.9%.
Excluding Turan 2020: RR 0.56 (95% CI, 0.49-0.64; I 2 = 13%, \(\tau\)2 = 0.04.
*Trials conducted in China.
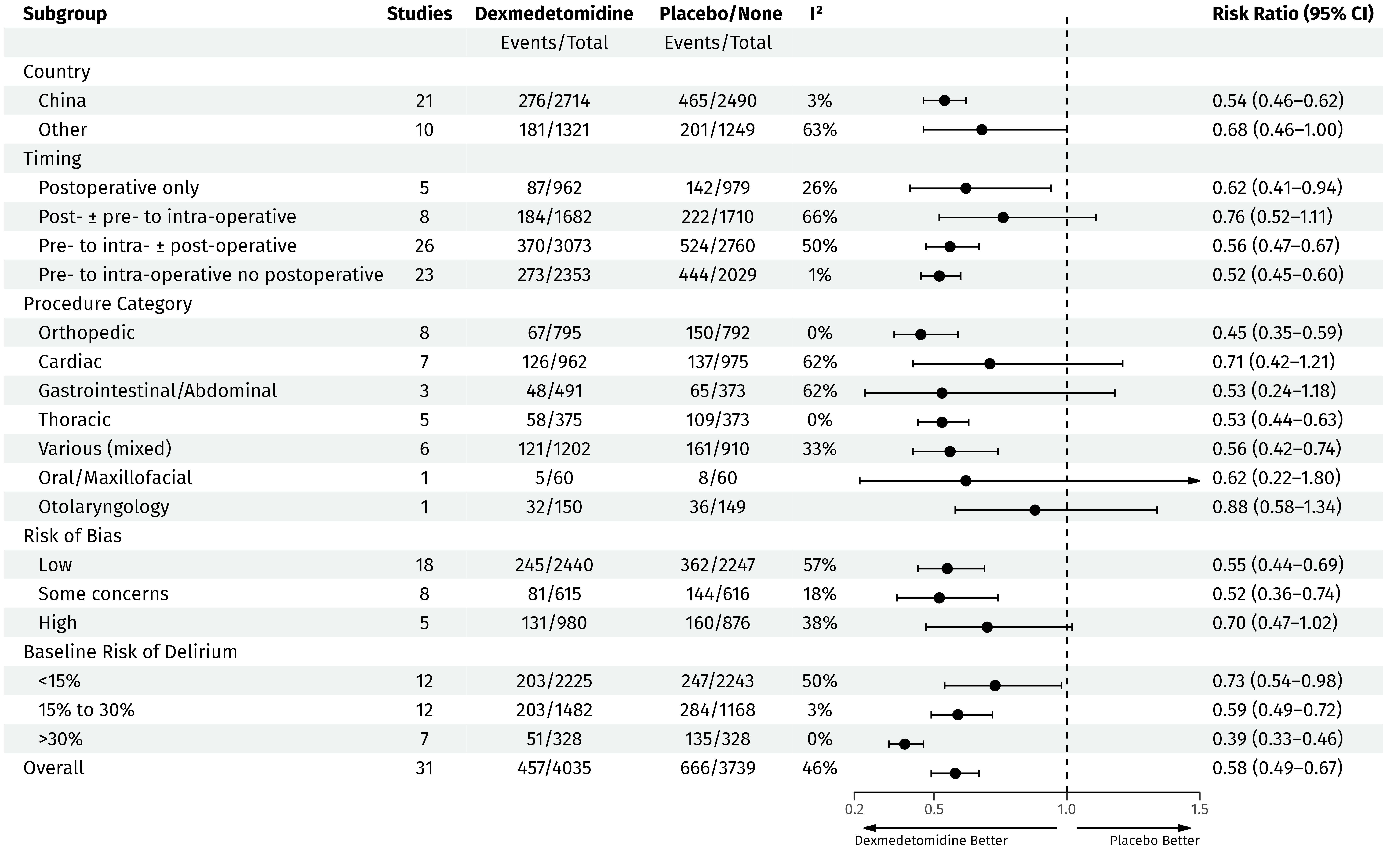
Subgroups
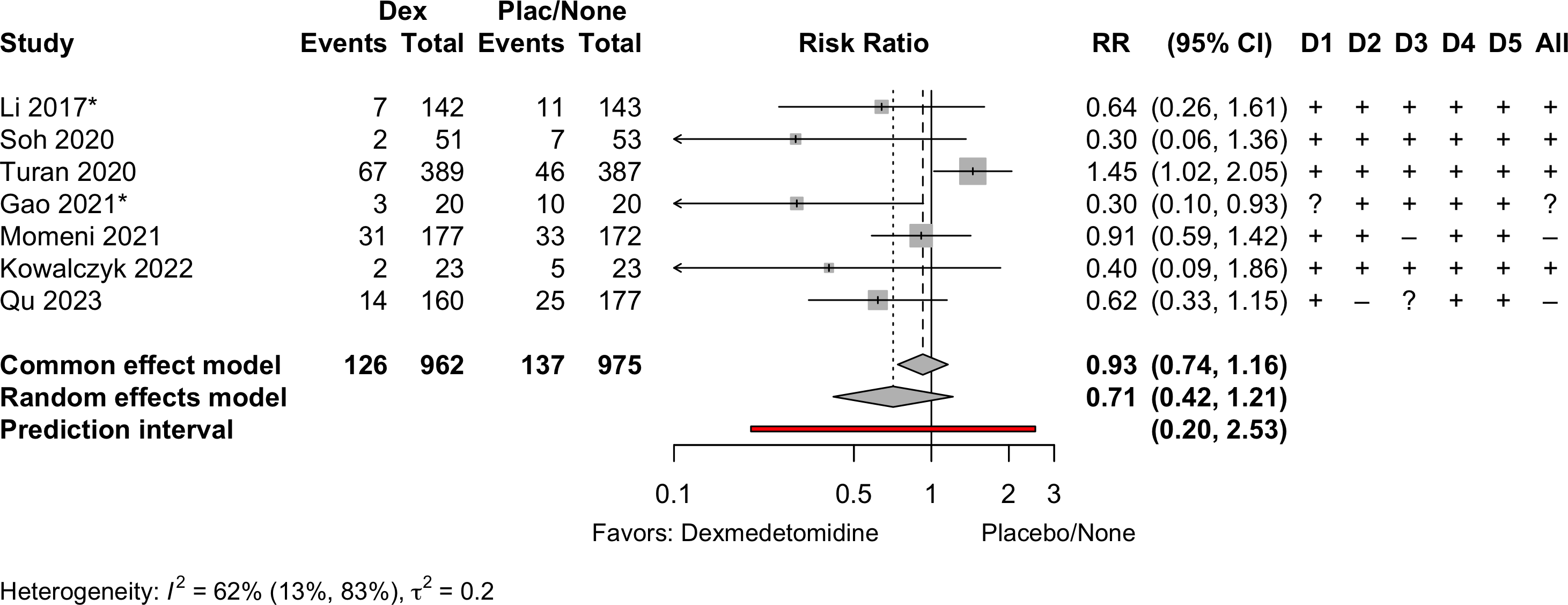
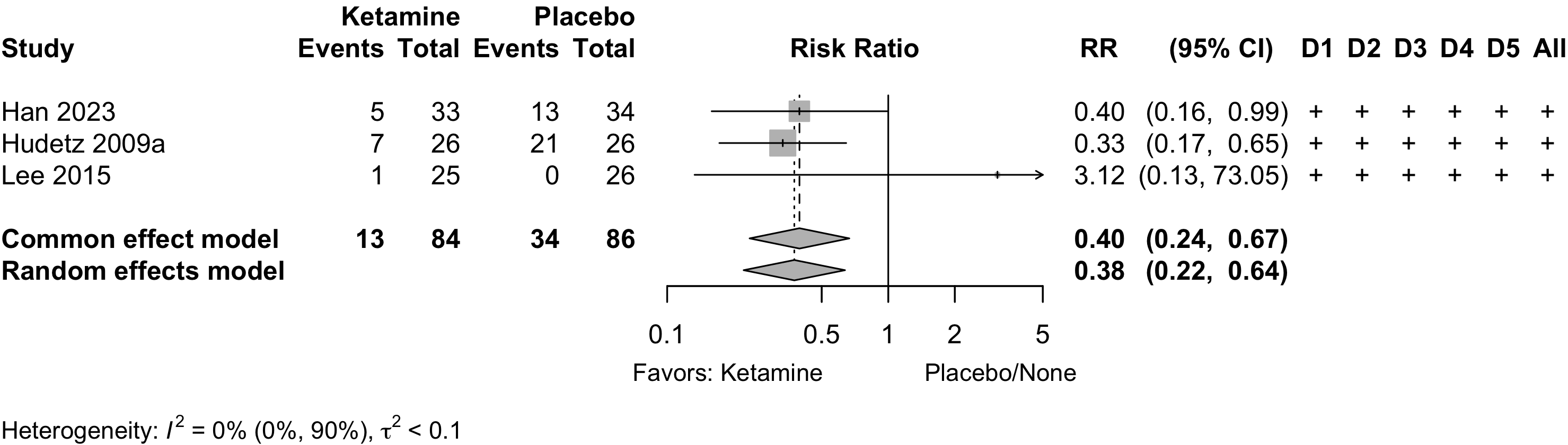
Ketamine
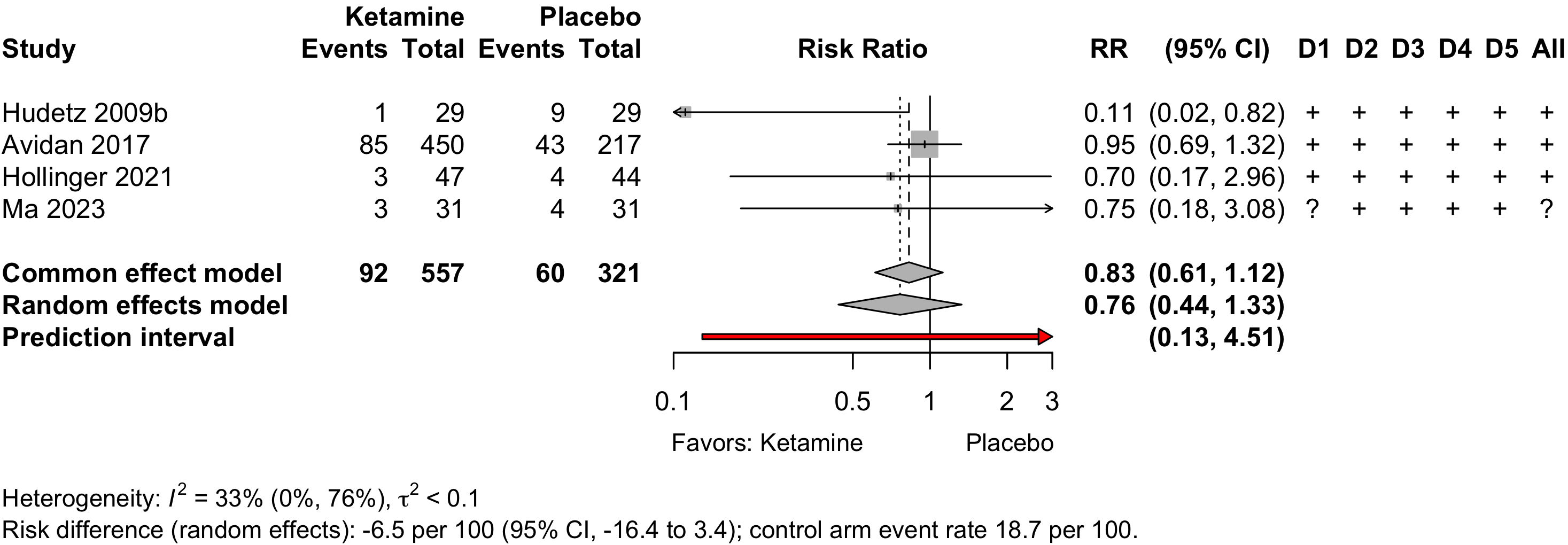
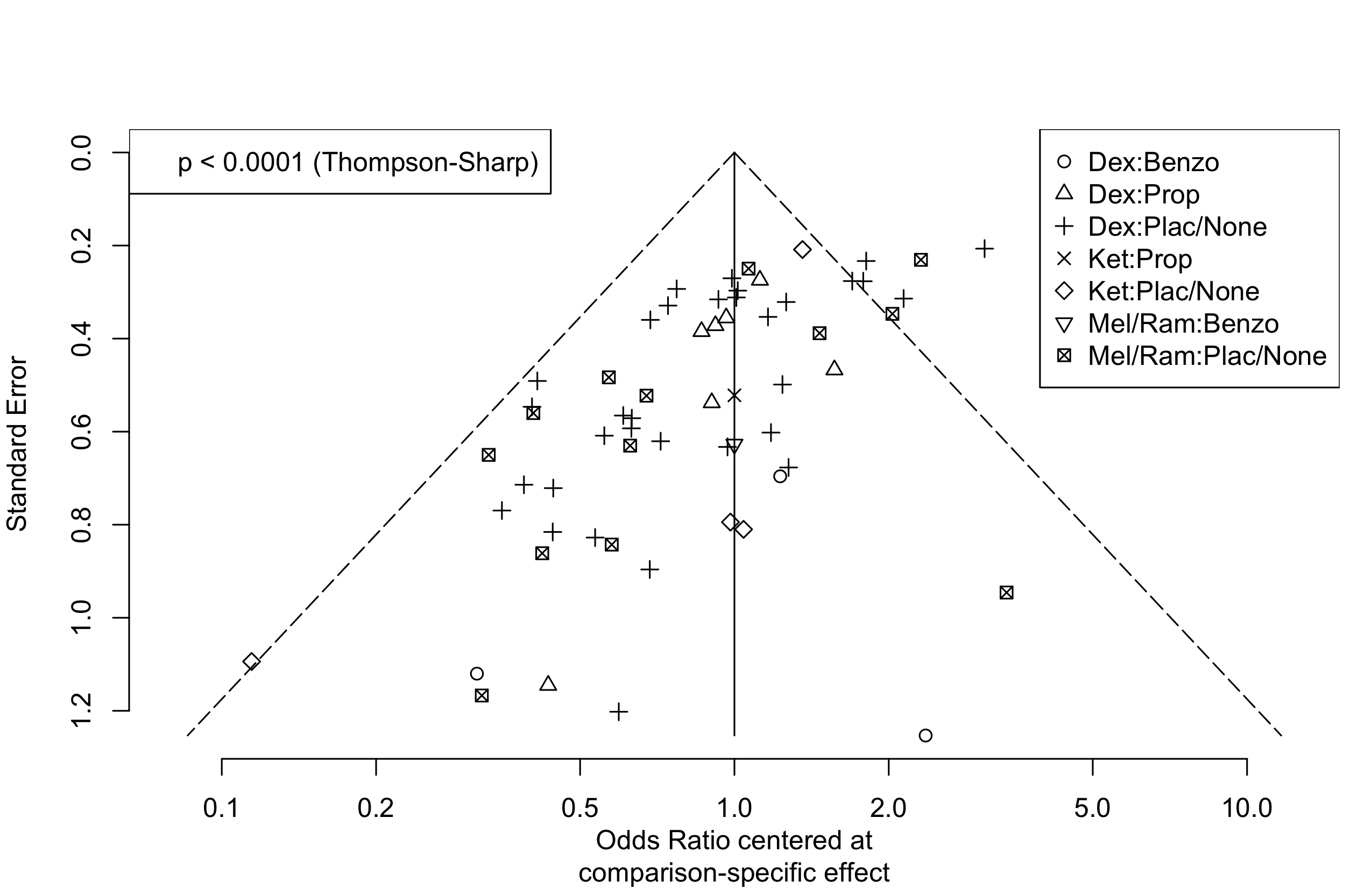
Risk of bias ratings: low +, some concerns ?, high – .
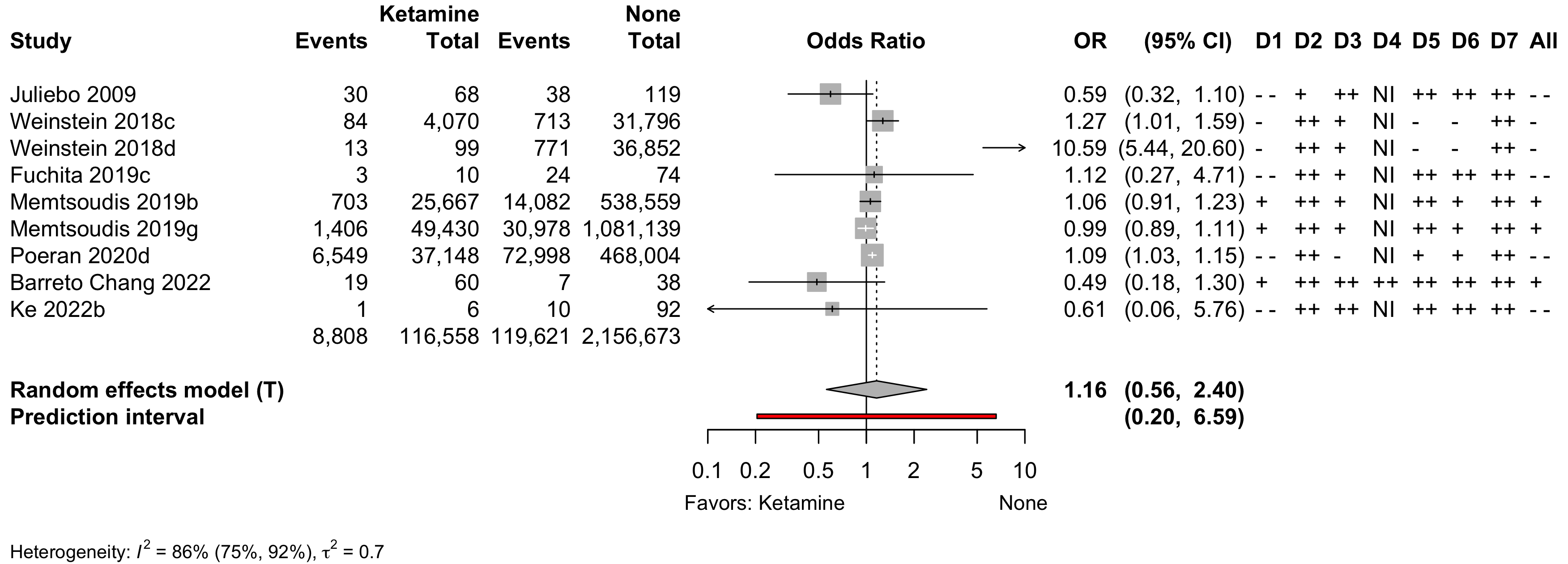
Risk of bias ratings: low ++, moderate +, serious -, critical - - ; NI: no information; NA: not applicable.
Confidence intervals may not exactly match published; variances were calculated from rounded figures as reported.
Multilevel model accounting for within-study dependent effects.
Weinstein 2018c intraoperative ketamine; Weinstein 2018d postoperative ketamine; Memtsoudis 2019b hip arthroplasty; Memtsoudis 2019g total knee arthroplasty.
Melatonin/Ramelteon
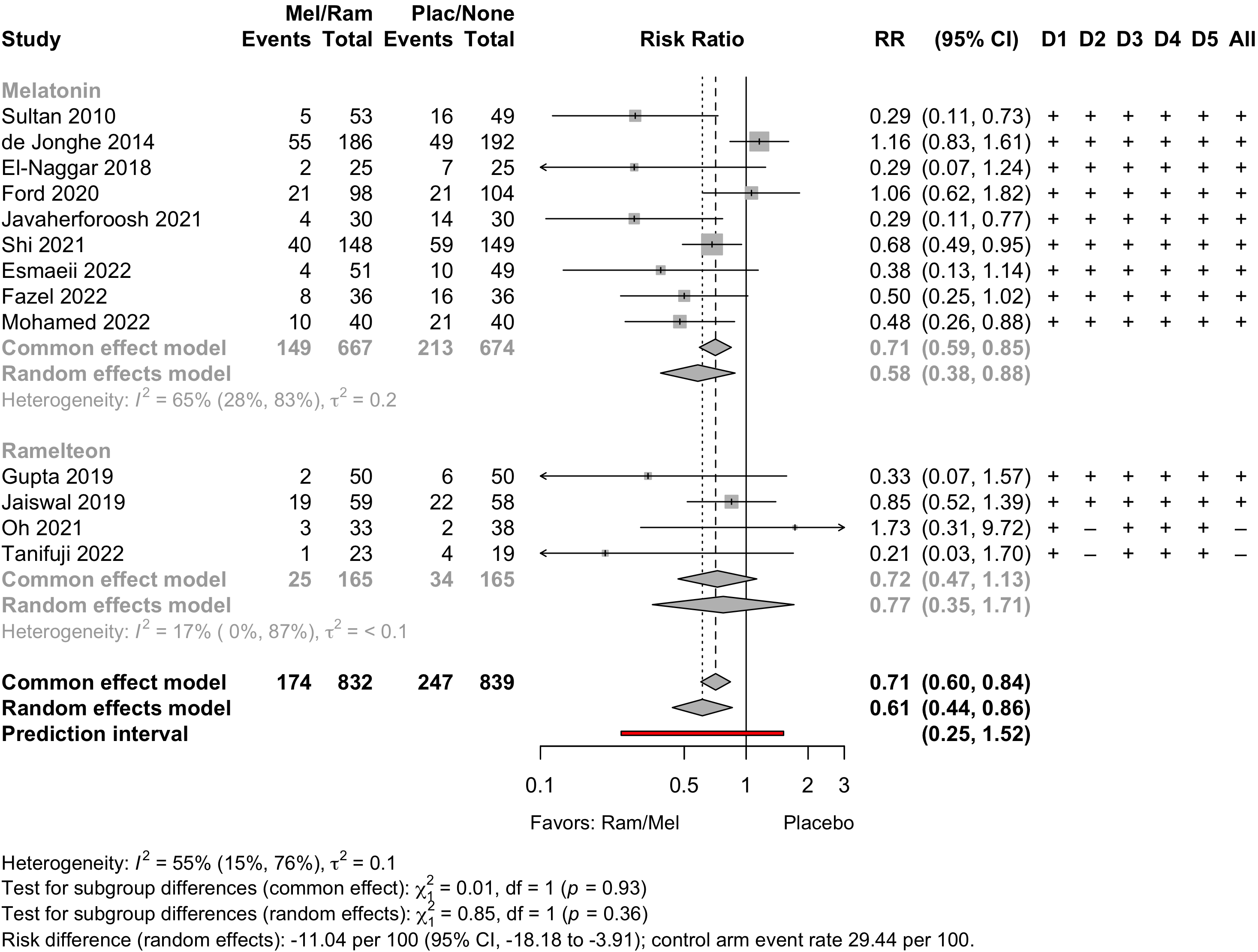
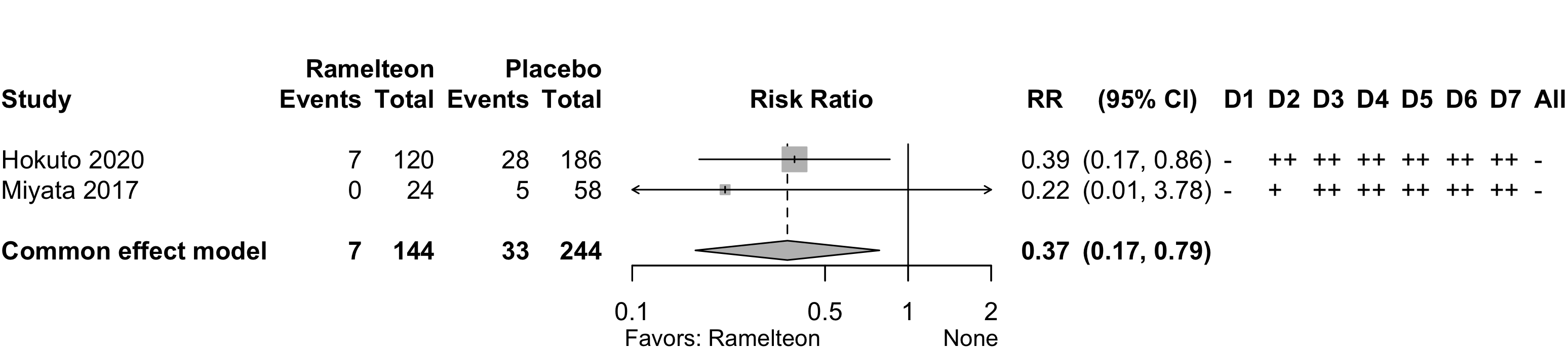
Risk of bias ratings: low ++, moderate +, serious -, critical - - ; NI: no information; NA: not applicable.
Network
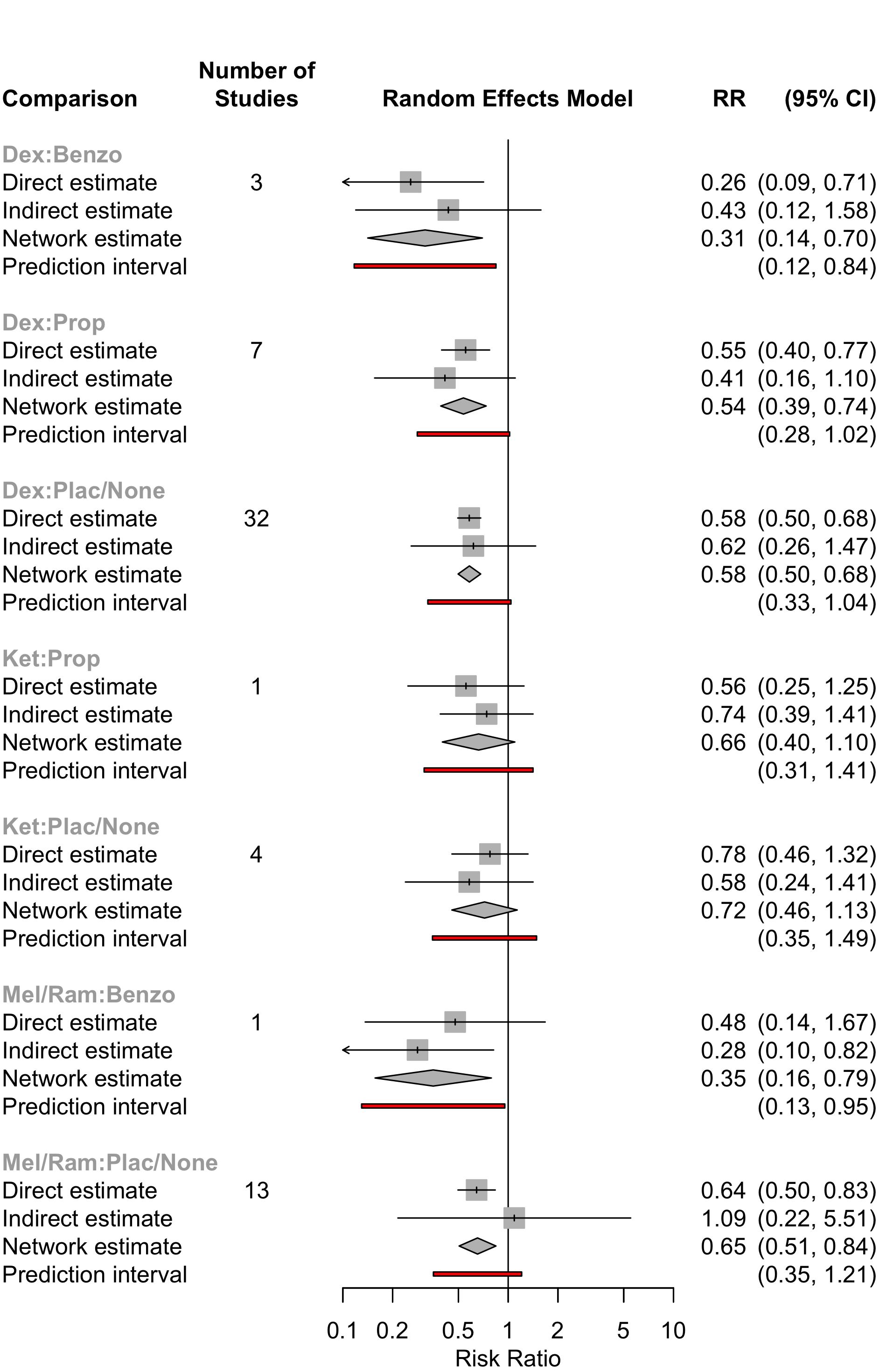
| Table 19. Summary of studies included in the network for delirium incidence. | |
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Interventions | 7 |
| Number of Studies | 61 |
| Total Number of Patients in Network | 12,550 |
| Total Possible Pairwise Comparisons | 21 |
| Total Number of Pairwise Comparisons With Direct Data | 8 |
| Is the network connected? | TRUE |
| Number of Two-arm Studies | 61 |
| Number of Multi-Arms Studies | 0 |
| Total Number of Events in Network | 1,997 |
| Number of Studies With No Zero Events | 61 |
| Number of Studies With At Least One Zero Event | 0 |
| Number of Studies with All Zero Events | 0 |
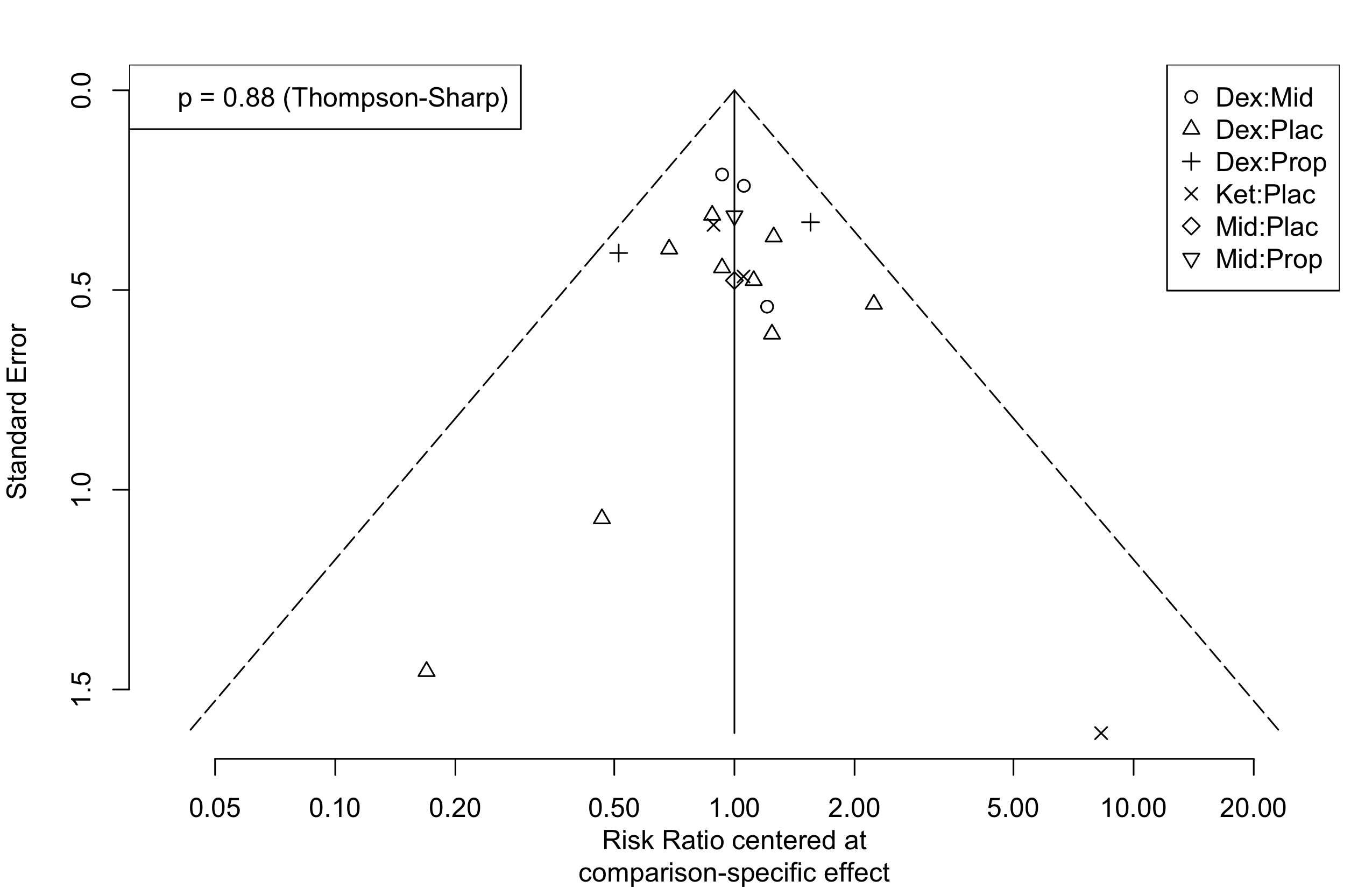
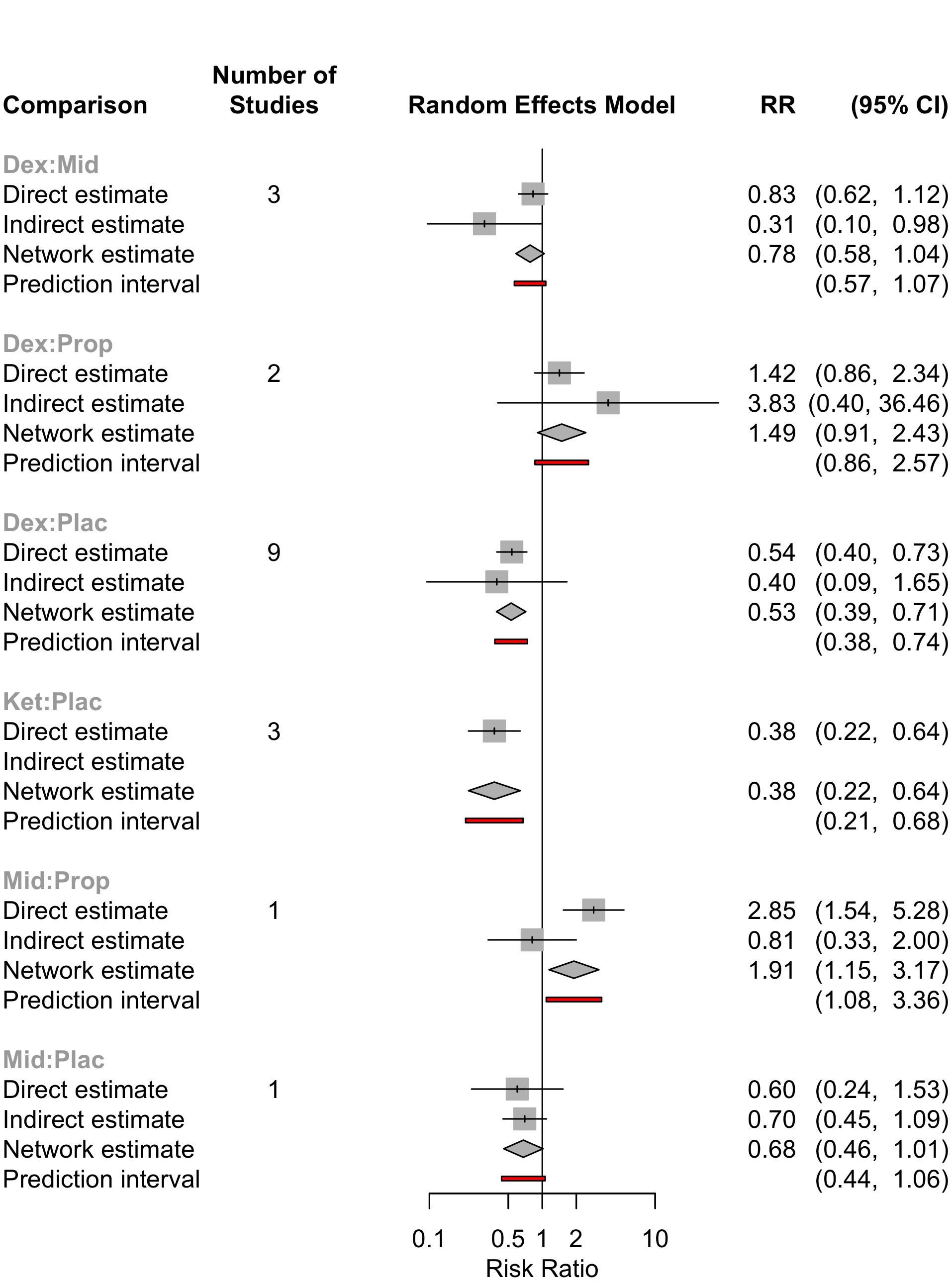
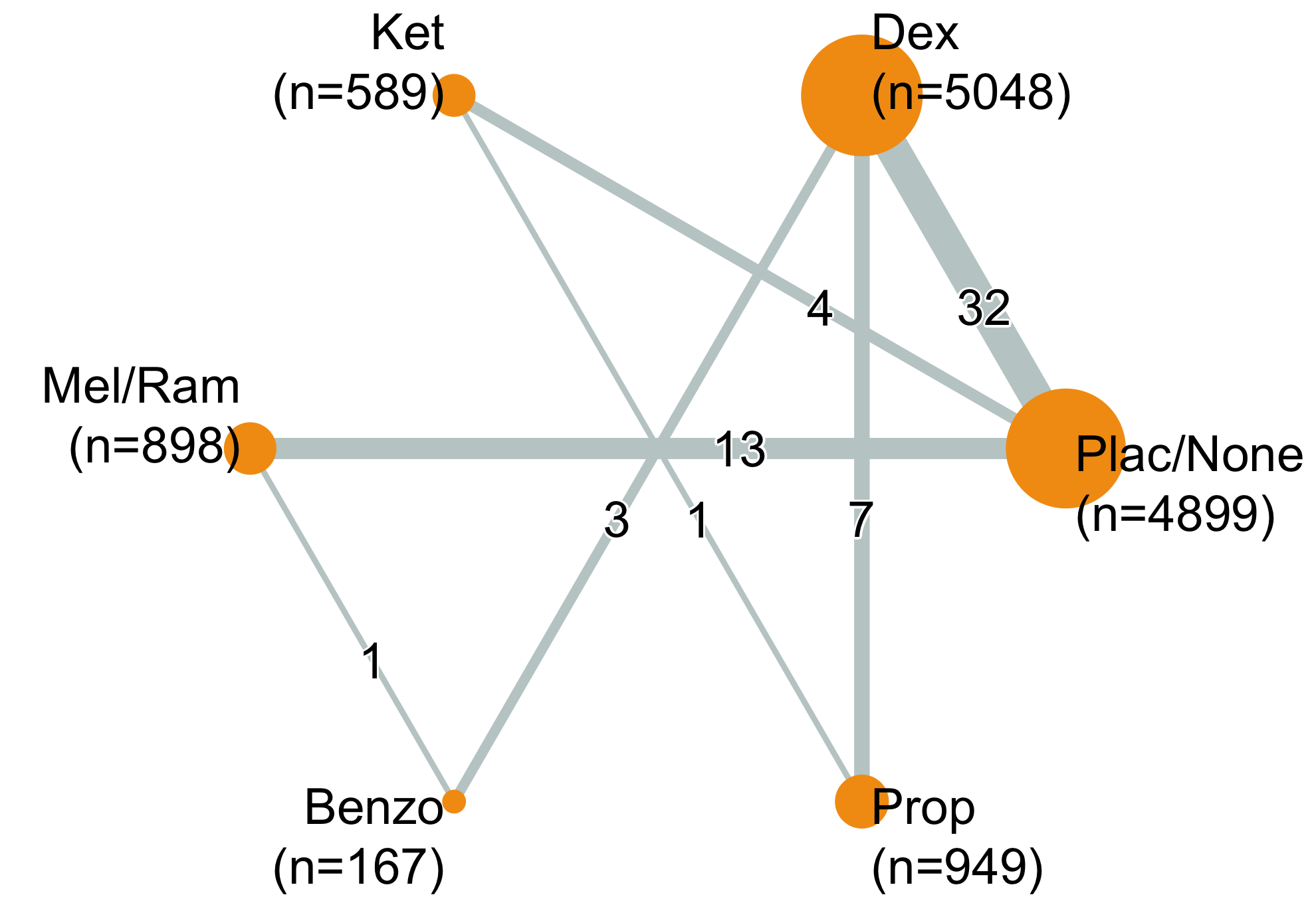
| Table 20. Summary of events by comparisons in the network for delirium incidence. | |||
| Comparison | Studies | Patients | Events (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzo vs. Dex | 3 | 192 | 26 (13.5) |
| Benzo vs. Mel | 1 | 137 | 13 (9.5) |
| Dex vs. Plac/None | 32 | 7,774 | 1,123 (14.4) |
| Dex vs. Prop | 7 | 1,834 | 234 (12.8) |
| Ket vs. Plac/None | 4 | 878 | 152 (17.3) |
| Ket vs. Prop | 1 | 64 | 28 (43.8) |
| Mel vs. Plac/None | 9 | 1,341 | 362 (27.0) |
| Plac/None vs. Ram | 4 | 330 | 59 (17.9) |
Dex |
0.26 |
0.55 |
0.58 | ||
0.81 |
Ket |
0.56 |
0.78 | ||
0.89 |
1.10 |
Mel/Ram |
0.48 |
0.64 | |
0.31 |
0.39 |
0.35 |
Benzo |
||
0.54 |
0.66 |
0.60 |
1.71 |
Prop |
|
0.58 |
0.72 |
0.65 |
1.85 |
1.09 |
Plac/None |
| Dex: Dexmedetomidine; Ket: Ketamine; Mel/Ram: Melatonin or Ramelteon; Mid: Midazolam; MS: Morphine; Prop: Propofol; Plac/None: Placebo or no comparator. | |||||
Neurocognitive Disorder
<30 days
Dexmedetomidine
| Study | N | Drug | Preop | Instrument | Dayb | Neurocognitive Disorder <30 days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMSEa | MMSE | DST | MoCA | Other | N (%) | 0 — 100% | RR (95% CI) | ||||
| GI/Abd - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 25 | Plac | ✓ |
7 | 5 (20.0) | — | ||||||
| 25 | Dex | 6 (24.0) | 1.20 (0.42-3.43) | ||||||||
| 45 | Plac | 29.3 (0.4) |
✓c |
3 | 29 (64.4) | — | |||||
| 43 | Dex | 29.4 (0.5) |
7 (16.3) | 0.25 (0.12-0.51) | |||||||
| 30 | Plac | 28.7 (2.1) |
✓d |
7 | 12 (40.0) | — | |||||
| 30 | Dex | 27.6 (3.2) |
11 (36.7) | 0.92 (0.48-1.74) | |||||||
| 30 | Dex | 28.0 (1.7) |
4 (13.3) | 0.33 (0.12-0.92) | |||||||
| 30 | Dex | 28.4 (2.6) |
2 (6.7) | 0.17 (0.04-0.68) | |||||||
| 45 | None | ✓e |
7 | 6 (13.3) | — | ||||||
| 45 | Dex | 4 (8.9) | 0.67 (0.20-2.20) | ||||||||
| 35 | Plac | 27.7 (1.9) |
✓ |
✓ |
3 | 10 (28.6) | — | ||||
| 34 | Rem | 27.7 (1.7) |
3 (8.8) | 0.31 (0.09-1.03) | |||||||
| 35 | Dex | 27.8 (2.1) |
3 (8.6) | 0.30 (0.09-1.00) | |||||||
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 38 | Plac | ✓f |
7 | 12 (31.6) | — | ||||||
| 39 | Ulin | 7 (17.9) | 0.57 (0.25-1.29) | ||||||||
| 39 | Dex/Ulin | 4 (10.3) | 0.32 (0.11-0.92) | ||||||||
| 38 | Dex | 6 (15.8) | 0.50 (0.21-1.19) | ||||||||
| 30 | Plac | ✓g |
7 | 5 (16.7) | — | ||||||
| 30 | Dex | 0 (0) | Not estimated | ||||||||
| 34 | Prop | 26 {25-28} |
✓ |
3 | 20 (58.8) | — | |||||
| 37 | Dex | 27 {25-28} |
9 (24.3) | 0.41 (0.22-0.78) | |||||||
| Various - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 100 | Mid | 25.0 (3.3) |
✓h |
7 | 28 (28.0) | — | |||||
| 98 | Dex | 24.9 (3.9) |
24 (24.5) | 0.87 (0.55-1.40) | |||||||
| 40 | Prop | 26.4 (1.3) |
✓i |
7 | 11 (27.5) | — | |||||
| 40 | Dex | 26.1 (1.2) |
8 (20.0) | 0.73 (0.33-1.62) | |||||||
| 101 | None | 27 {24-30} |
✓j |
7 | 10 (9.9) | — | |||||
| 108 | Dex | 27 {24-30} |
14 (13.0) | 1.31 (0.61-2.81) | |||||||
| 105 | Dex | 27 {24-30} |
5 (4.8) | 0.48 (0.17-1.36) | |||||||
| 102 | Dex | 27 {24-30} |
2 (2.0) | 0.20 (0.04-0.88) | |||||||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 76 | Dex | 28.3 (1.3) |
✓j |
7 | 13 (17.1) | — | |||||
| 75 | Dex | 28.5 (1.2) |
5 (6.7) | 0.39 (0.15-1.04) | |||||||
| 55 | Prop | ✓f |
✓ |
7 | 10 (18.2) | — | |||||
| 54 | Mid | 28 (51.9) | 2.85 (1.54-5.28) | ||||||||
| 55 | Dex | 22 (40.0) | 2.20 (1.15-4.20) | ||||||||
| 42 | Plac | 25.8 (0.6) |
✓ |
3 | 16 (38.1) | — | |||||
| 40 | Dex | 25.9 (0.4) |
7 (17.5) | 0.46 (0.21-1.00) | |||||||
| Ophtho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 50 | Plac | ✓k |
7 | 10 (20.0) | — | ||||||
| 50 | Mid | 6 (12.0) | 0.60 (0.24-1.53) | ||||||||
| 50 | Dex | 6 (12.0) | 0.60 (0.24-1.53) | ||||||||
| Thoracic - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 53 | Plac | 28.0 (0.9) |
✓l |
7 | 19 (35.8) | — | |||||
| 53 | Dex | 27.9 (0.9) |
7 (13.2) | 0.37 (0.17-0.80) | |||||||
| Urol - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 20 | Plac | ✓d |
✓d |
5 | 4 (20.0) | — | |||||
| 20 | Dex | 1 (5.0) | 0.25 (0.03-2.05) | ||||||||
| GI/Abd - Nonrandomized Trial | |||||||||||
| 48 | Plac | ✓ |
7 | 0 (0) | — | ||||||
| 48 | Dex | 0 (0) | Not estimated | ||||||||
| 60 | Plac | 28.9 (1.2) |
✓ |
3 | 8 (13.3) | — | |||||
| 80 | Dex | 28.9 (1.2) |
0 (0) | Not estimated | |||||||
| Mini-Mental State Exam; DST: Digit Span Test; MoCA: Montreal Cognitive Assessment; RR: risk ratio; Dex: Dexmedetomidine; Mid: Midazolam; Prop: Propofol; Ulin: ulinastatin; Plac/None: placebo or no intervention. | |||||||||||
| a Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | |||||||||||
| b Day of assessment. | |||||||||||
| c MMSE <24. | |||||||||||
| d Difference from baseline ≥1 SD. | |||||||||||
| e Not specified. | |||||||||||
| f Z ≥1.96. | |||||||||||
| g American Psychiatric Association postoperative cognitive dysfunction diagnostic criteria. | |||||||||||
| h Threshold not specified. | |||||||||||
| i Difference from baseline ≥2 SD. | |||||||||||
| j Difference from baseline >2 pts. | |||||||||||
| k MMSE <26. | |||||||||||
| l Z >2. | |||||||||||
Ketamine
| Study | N | Drug | Preop | Instrument | Dayb,b | Neurocognitive Disorder <30 days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMSEa,a | MMSE | DST | MoCA | Other | N (%) | 0 — 100% | RR (95% CI) | ||||
| GI/Abd - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 34 | Plac | 27.9 (1.6) |
✓ |
7 | 13 (38.2) | — | |||||
| 33 | Ket | 28.6 (1.1) |
5 (15.2) | 0.40 (0.16-0.99) | |||||||
| 31 | Plac | ✓ |
3 | 12 (38.7) | — | ||||||
| 31 | Ket | 5 (16.1) | 0.42 (0.17-1.04) | ||||||||
| Various - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 44 | Plac | 28.3 (2.3) |
✓c |
3 | 6 (13.6) | — | |||||
| 45 | Hal | 28.0 (1.3) |
7 (15.6) | 1.14 (0.42-3.13) | |||||||
| 47 | Ket | 27.7 (1.7) |
10 (21.3) | 1.56 (0.62-3.93) | |||||||
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 26 | Plac | ✓ |
7 | 21 (80.8) | — | ||||||
| 26 | Ket | 7 (26.9) | 0.33 (0.17-0.65) | ||||||||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 26 | Plac | 26 {24-28} |
✓d |
6 | 0 (0) | — | |||||
| 25 | Ket | 25 {24-28} |
1 (4.0) | Not estimated | |||||||
| Mini-Mental State Exam; DST: Digit Span Test; MoCA: Montreal Cognitive Assessment; RR: risk ratio; Ket: ketamine; Hal: haloperidol; Plac: placebo. | |||||||||||
| Mini-Mental State Exam; DST: Digit Span Test; MoCA: Montreal Cognitive Assessment; RR: risk ratio; Dex: Dexmedetomidine; Mid: Midazolam; Prop: Propofol; Ulin: ulinastatin; Plac/None: placebo or no intervention. | |||||||||||
| a Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | |||||||||||
| b Day of assessment. | |||||||||||
| c MMSE <24. | |||||||||||
| d Z ≥1.96. | |||||||||||
Melatonin/Ramelteon
No studies
Pooled
Dexmedetomidine
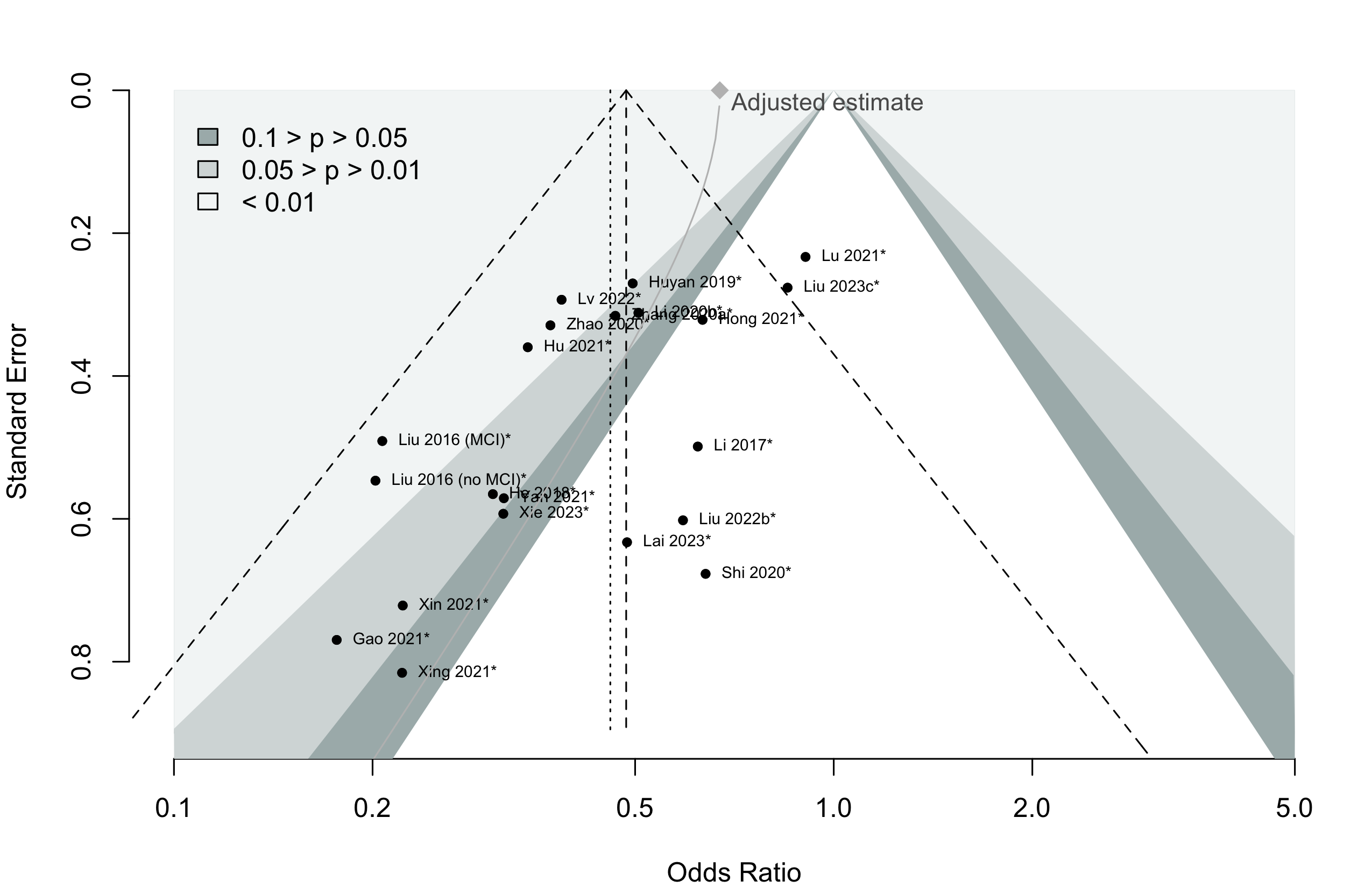
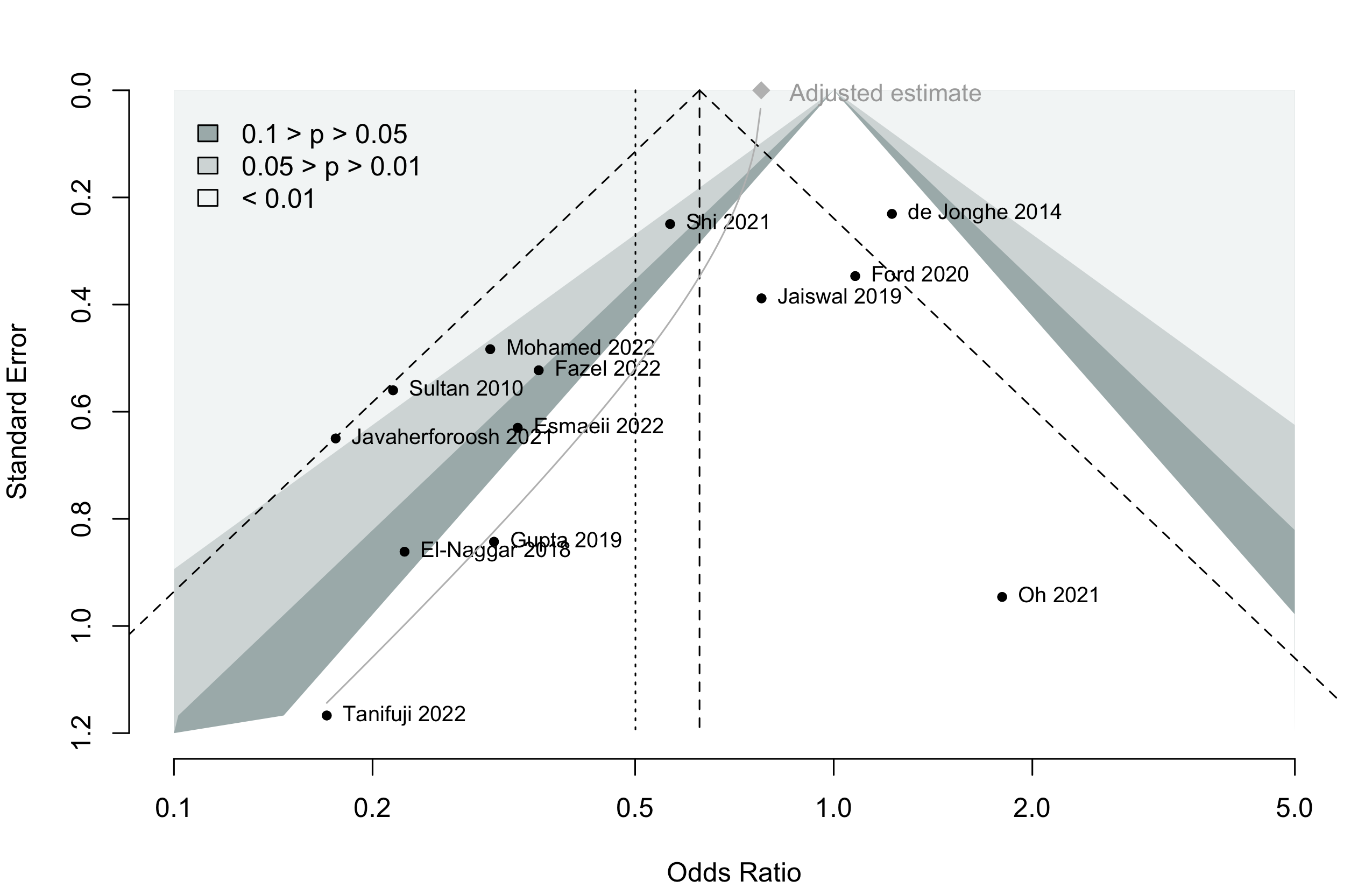
Risk of bias ratings: low +, some concerns ?, high – .
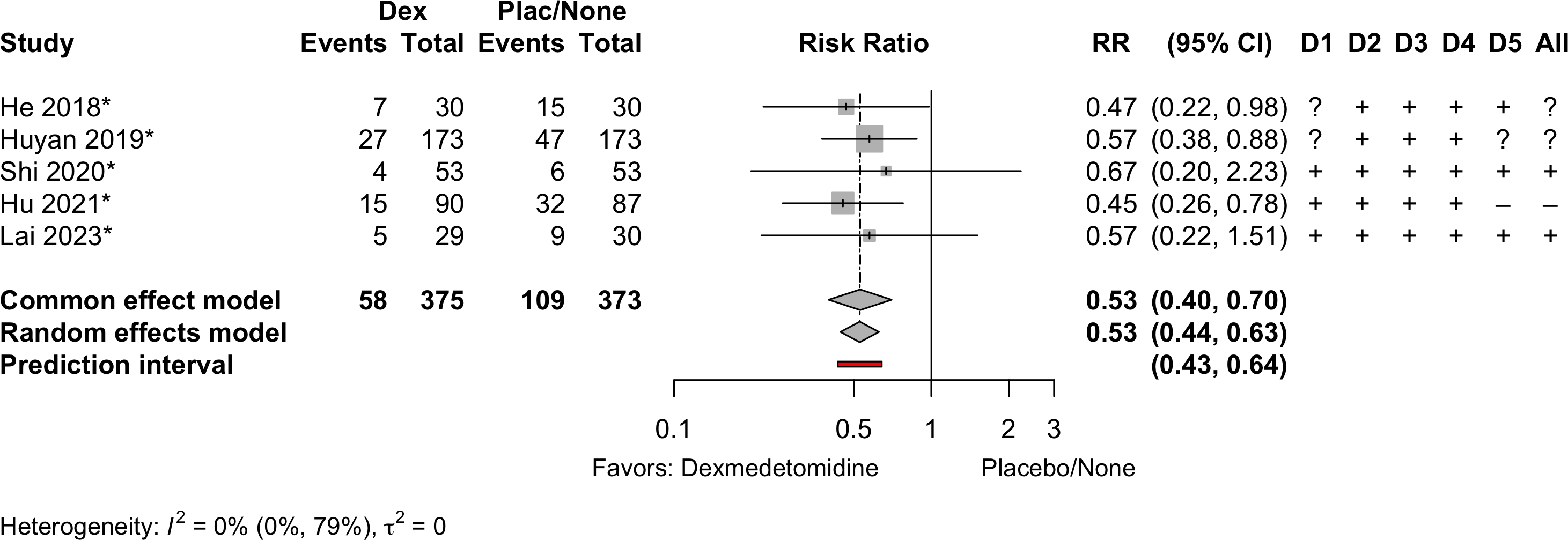
Neurocognitive recovery a designated primary outcome in 19.4%; a secondary outcome in 6.5%.
*Trials conducted in China.
Ketamine
Risk of bias ratings: low +, some concerns ?, high – .
Too few studies to examine small study effects.
Network
| Table 24. Summary of studies included in the network for neurocognitive disorder <30 days. | |
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Interventions | 5 |
| Number of Studies | 15 |
| Total Number of Patients in Network | 1,720 |
| Total Possible Pairwise Comparisons | 10 |
| Total Number of Pairwise Comparisons With Direct Data | 6 |
| Is the network connected? | TRUE |
| Number of Two-arm Studies | 13 |
| Number of Multi-Arms Studies | 2 |
| Total Number of Events in Network | 335 |
| Number of Studies With No Zero Events | 13 |
| Number of Studies With At Least One Zero Event | 2 |
| Number of Studies with All Zero Events | 0 |
| Table 25. Summary of events by comparisons in the network for neurocognitive disorder <30 days. | |||
| Comparison | Studies | Patients | Events (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dex vs. Mid | 3 | 407 | 114 (28.0) |
| Dex vs. Plac | 9 | 1,058 | 151 (14.3) |
| Dex vs. Prop | 2 | 190 | 51 (26.8) |
| Ket vs. Plac | 3 | 170 | 47 (27.6) |
| Mid vs. Plac | 1 | 100 | 16 (16.0) |
| Mid vs. Prop | 1 | 109 | 38 (34.9) |
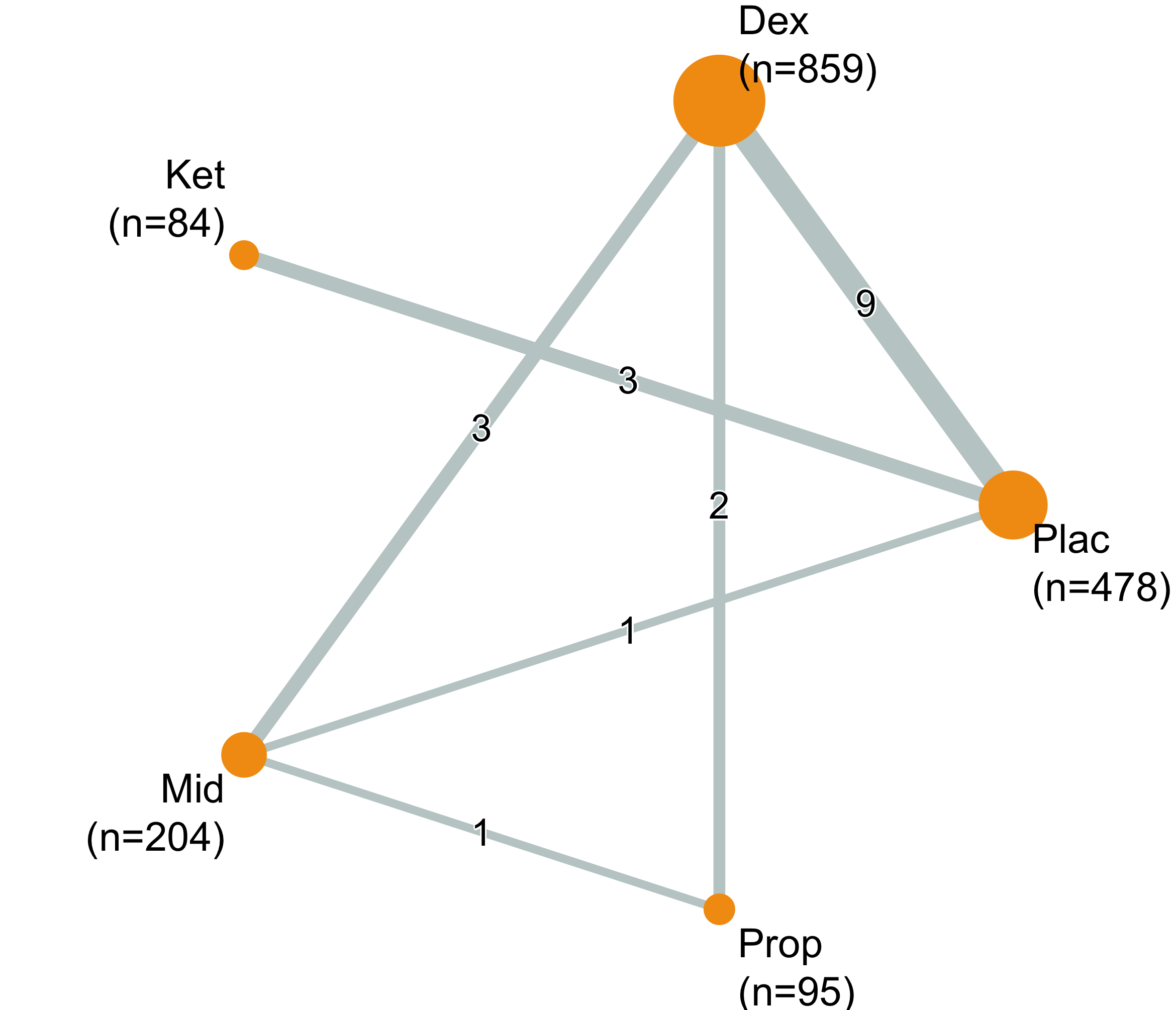
Zhao 2020 no intervention (usual care) arm included as placebo.
Dex |
0.83 |
1.42 |
0.54 | |
1.41 |
Ket |
0.38 | ||
0.78 |
0.55 |
Mid |
2.85 |
0.60 |
1.49 |
1.06 |
1.91 |
Prop |
|
0.53 |
0.38 |
0.68 |
0.36 |
Plac |
| Dex: Dexmedetomidine; Ket: ketamine; Mid: midazolam; Prop: propofol; Ulin: ulinastatin; Prop: Propofol; Plac/None: Placebo or no intervention. | ||||
Neurocognitive Disorder
30 days to 1 year
Dexmedetomidine, Ketamine, and Melatonin
| Study | N | Drug | Preop | Instrument | Dayb | Neurocognitive Disorder 30 days to 1 yr | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMSEa | MMSE | DST | MoCA | Other | N (%) | 0 — 100% | RR (95% CI) | ||||
| Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||||||
| 151 | Plac | 23 {10-28} |
✓ |
90 | 105 (69.5) | — | |||||
| 147 | Mel | 23 {12-29} |
87 (59.2) | 0.85 (0.72-1.01) | |||||||
| 55 | Prop | ✓c |
365 | 5 (9.1) | — | ||||||
| 54 | Mid | 7 (13.0) | 1.43 (0.48-4.22) | ||||||||
| 55 | Dex | 6 (10.9) | 1.20 (0.39-3.70) | ||||||||
| 100 | Mid | 25.0 (3.3) |
✓d |
90 | 7 (7.0) | — | |||||
| 98 | Dex | 24.9 (3.9) |
9 (9.2) | 1.31 (0.51-3.38) | |||||||
| 20 | Plac | 28.4 (1.3) |
✓ |
90 | 2 (10.0) | — | |||||
| 20 | Dex | 28.5 (1.4) |
0 (0) | Not estimated | |||||||
| 34 | Plac | 27.9 (1.6) |
✓ |
90 | 5 (14.7) | — | |||||
| 33 | Ket | 28.6 (1.1) |
2 (6.1) | 0.41 (0.09-1.98) | |||||||
| 30 | Plac | ✓e |
90f | 20 (66.7) | — | ||||||
| 30 | Ket | 7 (23.3) | 0.35 (0.17-0.70) | ||||||||
| 30 | Dex | 5 (16.7) | 0.25 (0.11-0.58) | ||||||||
| Mini-Mental State Exam; DST: Digit Span Test; MoCA: Montreal Cognitive Assessment; RR: risk ratio; Dex: dexmedetomidine: Mel: melatonin; Plac: placebo. | |||||||||||
| a Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | |||||||||||
| b Day of assessment. | |||||||||||
| c Z ≥1.96. | |||||||||||
| d Threshold not specified. | |||||||||||
| e Failed at least 2 of Visual Verbal Learning Tests, Stroop color word test, Letter Digit Coding Test, or Concept Shifting Test | |||||||||||
| f Assumed to be 90 days based on time of final reported neuropsychological assessment. | |||||||||||
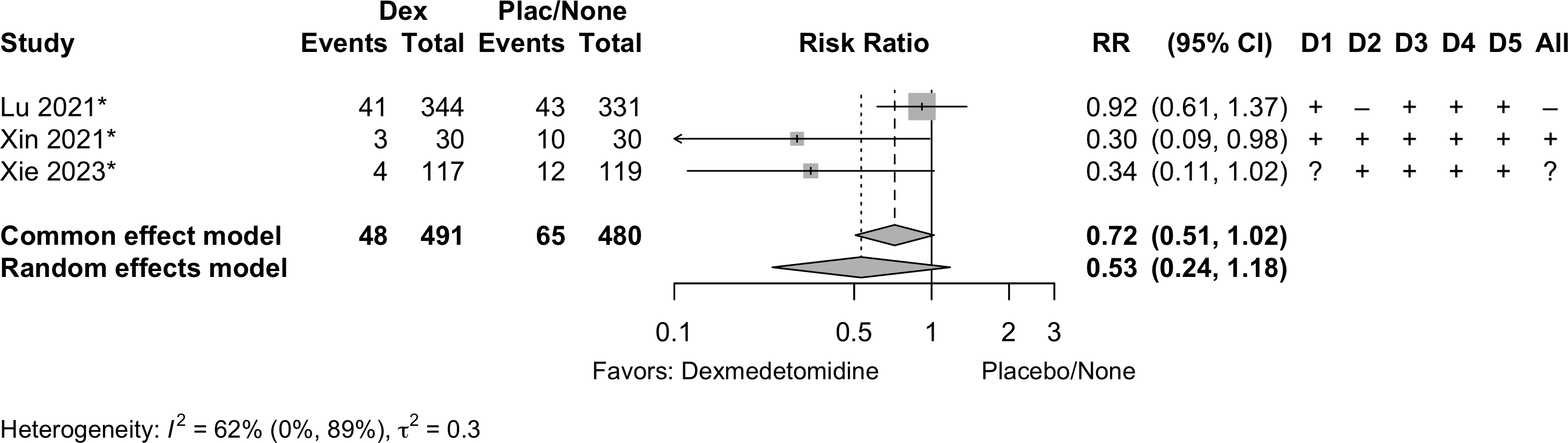
Pooled
Dexmedetomidine
Ketamine
Network (exploratory)
Physical Function
| Study | N | Arm | Agea | Scale | Range | Days | Ratinga | SMD (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30-90 days | ||||||||
| 192 | Plac | 83.4 (7.5) |
Katz ADL score | 15→0 | 90 | 9 [5-13] |
||
| 186 | Mel | 84.1 (8.0) |
9 [5-13] |
0.00 (-0.20 to 0.20) | ||||
| >90 days | ||||||||
| 31 | Prop | 78.8 |
SF-36 physical | 0→100 | 182.5 | 73.7 |
||
| 30 | Dex | 78.7 |
76.1 |
0.39 (-1.57 to 2.34) | ||||
| SMD: standardized mean difference | ||||||||
| a Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | ||||||||
Complications
Dexmedetomidine
Bradycardia
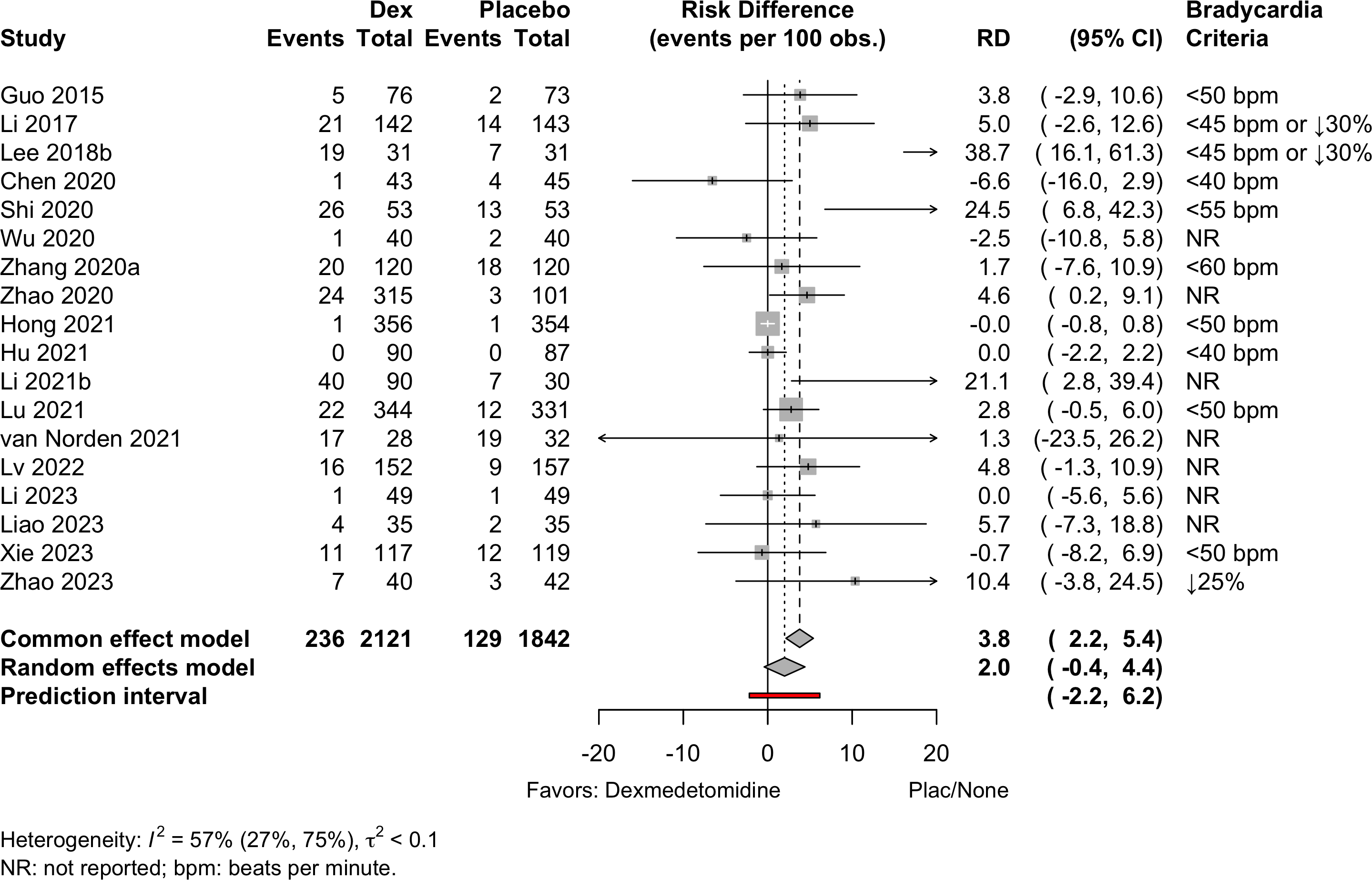
| Study | N | Arm | Age | Surgery | N (%) | 0 – 100% | RD (95% CI) | Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Randomized Clinical Trial | ||||||||
| 45 | Plac | 65.4 (11.7) |
GI/Abd | 4 (8.9) | — | <40 bpm | ||
| 43 | Dex | 64.9 (11.4) |
1 (2.3) | -6.6% (-16.0, 2.9) | ||||
| 87 | Plac | 69.1 (5.1) |
Thoracic | 0 (0) | — | <40 bpm | ||
| 90 | Dex | 69.6 (4.5) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-2.2, 2.2) | ||||
| 73 | Plac | 71.3 (5.1) |
Oralmax | 2 (2.7) | — | <50 bpm | ||
| 76 | Dex | 70.7 (5.2) |
5 (6.6) | 3.8% (-2.9, 10.6) | ||||
| 20 | Mid | 60.5 (8.2) |
Oralmax | 2 (10.0) | — | <50 bpm | ||
| 20 | Dex | 60.0 (10.1) |
8 (40.0) | 30.0% (4.8, 55.2) | ||||
| 354 | Plac | 71.0 (5.0) |
Ortho | 1 (0.3) | — | <50 bpm | ||
| 356 | Dex | 71.0 (5.0) |
1 (0.3) | -0.0% (-0.8, 0.8) | ||||
| 331 | Plac | 70.4 (6.5) |
GI/Abd | 12 (3.6) | — | <50 bpm | ||
| 344 | Dex | 70.1 (5.8) |
22 (6.4) | 2.8% (-0.5, 6.0) | ||||
| 119 | Plac | 68.6 (5.5) |
GI/Abd | 12 (10.1) | — | <50 bpm | ||
| 117 | Dex | 67.9 (5.6) |
11 (9.4) | -0.7% (-8.2, 6.9) | ||||
| 53 | Plac | 68.7 (3.4) |
Thoracic | 13 (24.5) | — | <55 bpm | ||
| 53 | Dex | 68.7 (4.6) |
26 (49.1) | 24.5% (6.8, 42.3) | ||||
| 120 | Plac | 79.0 (6.8) |
Ortho | 18 (15.0) | — | <60 bpm | ||
| 120 | Dex | 78.1 (6.4) |
20 (16.7) | 1.7% (-7.6, 10.9) | ||||
| 143 | Plac | 67.5 (5.3) |
Cardiac | 14 (9.8) | — | <45 bpm or ↓30% | ||
| 142 | Dex | 66.4 (5.4) |
21 (14.8) | 5.0% (-2.6, 12.6) | ||||
| 31 | Plac | 67.2 (5.0) |
Ortho | 7 (22.6) | — | <45 bpm or ↓30% | ||
| 33 | Preg | 68.4 (5.1) |
8 (24.2) | 1.7% (-19.1, 22.4) | ||||
| 29 | Dex/Preg | 65.4 (9.7) |
19 (65.5) | 42.9% (20.2, 65.6) | ||||
| 31 | Dex | 68.8 (5.9) |
19 (61.3) | 38.7% (16.1, 61.3) | ||||
| 42 | Plac | 69.7 (7.2) |
Ortho | 3 (7.1) | — | ↓25% | ||
| 40 | Dex | 70.9 (7.2) |
7 (17.5) | 10.4% (-3.8, 24.5) | ||||
| 40 | Plac | 67.7 (8.8) |
Cardiac | 2 (5.0) | — | NR | ||
| 40 | Dex | 68.2 (8.6) |
1 (2.5) | -2.5% (-10.8, 5.8) | ||||
| 101 | None | 69.2 (4.1) |
Various | 3 (3.0) | — | NR | ||
| 108 | Dex | 70.0 (4.5) |
8 (7.4) | 4.4% (-1.5, 10.4) | ||||
| 105 | Dex | 69.4 (3.9) |
8 (7.6) | 4.6% (-1.4, 10.7) | ||||
| 102 | Dex | 69.3 (4.1) |
8 (7.8) | 4.9% (-1.3, 11.1) | ||||
| 30 | Plac | 73.4 (5.1) |
GI/Abd | 7 (23.3) | — | NR | ||
| 30 | Dex | 74.7 (2.6) |
8 (26.7) | 3.3% (-18.6, 25.2) | ||||
| 30 | Dex | 71.2 (3.5) |
12 (40.0) | 16.7% (-6.5, 39.8) | ||||
| 30 | Dex | 69.8 (4.3) |
20 (66.7) | 43.3% (20.7, 66.0) | ||||
| 32 | Plac | 70.5 (6.2) |
Various | 19 (59.4) | — | NR | ||
| 28 | Dex | 70.4 (7.1) |
17 (60.7) | 1.3% (-23.5, 26.2) | ||||
| 157 | Plac | 68.4 (6.6) |
Various | 9 (5.7) | — | NR | ||
| 152 | Dex | 67.9 (5.9) |
16 (10.5) | 4.8% (-1.3, 10.9) | ||||
| 49 | None | 68.5 (2.2) |
Ortho | 1 (2.0) | — | NR | ||
| 49 | Dex | 67.7 (2.8) |
1 (2.0) | 0.0% (-5.6, 5.6) | ||||
| 35 | Plac | 69.7 (2.5) |
GI/Abd | 2 (5.7) | — | NR | ||
| 34 | Rem | 70.1 (3.6) |
0 (0) | -5.7% (-14.9, 3.5) | ||||
| 35 | Dex | 71.3 (3.6) |
4 (11.4) | 5.7% (-7.3, 18.8) | ||||
| Nonrandomized Trial | ||||||||
| 50 | Plac | 68.3 (2.1) |
GI/Abd | 3 (6.0) | — | <55 bpm | ||
| 60 | Dex | 68.4 (3.3) |
4 (6.7) | 0.7% (-8.5, 9.8) | ||||
| 46 | None | 67.3 (2.1) |
Thoracic | 2 (4.3) | — | NR | ||
| 41 | Dex | 67.4 (3.3) |
1 (2.4) | -1.9% (-9.5, 5.6) | ||||
| RD: risk difference; Dex: Dexmedetomidine; Dex/Preg: Dexmedetomidine/Pregabalin; Mid: Midazolam; Prop: Propofol; Ram: ramelteon; Plac: placebo; None: no active or placebo comparator; GI/Abd: gastrointestinal/abdominal; Ortho: orthopedic; Oralmax: oral or maxilofacial. | ||||||||
| a Nonrandomized Trial | ||||||||
Pooled
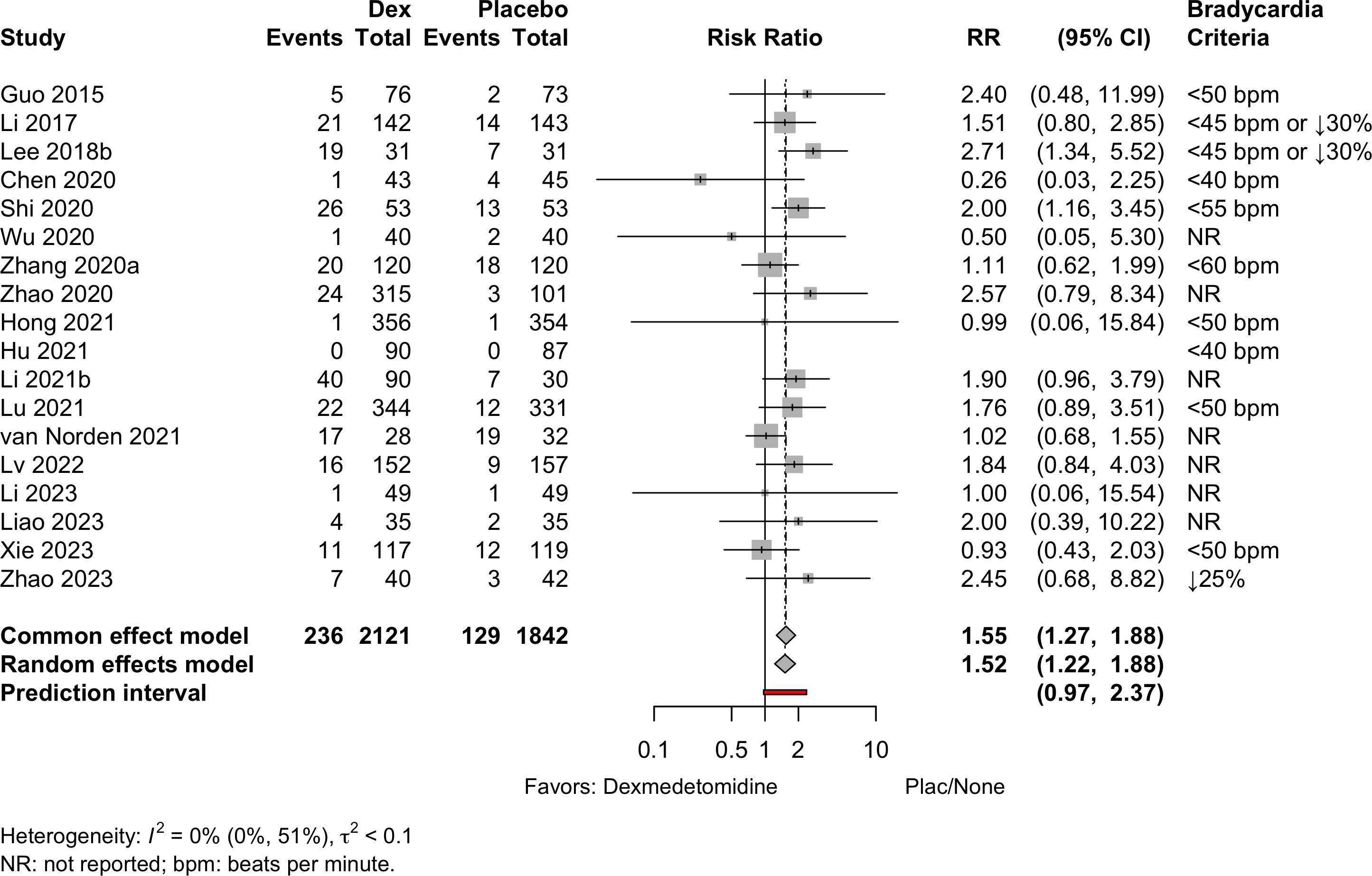
Similar arms combined in Li 2021b and Zhao 2020.
Hypotension
| Study | N | Arm | Age | Surgery | N (%) | 0 – 100% | RD (95% CI) | Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Randomized Clinical Trial | ||||||||
| 63 | Plac | 67.9 (6.6) |
GI/Abd | 0 (0) | — | MAP <60 | ||
| 59 | Dex | 66.2 (7.5) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-3.2, 3.2) | ||||
| 40 | Prop | 64.7 (5.9) |
Various | 4 (10.0) | — | MAP ≤70 | ||
| 40 | Dex | 66.2 (6.6) |
7 (17.5) | 7.5% (-7.5, 22.5) | ||||
| 20 | Mid | 60.5 (8.2) |
Oralmax | 3 (15.0) | — | ↓MAP >20% | ||
| 20 | Dex | 60.0 (10.1) |
4 (20.0) | 5.0% (-18.5, 28.5) | ||||
| 31 | Plac | 67.2 (5.0) |
Ortho | 11 (35.5) | — | SBP <90 | ||
| 33 | Preg | 68.4 (5.1) |
14 (42.4) | 6.9% (-16.9, 30.8) | ||||
| 29 | Dex/Preg | 65.4 (9.7) |
21 (72.4) | 36.9% (13.5, 60.3) | ||||
| 31 | Dex | 68.8 (5.9) |
19 (61.3) | 25.8% (1.8, 49.8) | ||||
| 60 | Plac | 72.1 (5.9) |
Oralmax | 1 (1.7) | — | SBP <90 | ||
| 60 | Dex | 71.3 (6.7) |
3 (5.0) | 3.3% (-3.1, 9.7) | ||||
| 60 | Plac | 66.7 (4.1) |
Urol | 0 (0) | — | SBP <90 | ||
| 60 | Dex | 65.6 (3.4) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-3.2, 3.2) | ||||
| 206 | Plac | 70.0 {65-75} |
Cardiac | 13 (6.3) | — | SBP <90 | ||
| 188 | Dex | 67.5 {63-73} |
20 (10.6) | 4.3% (-1.2, 9.8) | ||||
| 61 | Prop | 70.0 {64-79} |
Cardiac | 21 (34.4) | — | SBP <90 ≥5 min | ||
| 59 | Dex | 66.5 {63-74} |
21 (35.6) | 1.2% (-15.9, 18.2) | ||||
| 30 | Plac | 68.0 [66-71] |
GI/Abd | 6 (20.0) | — | SBP <95 | ||
| 30 | Dex | 69.0 [67-70] |
4 (13.3) | -6.7% (-25.5, 12.1) | ||||
| 30 | Mid | 66.7 (5.6) |
Cardiac | 0 (0) | — | ↓SBP >20% | ||
| 30 | Dex | 65.3 (4.8) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-6.3, 6.3) | ||||
| 331 | Plac | 70.4 (6.5) |
GI/Abd | 45 (13.6) | — | ↓SBP >20% or <80 | ||
| 344 | Dex | 70.1 (5.8) |
30 (8.7) | -4.9% (-9.6, -0.1) | ||||
| 120 | Plac | 79.0 (6.8) |
Ortho | 8 (6.7) | — | ↓SBP >20% or <90 | ||
| 120 | Dex | 78.1 (6.4) |
10 (8.3) | 1.7% (-5.0, 8.3) | ||||
| 53 | Plac | 68.7 (3.4) |
Thoracic | 4 (7.5) | — | ↓SBP >20% or <95 | ||
| 53 | Dex | 68.7 (4.6) |
6 (11.3) | 3.8% (-7.3, 14.9) | ||||
| 73 | Plac | 71.3 (5.1) |
Oralmax | 2 (2.7) | — | ↓SBP >30% | ||
| 76 | Dex | 70.7 (5.2) |
4 (5.3) | 2.5% (-3.7, 8.8) | ||||
| 354 | Plac | 71.0 (5.0) |
Ortho | 3 (0.8) | — | ↓SBP >30% or <90 | ||
| 356 | Dex | 71.0 (5.0) |
2 (0.6) | -0.3% (-1.5, 0.9) | ||||
| 143 | Plac | 67.5 (5.3) |
Cardiac | 10 (7.0) | — | ↓SPB >30% ≥15 min | ||
| 142 | Dex | 66.4 (5.4) |
10 (7.0) | 0.0% (-5.9, 6.0) | ||||
| 42 | Plac | 69.7 (7.2) |
Ortho | 6 (14.3) | — | <20% from baseline | ||
| 40 | Dex | 70.9 (7.2) |
8 (20.0) | 5.7% (-10.6, 22.0) | ||||
| 201 | Plac | 74.0 {71-78} |
Various | 95 (47.3) | — | NS | ||
| 189 | Dex | 74.0 {71-78} |
102 (54.0) | 6.7% (-3.2, 16.6) | ||||
| 393 | Plac | 62.0 (12.0) |
Cardiac | 140 (35.6) | — | NS | ||
| 395 | Dex | 63.0 (11.0) |
224 (56.7) | 21.4% (14.6, 28.1) | ||||
| 101 | None | 69.2 (4.1) |
Various | 6 (5.9) | — | NS | ||
| 108 | Dex | 70.0 (4.5) |
15 (13.9) | 7.9% (-0.0, 15.9) | ||||
| 105 | Dex | 69.4 (3.9) |
6 (5.7) | -0.2% (-6.6, 6.2) | ||||
| 102 | Dex | 69.3 (4.1) |
7 (6.9) | 0.9% (-5.8, 7.7) | ||||
| 75 | Plac | 69.1 (5.1) |
Thoracic | 32 (42.7) | — | NS | ||
| 77 | Dex | 69.6 (4.5) |
42 (54.5) | 17.8% (2.7, 32.8) | ||||
| 30 | Plac | 73.4 (5.1) |
GI/Abd | 8 (26.7) | — | NS | ||
| 30 | Dex | 74.7 (2.6) |
11 (36.7) | 10.0% (-13.4, 33.4) | ||||
| 30 | Dex | 71.2 (3.5) |
10 (33.3) | 6.7% (-16.5, 29.8) | ||||
| 30 | Dex | 69.8 (4.3) |
21 (70.0) | 43.3% (20.5, 66.1) | ||||
| 55 | Plac | 69.2 (3.8) |
Ortho | 1 (1.8) | — | NS | ||
| 55 | Dex | 68.3 (3.9) |
1 (1.8) | 0.0% (-5.0, 5.0) | ||||
| 157 | Plac | 68.4 (6.6) |
Various | 13 (8.3) | — | NS | ||
| 152 | Dex | 67.9 (5.9) |
52 (34.2) | 25.9% (17.2, 34.6) | ||||
| 49 | None | 68.5 (2.2) |
Ortho | 3 (6.1) | — | NS | ||
| 49 | Dex | 67.7 (2.8) |
1 (2.0) | -4.1% (-11.9, 3.7) | ||||
| 35 | Plac | 69.7 (2.5) |
GI/Abd | 2 (5.7) | — | NS | ||
| 35 | Dex | 71.3 (3.6) |
3 (8.6) | 2.9% (-9.2, 14.9) | ||||
| Nonrandomized Trial | ||||||||
| 50 | Plac | 68.3 (2.1) |
GI/Abd | 6 (12.0) | — | SBP <90 | ||
| 60 | Dex | 68.4 (3.3) |
5 (8.3) | -3.7% (-15.1, 7.7) | ||||
| 46 | None | 67.3 (2.1) |
Thoracic | 1 (2.2) | — | NS | ||
| 41 | Dex | 67.4 (3.3) |
1 (2.4) | 0.3% (-6.1, 6.6) | ||||
| Retrospective Cohort | ||||||||
| 30 | None | 67.9 (5.0) |
Ortho | 1 (3.3) | — | NS | ||
| 30 | Dex | 67.3 (5.5) |
1 (3.3) | 0.0% (-9.1, 9.1) | ||||
| RD: risk difference; MAP: mean arterial blood pressure; Dex: Dexmedetomidine; Dex/Preg: Dexmedetomidine/Pregabalin; Mid: Midazolam; Prop: Propofol; Rem: remimazolam; Plac: placebo; None: no active or placebo comparator; GI/Abd: gastrointestinal/abdominal; Ortho: orthopedic; Urol: urologic; Oralmax: oral or maxilofacial; NS: not specified. | ||||||||
| a Nonrandomized Trial | ||||||||
Pooled
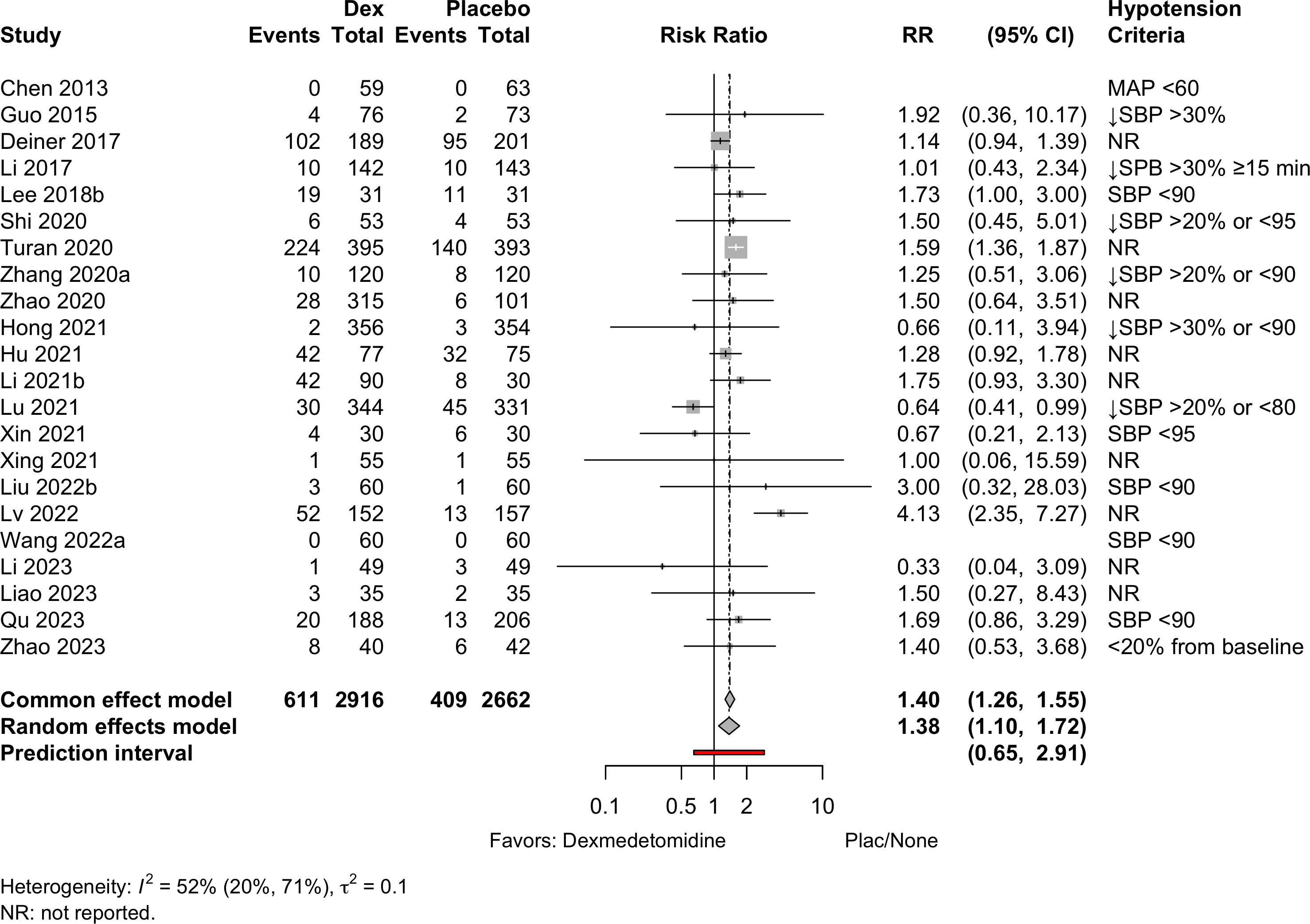
Similar arms combined in Li 2021b and Zhao 2020.
Other
| Study | N | Arm | Age | Surgery | N (%) | 0 – 100% | RD (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myocardial Infarction | |||||||
| 283 | None | 73.5 (6.2) |
Cardiac | 5 (1.8) | — | ||
| 222 | Dex | 73.6 (6.1) |
3 (1.4) | -0.4% (-2.6, 1.7) | |||
| 390 | Plac | 62.0 (12.0) |
Cardiac | 3 (0.8) | — | ||
| 394 | Dex | 63.0 (11.0) |
3 (0.8) | -0.0% (-1.2, 1.2) | |||
| 331 | Plac | 70.4 (6.5) |
GI/Abd | 0 (0) | — | ||
| 344 | Dex | 70.1 (5.8) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-0.6, 0.6) | |||
| 157 | Plac | 74.0 {71-78} |
Various | 0 (0) | — | ||
| 147 | Dex | 74.0 {71-78} |
1 (0.7) | 0.7% (-1.2, 2.5) | |||
| Cardiac Arrest | |||||||
| 283 | None | 73.5 (6.2) |
Cardiac | 3 (1.1) | — | ||
| 222 | Dex | 73.6 (6.1) |
2 (0.9) | -0.2% (-1.9, 1.6) | |||
| Other Arrhythmia | |||||||
| 390 | Plac | 62.0 (12.0) |
Cardiac | 134 (34.4) | — | ||
| 394 | Dex | 63.0 (11.0) |
121 (30.7) | -3.6% (-10.2, 2.9) | |||
| 20 | Plac | 71.4 (4.5) |
Cardiac | 0 (0) | — | ||
| 20 | Dex | 71.4 (4.5) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-9.2, 9.2) | |||
| 55 | Plac | 69.2 (3.8) |
Ortho | 1 (1.8) | — | ||
| 55 | Dex | 68.3 (3.9) |
1 (1.8) | 0.0% (-5.0, 5.0) | |||
| Stroke | |||||||
| 283 | None | 73.5 (6.2) |
Cardiac | 5 (1.8) | — | ||
| 222 | Dex | 73.6 (6.1) |
2 (0.9) | -0.9% (-2.8, 1.1) | |||
| 92 | Prop | 72.4 (6.2) |
Cardiac | 3 (3.3) | — | ||
| 91 | Dex | 72.7 (6.4) |
4 (4.4) | 1.1% (-4.4, 6.7) | |||
| 143 | Plac | 67.5 (5.3) |
Cardiac | 3 (2.1) | — | ||
| 142 | Dex | 66.4 (5.4) |
3 (2.1) | 0.0% (-3.3, 3.3) | |||
| 53 | Plac | 65.0 [37-83] |
Cardiac | 2 (3.8) | — | ||
| 51 | Dex | 65.0 [23-82] |
3 (5.9) | 2.1% (-6.1, 10.4) | |||
| 390 | Plac | 62.0 (12.0) |
Cardiac | 4 (1.0) | — | ||
| 394 | Dex | 63.0 (11.0) |
4 (1.0) | -0.0% (-1.4, 1.4) | |||
| 205 | Plac | 70.0 {65-75} |
Cardiac | 1 (0.5) | — | ||
| 183 | Dex | 67.5 {63-73} |
0 (0) | -0.5% (-1.9, 0.9) | |||
| 331 | Plac | 70.4 (6.5) |
GI/Abd | 0 (0) | — | ||
| 344 | Dex | 70.1 (5.8) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-0.6, 0.6) | |||
| 157 | Plac | 74.0 {71-78} |
Various | 1 (0.6) | — | ||
| 147 | Dex | 74.0 {71-78} |
0 (0) | -0.6% (-2.4, 1.1) | |||
| Acute Kidney Injury | |||||||
| 283 | None | 73.5 (6.2) |
Cardiac | 13 (4.6) | — | ||
| 222 | Dex | 73.6 (6.1) |
13 (5.9) | 1.3% (-2.7, 5.2) | |||
| 143 | Plac | 67.5 (5.3) |
Cardiac | 44 (30.8) | — | ||
| 142 | Dex | 66.4 (5.4) |
37 (26.1) | -4.7% (-15.2, 5.7) | |||
| 53 | Plac | 65.0 [37-83] |
Cardiac | 17 (32.1) | — | ||
| 51 | Dex | 65.0 [23-82] |
7 (13.7) | -18.3% (-34.1, -2.6) | |||
| 390 | Plac | 62.0 (12.0) |
Cardiac | 30 (7.7) | — | ||
| 394 | Dex | 63.0 (11.0) |
41 (10.4) | 2.7% (-1.3, 6.7) | |||
| 20 | Plac | 71.4 (4.5) |
Cardiac | 1 (5.0) | — | ||
| 20 | Dex | 71.4 (4.5) |
1 (5.0) | 0.0% (-13.5, 13.5) | |||
| 203 | Plac | 70.0 {59-81} |
Cardiac | 2 (1.0) | — | ||
| 205 | Dex | 71.0 {61-81} |
2 (1.0) | -0.0% (-1.9, 1.9) | |||
| Pulmonary | |||||||
| 143 | Plac | 67.5 (5.3) |
Cardiac | 27 (18.9) | — | ||
| 142 | Dex | 66.4 (5.4) |
15 (10.6) | -8.3% (-16.5, -0.2) | |||
| 20 | Plac | 71.4 (4.5) |
Cardiac | 5 (25.0) | — | ||
| 20 | Dex | 71.4 (4.5) |
4 (20.0) | -5.0% (-30.8, 20.8) | |||
| Pneumonia | |||||||
| 53 | Plac | 65.0 [37-83] |
Cardiac | 6 (11.3) | — | ||
| 51 | Dex | 65.0 [23-82] |
7 (13.7) | 2.4% (-10.3, 15.1) | |||
| 119 | Plac | 68.6 (5.5) |
GI/Abd | 6 (5.0) | — | ||
| 117 | Dex | 67.9 (5.6) |
4 (3.4) | -1.6% (-6.8, 3.5) | |||
| 157 | Plac | 74.0 {71-78} |
Various | 1 (0.6) | — | ||
| 147 | Dex | 74.0 {71-78} |
3 (2.0) | 1.4% (-1.2, 4.0) | |||
| Pulmonary Congestiond,e | |||||||
| 157 | Plac | 74.0 {71-78} |
Various | 0 (0) | — | ||
| 147 | Dex | 74.0 {71-78} |
1 (0.7) | 0.7% (-1.2, 2.5) | |||
| Pulmonary Embolism | |||||||
| 157 | Plac | 74.0 {71-78} |
Various | 1 (0.6) | — | ||
| 147 | Dex | 74.0 {71-78} |
1 (0.7) | 0.0% (-1.8, 1.9) | |||
| Respiratory Depression/Failure | |||||||
| 40 | Plac | 67.7 (8.8) |
Cardiac | 5 (12.5) | — | ||
| 40 | Dex | 68.2 (8.6) |
3 (7.5) | -5.0% (-18.1, 8.1) | |||
| 45 | Plac | 65.4 (11.7) |
GI/Abd | 3 (6.7) | — | ||
| 43 | Dex | 64.9 (11.4) |
0 (0) | -6.7% (-14.9, 1.6) | |||
| 73 | Plac | 71.3 (5.1) |
Oralmax | 0 (0) | — | ||
| 76 | Dex | 70.7 (5.2) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-2.6, 2.6) | |||
| 20 | Mid | 60.5 (8.2) |
Oralmax | 7 (35.0) | — | ||
| 20 | Dex | 60.0 (10.1) |
1 (5.0) | -30.0% (-53.0, -7.0) | |||
| 157 | Plac | 74.0 {71-78} |
Various | 1 (0.6) | — | ||
| 147 | Dex | 74.0 {71-78} |
2 (1.4) | 0.7% (-1.5, 3.0) | |||
| 101 | None | 69.2 (4.1) |
Various | 0 (0) | — | ||
| 108 | Dex | 70.0 (4.5) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-1.9, 1.9) | |||
| 105 | Dex | 69.4 (3.9) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-1.9, 1.9) | |||
| 102 | Dex | 69.3 (4.1) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-1.9, 1.9) | |||
| RD: risk difference. | |||||||
| a Retrospective Cohort | |||||||
| b Unspecified | |||||||
| c Pulmonary infection, pneumothorax, or pleural effusion needing intervention. | |||||||
| d Pulmonary congestion includes heart failure diagnosis. | |||||||
| e Includes unspecified, composite, respiratory depression, pleural effusion. | |||||||
Pooled
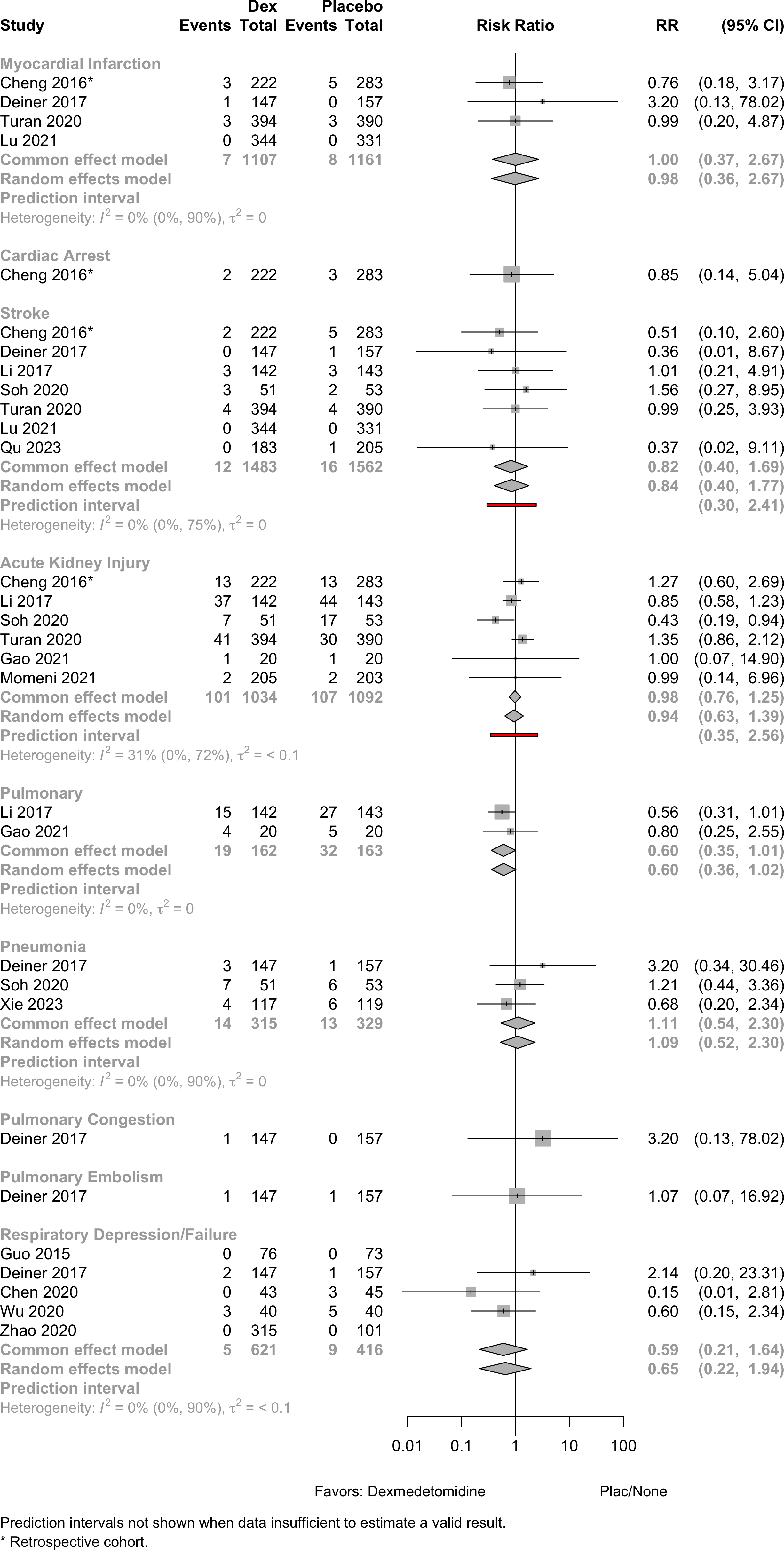
Ketamine
| Study | N | Arm | Age | Surgery | N (%) | 0 – 100% | RD (95% CI) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bradycardia | ||||||||
| 31 | Plac | 70.5 (4.2) |
GI/Abd | 6 (19.4) | — | <50 bpm | ||
| 31 | Ket | 69.5 (4.3) |
12 (38.7) | 19.4% (-2.7, 41.4) | ||||
| Hypotension | ||||||||
| 31 | Plac | 70.5 (4.2) |
GI/Abd | 19 (61.3) | — | ↓SBP >30% or <80 | ||
| 31 | Ket | 69.5 (4.3) |
9 (29.0) | -32.3% (-55.7, -8.8) | ||||
| Acute Kidney Injury | ||||||||
| 75 | Plac | 65.0 (14.0) |
Ortho | 10 (13.3) | — | |||
| 79 | Ket | 64.0 (13.0) |
9 (11.4) | -1.9% (-12.3, 8.5) | ||||
Ramelteon
| Study | N | Arm | Age | Surgery | N (%) | 0 – 100% | RD (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arrhythmiaa | |||||||
| 58 | None | 76.5 [70-87] |
Thoracic | 5 (8.6) | — | ||
| 24 | Ram | 79.0 [70-89] |
0 (0) | -8.6% (-17.8, 0.6) | |||
| Pulmonary | |||||||
| 186 | None | 69.0 [30-88] |
GI/Abd | 4 (2.2) | — | ||
| 120 | Ram | 71.0 [34-85] |
4 (3.3) | 1.2% (-2.6, 5.0) | |||
| Pneumonia | |||||||
| 186 | None | 69.0 [30-88] |
GI/Abd | 3 (1.6) | — | ||
| 120 | Ram | 71.0 [34-85] |
2 (1.7) | 0.1% (-2.9, 3.0) | |||
| 58 | None | 76.5 [70-87] |
Thoracic | 4 (6.9) | — | ||
| 24 | Ram | 79.0 [70-89] |
1 (4.2) | -2.7% (-13.0, 7.6) | |||
| a Not otherwise specified. | |||||||
| b Before-After/Time Series | |||||||
Length of Stay
Dexmedetomidine
| Study | N | Comparator | PSa | Ageb | LOSb | 0 – 25 days | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 92 | Prop | NR | 72.4 (6.2) |
7.0 [4-74] |
Canada | ||
| 91 | Dex | NR | 72.7 (6.4) |
7.0 [4-35] |
|||
| 24 | Plac | 123 | 72.0 (4.0) |
4.6 (1.1) |
China | ||
| 24 | Dex | 123 | 70.0 (3.0) |
4.6 (1.3) |
|||
| 143 | Plac | 234 | 67.5 (5.3) |
9.0 {8-10} |
China | ||
| 142 | Dex | 234 | 66.4 (5.4) |
9.0 {8-10} |
|||
| 61 | Prop | NR | 70.0 {64-79} |
8.0 {6-11} |
USA | ||
| 59 | Dex | NR | 66.5 {63-74} |
8.0 {6-10} |
|||
| 54 | Plac | NR | 65.0 [37-83] |
15.0 {11-21} |
South Korea | ||
| 54 | Dex | NR | 65.0 [23-82] |
12.0 {10-17} |
|||
| 396 | Plac | 1234 | 62.0 (12.0) |
6.0 {5-7} |
USA | ||
| 398 | Dex | 1234 | 63.0 (11.0) |
6.0 {5-8} |
|||
| 20 | Plac | 23 | 71.4 (4.5) |
13.0 (2.0) |
China | ||
| 20 | Dex | 23 | 71.4 (4.5) |
10.0 (1.0) |
|||
| 203 | Plac | NR | 70.0 {59-81} |
7.0 {7-10} |
Belgium | ||
| 205 | Dex | NR | 71.0 {61-81} |
8.0 {7-10} |
|||
| 33 | Prop | NR | 78.8 |
12.2 |
Canada | ||
| 34 | Dex | NR | 78.7 |
10.2 |
|||
| 206 | Plac | NR | 70.0 {65-75} |
6.0 {5-7} |
USA | ||
| 188 | Dex | NR | 67.5 {63-73} |
6.0 {5-8} |
|||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 148 | Prop | 23 | 74.0 (6.0) |
6.8 (2.0) |
China | ||
| 148 | Dex | 23 | 76.0 (7.0) |
6.3 (1.6) |
|||
| 354 | Plac | 1234 | 71.0 (5.0) |
5.0 {5-6} |
China | ||
| 356 | Dex | 1234 | 71.0 (5.0) |
5.0 {5-6} |
|||
| 50 | Plac | 12 | 72.7 (4.3) |
16.1 (0.7) |
China | ||
| 50 | Dex | 12 | 73.2 (5.8) |
13.2 (0.9) |
|||
| 48 | Plac | 123 | 67.2 (5.2) |
5.0 (0.8) |
China | ||
| 47 | Dex | 123 | 68.2 (6.0) |
4.2 (0.7) |
|||
| 52 | Dex | 23 | 70.8 (4.4) |
7.0 {6-10} |
China | ||
| 53 | Dex | 23 | 71.8 (5.5) |
7.0 {7-11} |
|||
| GI/Abd - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 331 | Plac | 123 | 70.4 (6.5) |
15.0 {11-18} |
China | ||
| 344 | Dex | 123 | 70.1 (5.8) |
13.0 {10-17} |
|||
| 45 | None | 23 | 68.5 (3.8) |
25.5 (8.6) |
China | ||
| 45 | Dex | 23 | 68.5 (3.8) |
17.9 (8.1) |
|||
| 119 | Plac | NR | 68.6 (5.5) |
11.6 (8.5) |
China | ||
| 117 | Dex | NR | 67.9 (5.6) |
11.7 (9.1) |
|||
| Thoracic - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 173 | Plac | 23 | 71.0 (6.0) |
9.0 {7-11} |
China | ||
| 173 | Dex | 23 | 70.0 (5.0) |
8.0 {6-10} |
|||
| ENT - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 149 | Plac | NR | 70.1 (4.2) |
13.0 {10-15} |
China | ||
| 150 | Dex | NR | 70.4 (5.0) |
13.0 {9-15} |
|||
| Oralmax - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 60 | Plac | 12 | 72.1 (5.9) |
9.0 (2.8) |
China | ||
| 60 | Dex | 12 | 71.3 (6.7) |
9.0 (2.5) |
|||
| Various - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 201 | Plac | 1234 | 74.0 {71-78} |
4.0 {3-6} |
USA | ||
| 189 | Dex | 1234 | 74.0 {71-78} |
4.0 {3-6} |
|||
| 310 | Plac | 123 | 69.0 (6.4) |
10.3 (9.4) |
China | ||
| 309 | Dex | 123 | 69.0 (6.6) |
10.0 (7.6) |
|||
| 32 | Plac | 1234 | 70.5 (6.2) |
21.0 (15.6) |
Germany | ||
| 28 | Dex | 1234 | 70.4 (7.1) |
23.5 (20.3) |
|||
| 157 | Plac | NR | 68.4 (6.6) |
17.2 (6.3) |
China | ||
| 152 | Dex | NR | 67.9 (5.9) |
15.6 (4.2) |
|||
| Cardiac - Retrospective Cohort | |||||||
| 209 | Prop | NR | 62.0 (13.0) |
8.3 (4.4) |
USA | ||
| 69 | Dex | NR | 63.0 (13.0) |
7.8 (3.1) |
|||
| NR: not reported | |||||||
| a ASA Physical Status. | |||||||
| b Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | |||||||
Ketamine
| Study | N | Comparator | PSa | Ageb | LOSb | 0 – 25 days | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 26 | Plac | 34 | 67.0 (8.0) |
7.0 (3.0) |
USA | ||
| 26 | Ket | 34 | 68.0 (7.0) |
8.0 (4.0) |
|||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 75 | Plac | NR | 65.0 (14.0) |
8.3 (1.6) |
France | ||
| 79 | Ket | NR | 64.0 (13.0) |
8.8 (3.2) |
|||
| Spine - Prospective Cohort | |||||||
| 38 | None | 123 | 71.0 {68-78} |
4.0 {3-6} |
USA | ||
| 60 | Ket | 123 | 70.0 {67-75} |
4.0 {2-6} |
|||
| NR: not reported | |||||||
| a ASA Physical Status. | |||||||
| b Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | |||||||
Melatonin or ramelteon
| Study | N | Comparator | PSa | Ageb | LOSb | 0 – 25 days | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 104 | Plac | NR | 67.6 (8.0) |
7.0 {6-8} |
Australia | ||
| 98 | Mel | NR | 69.0 (8.3) |
8.0 {6-10} |
|||
| 149 | Plac | NR | 71.6 (6.6) |
13.4 (6.6) |
China | ||
| 148 | Mel | NR | 71.5 (6.7) |
15.9 (9.7) |
|||
| Ortho - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 192 | Plac | NR | 83.4 (7.5) |
11.0 {8-17} |
Netherlands | ||
| 186 | Mel | NR | 84.1 (8.0) |
11.0 {6-14} |
|||
| 70 | Plac | 123 | 74.6 (5.4) |
7.0 [5-21] |
China | ||
| 69 | Mel | 123 | 74.5 (5.7) |
7.0 [5-19] |
|||
| Thoracic - Randomized Clinical Trial | |||||||
| 58 | Plac | NR | 56.1 (15.8) |
12.0 {10-14} |
USA | ||
| 59 | Ram | NR | 58.1 (14.1) |
12.0 {10-16} |
|||
| Thoracic - Before-After/Time Series | |||||||
| 58 | None | NR | 76.5 [70-87] |
13.6 (7.8) |
Japan | ||
| 24 | Ram | NR | 79.0 [70-89] |
13.5 (9.6) |
|||
| GI/Abd - Before-After/Time Series | |||||||
| 186 | None | 123 | 69.0 [30-88] |
9.0 [5-162] |
Japan | ||
| 120 | Ram | 123 | 71.0 [34-85] |
9.0 [4-80] |
|||
| NR: not reported | |||||||
| a ASA Physical Status. | |||||||
| b Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | |||||||
Pooled
Dexmedetomidine
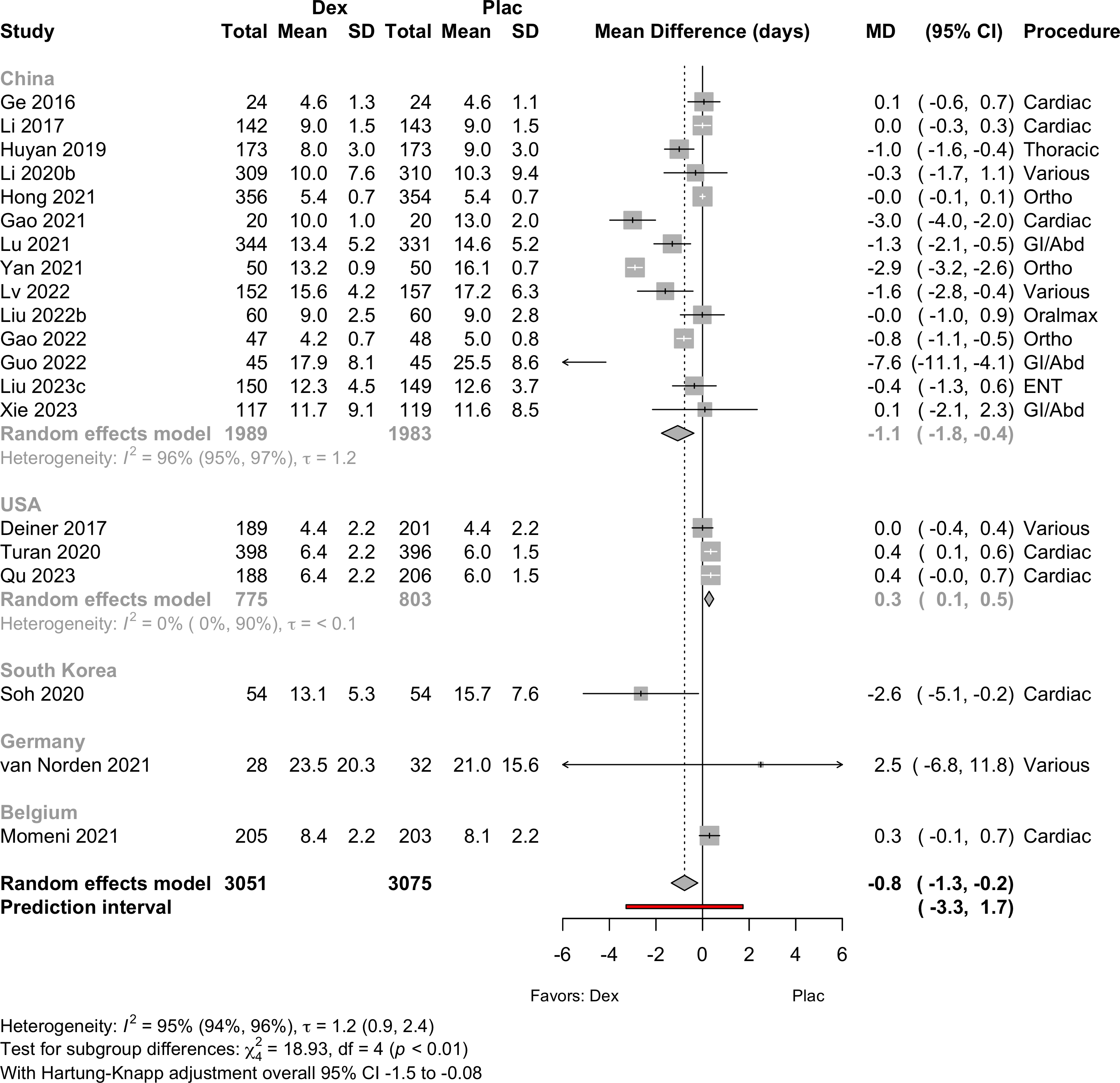
When the mean or standard deviation were not reported, they were imputed from from the median, interquartile range, and/or range. Hartung-Knapp adjustment not applied owing to interest in subgroups.
Melatonin/Ramelteon
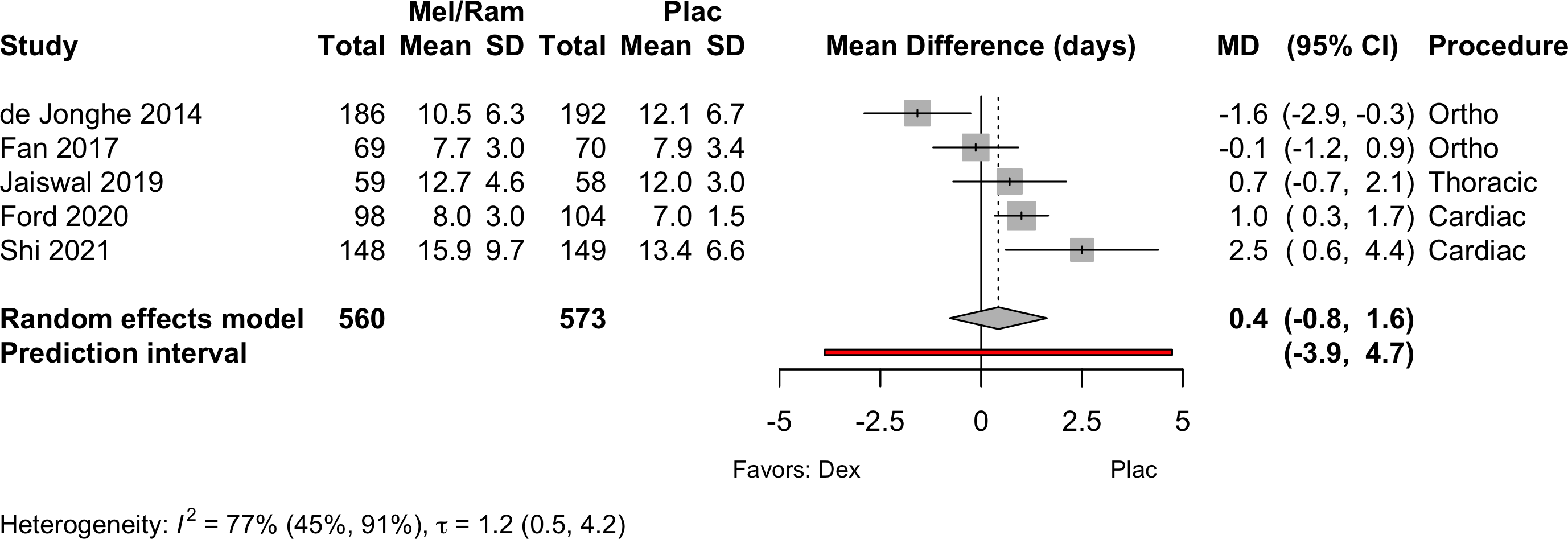
When the mean or standard deviation were not reported, they were imputed from from the median, interquartile range, and/or range.
Mortality
Dexmedetomidine
| Study | N | Drug | Surgery | ASA | Agea | Mortality | RD (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | N (%) | 0 - 100% | ||||||
| Hospital | ||||||||
| 92 | Prop | Cardiac | NR | 72.4 (6.2) |
0 (0) | — | ||
| 91 | Dex | 72.7 (6.4) |
1 (1.1) | 1.1% (-1.9, 4.1) | ||||
| 201 | Plac | Various | 1234 | 74.0 {71-78} |
3 (1.5) | — | ||
| 189 | Dex | 74.0 {71-78} |
1 (0.5) | -1.0% (-2.9, 1.0) | ||||
| 39 | Plac | Cardiac | 123 | 70.0 (4.9) |
1 (2.6) | — | ||
| 39 | Ulin | 70.6 (4.4) |
0 (0) | -2.6% (-9.4, 4.3) | ||||
| 39 | Dex/Ulin | 69.6 (5.0) |
0 (0) | -2.6% (-9.4, 4.3) | ||||
| 39 | Dex | 69.8 (5.1) |
1 (2.6) | 0.0% (-7.0, 7.0) | ||||
| 387 | Plac | Cardiac | 1234 | 62.0 (12.0) |
1 (0.3) | — | ||
| 391 | Dex | 63.0 (11.0) |
1 (0.3) | -0.0% (-0.7, 0.7) | ||||
| 53 | Plac | Cardiac | NR | 65.0 [37-83] |
1 (1.9) | — | ||
| 50 | Dex | 65.0 [23-82] |
1 (2.0) | 0.1% (-5.2, 5.4) | ||||
| 203 | Plac | Cardiac | NR | 70.0 {59-81} |
10 (4.9) | — | ||
| 205 | Dex | 71.0 {61-81} |
1 (0.5) | -4.4% (-7.6, -1.3) | ||||
| 33 | Prop | Cardiac | NR | 78.8 |
0 (0) | — | ||
| 33 | Dex | 78.7 |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-5.7, 5.7) | ||||
| 206 | Plac | Cardiac | NR | 70.0 {65-75} |
1 (0.5) | — | ||
| 188 | Dex | 67.5 {63-73} |
3 (1.6) | 1.1% (-0.9, 3.1) | ||||
| 30-day | ||||||||
| 135 | Plac | Cardiac | 234 | 67.5 (5.3) |
4 (3.0) | — | ||
| 139 | Dex | 66.4 (5.4) |
2 (1.4) | -1.5% (-5.0, 2.0) | ||||
| 310 | Plac | Various | 123 | 69.0 (6.4) |
1 (0.3) | — | ||
| 309 | Dex | 69.0 (6.6) |
0 (0) | -0.3% (-1.2, 0.6) | ||||
| 354 | Plac | Ortho | 1234 | 71.0 (5.0) |
0 (0) | — | ||
| 356 | Dex | 71.0 (5.0) |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-0.6, 0.6) | ||||
| 331 | Plac | GI/Abd | 123 | 70.4 (6.5) |
0 (0) | — | ||
| 344 | Dex | 70.1 (5.8) |
1 (0.3) | 0.3% (-0.5, 1.1) | ||||
| 157 | Plac | Various | NR | 68.4 (6.6) |
7 (4.5) | — | ||
| 152 | Dex | 67.9 (5.9) |
5 (3.3) | -1.2% (-5.5, 3.1) | ||||
| 206 | Plac | Cardiac | NR | 70.0 {65-75} |
1 (0.5) | 0.0% (-1.3, 1.3) | ||
| 188 | Dex | 67.5 {63-73} |
3 (1.6) | 1.1% (-0.9, 3.1) | ||||
| 119 | Plac | GI/Abd | NR | 68.6 (5.5) |
2 (1.7) | — | ||
| 117 | Dex | 67.9 (5.6) |
1 (0.9) | -0.8% (-3.7, 2.0) | ||||
| 90-day | ||||||||
| 32 | Plac | Various | 1234 | 70.5 (6.2) |
5 (15.6) | — | ||
| 28 | Dex | 70.4 (7.1) |
0 (0) | -15.6% (-29.2, -2.1) | ||||
| 206 | Plac | Cardiac | NR | 70.0 {65-75} |
1 (0.5) | 0.0% (-1.3, 1.3) | ||
| 188 | Dex | 67.5 {63-73} |
4 (2.1) | 1.6% (-0.6, 3.9) | ||||
| ASA PS: American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status; RD: risk difference; GI: gastrointestinal; Abd: abdominal (includes hepatic); Ortho: orthopedic; Various: more that one procedure category; Dex: Dexmedetomidine; Ulin: Ulinastatin; MS: morphine sulfate; Plac; placebo. | ||||||||
| a Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | ||||||||
Ketamine
No studies
Melatonin/Ramelteon
| Study | N | Drug | Surgery | ASA | Agea | Mortality | RD (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | N (%) | 0 - 100% | ||||||
| Hospital | ||||||||
| 192 | Plac | Ortho | NR | 83.4 (7.5) |
4 (2.1) | — | ||
| 186 | Mel | 84.1 (8.0) |
4 (2.2) | 0.1% (-2.8, 3.0) | ||||
| 58 | Plac | Thoracic | NR | 56.1 (15.8) |
4 (6.9) | — | ||
| 59 | Ram | 58.1 (14.1) |
3 (5.1) | -1.8% (-10.4, 6.8) | ||||
| 30-day | ||||||||
| 149 | Plac | Cardiac | NR | 71.6 (6.6) |
21 (14.1) | — | ||
| 148 | Mel | 71.5 (6.7) |
18 (12.2) | -1.9% (-9.6, 5.7) | ||||
| 186 | None | GI/Abd | 123 | 69.0 [30-88] |
0 (0) | — | ||
| 120 | Ram | 71.0 [34-85] |
0 (0) | 0.0% (-1.4, 1.4) | ||||
| 90-day | ||||||||
| 192 | Plac | Ortho | 83.4 (7.5) |
41 (21.4) | 19.3% (13.1, 25.4) | |||
| 186 | Mel | 84.1 (8.0) |
39 (21.0) | 18.9% (12.7, 25.1) | ||||
| ASA PS: American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status; RD: risk difference; GI: gastrointestinal; Abd: abdominal (includes hepatic); Ortho: orthopedic; Various: more that one procedure category; Ram: ramelteon; Mel: melatonin; Plac; placebo. | ||||||||
| a Mean Med (SD)[Range]{IQR}. | ||||||||
| b Randomized clinical trial. | ||||||||
| c Before-after design. | ||||||||
Pooled
Dexmedetomidine
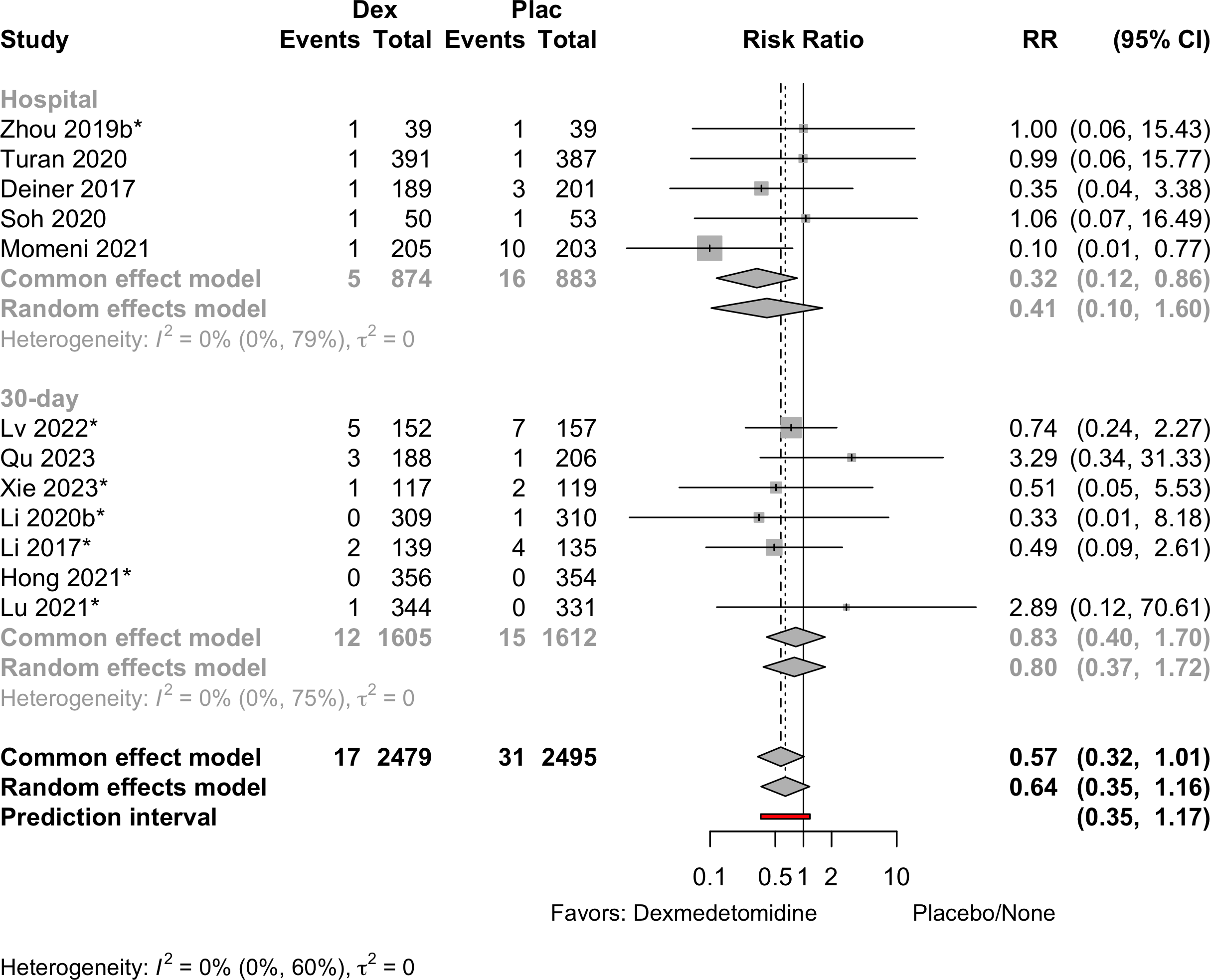
Melatonin/Ramelteon
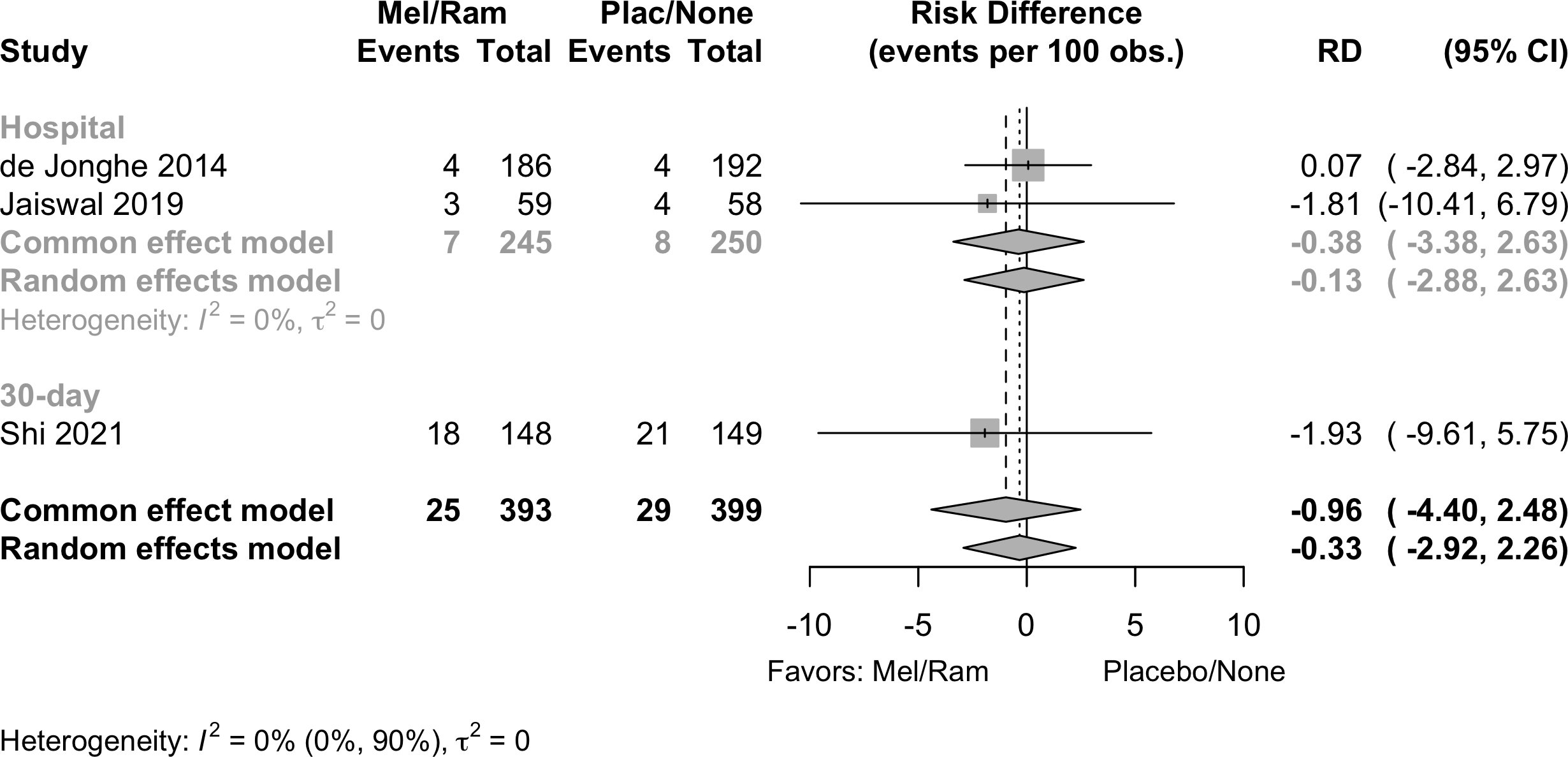
Risk of Bias
Randomized
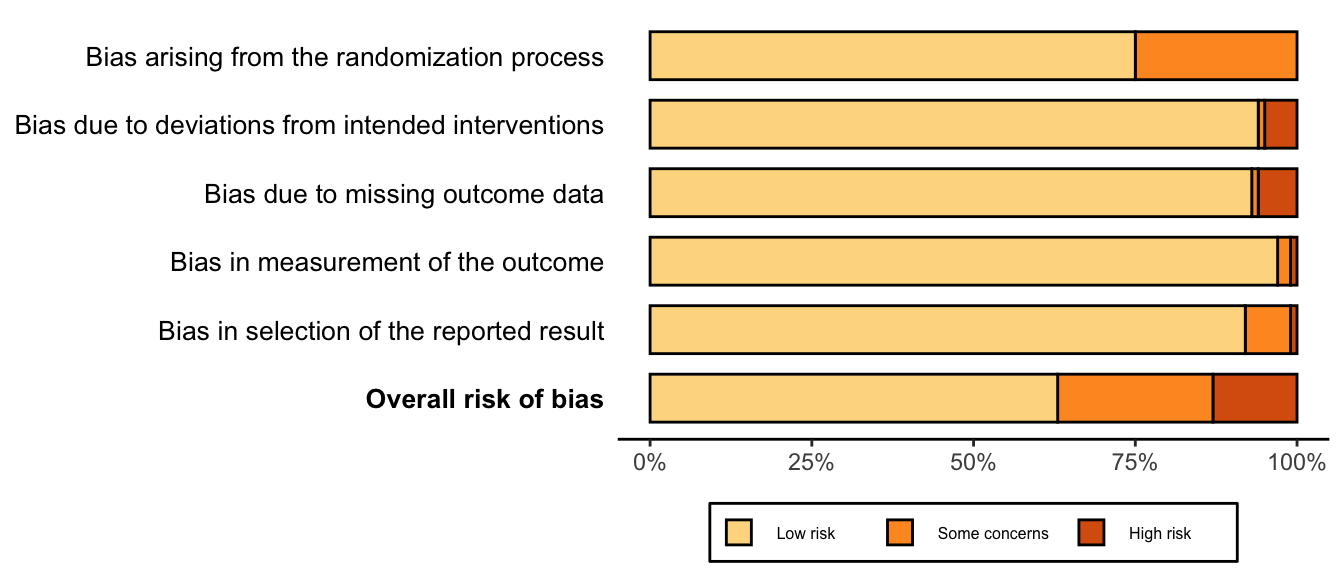
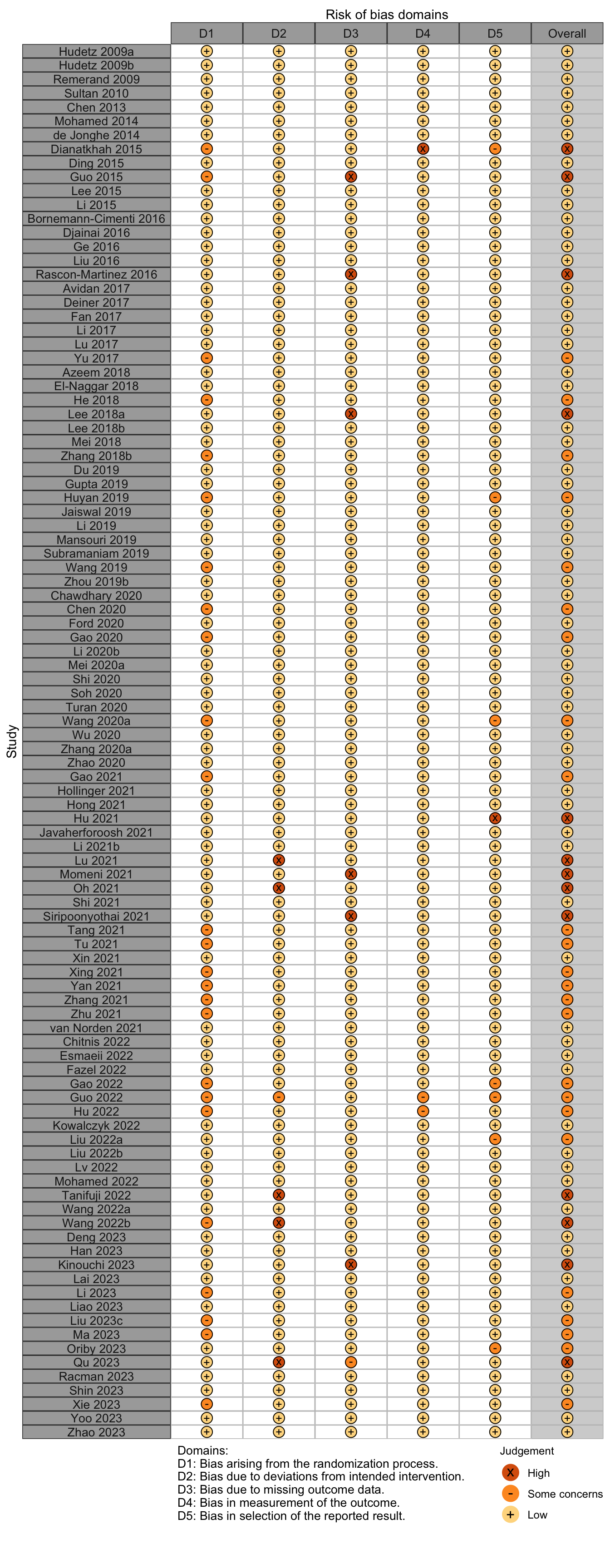
Nonrandomized